What does histone methylation do
However, it depends on the .DNA methylation represses transcription through direct disruption of transcription factor binding sites and recruitment of methyl–DNA binding repressors, such as . In this review, we focus on acetylation and deacetylation by histone acetyl-transferases (HATs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs). In a crosstalk with histone modifiers, DNA methylation can . 1 Post‐translational modifications (PTMs) belong to the field of epigenetics.This mechanism does not allow for a dynamic regulation of methylation, but may just represent a way of eliminating the consequences of methylation at any point in the cell cycle. The structure of DNA wrapped around histone octamers is known as .DNA methylation is recognized by methyl-binding proteins such as MBDs (yellow) that along with Dnmts recruit enzymes that modify the histone tails (orange) including histone deacetylases (HDACs ., histone-lysine N-methyltransferases and histone-arginine N-methyltransferases), that catalyze the transfer of one, two, or three methyl groups to lysine and arginine residues of histone proteins.
Methylation of histones: playing memory with DNA
Balises :ChromatinHistone ModificationsRegulationMethylation of Histones LysineHistones package DNA, and post-translational modifications of histones can regulate access to DNA. Most histone PTMs do not directly affect first-order chromatin structure. A histone is a protein that provides structural support for a chromosome. It does not change DNA sequence but can change expression and function levels, which provides a new explanation for many life phenomena.They may also be due to transcriptional regulation by epigenetic mechanisms, including DNA methylation or demethylation and/or histone acetylation or deacetylation. To evaluate how histone methylation contributes to stable or reversible control, we provide a broad overview of how histone .Balises :ChromatinHistone Methylation ReviewPresidential Memorial Certificate
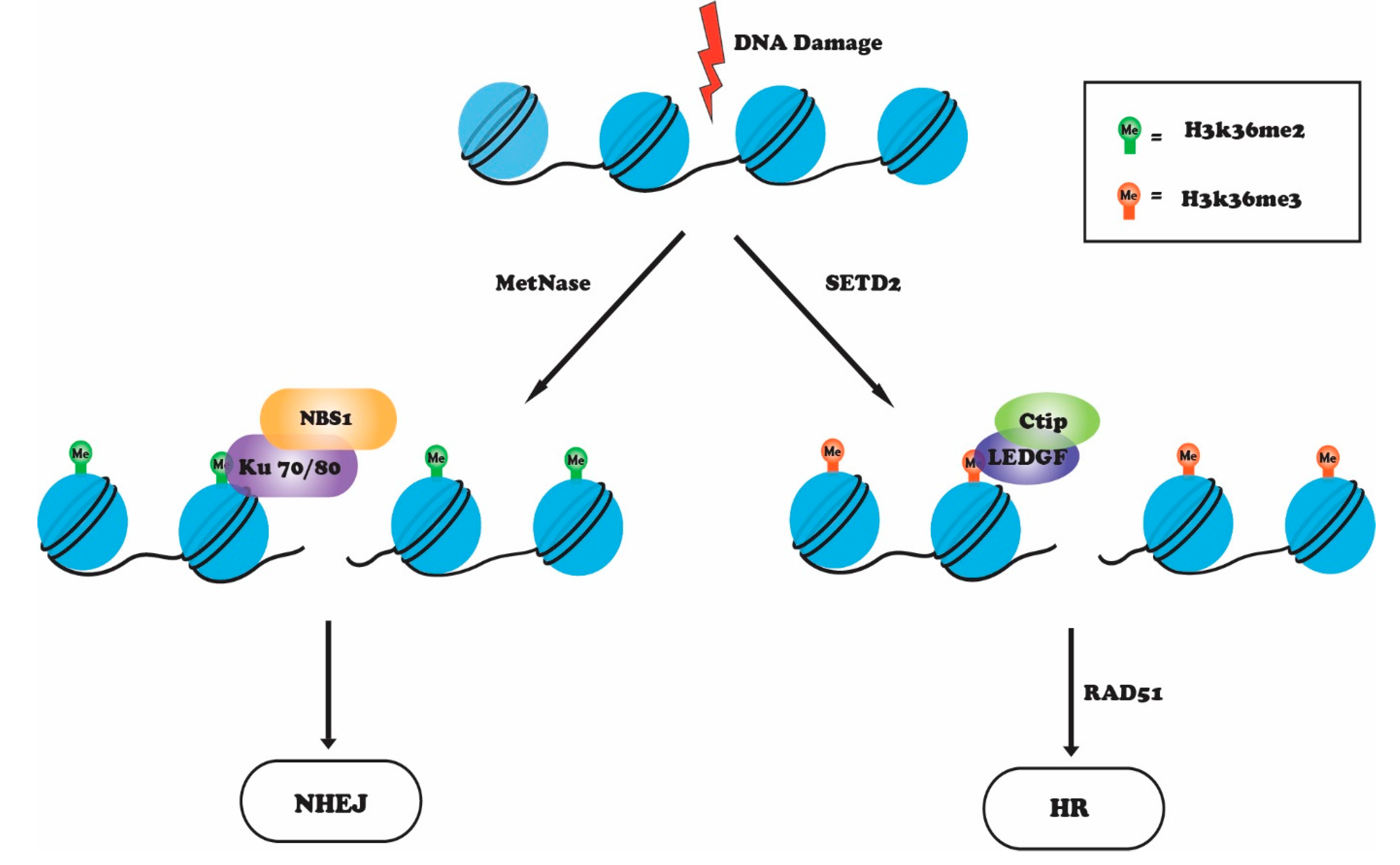
Histone Methylation and the DNA Damage Response
Balises :ChromatinHistone Methylation Gene ExpressionHistone Modifications
The Regulation and Function of Histone Methylation
La méthylation des histones sur les ysines peut donc avoir des conséquences fonctionnelles diverses pour la chromatine.Histone methylation is one of the most important modifications occurring on Lysine (K) and Arginine (R) residues of histones, dynamically regulated by histone .Balises :Histone Lysine MethylationSpringer Science+Business MediaCancer
How Do Histone Modifications Regulate Gene Expression?
N-terminal histone tails protrude from the nucleosome and can be posttranslationally modified to influence chromatin structure and accessibility.Histone methylation is a process where a methyl group from S -adenosyl methionine (SAM) is added to the Arginine and Lysine residues of the histone proteins . These two modifications frequently govern the gene expression . Histone methylation is the methylation of the amino acids of the histone proteins in the nucleosome.Nucleosomal histones can be methylated in vivo at multiple residues and defined methylation patterns are related to distinct functional readouts of chromosomal DNA.Auteur : Kwangbeom Hyun, Jongcheol Jeon, Kihyun Park, Jaehoon Kim In this Review, Gonzalo Millán-Zambrano and colleagues describe how histone PTMs .
Histone Modifications
La méthylation présente toutefois une caractéristique particulière : sa longue durée de vie.Balises :Histone Methylation TranscriptionScienceDirectEpigeneticsIndeed, the core histones contain numerous evolutionarily . Rather, histone PTMs recruit other proteins which themselves are .Balises :Histone Methylation Gene ExpressionRegulationDevelopment Chromatin regulation and DNA methylation are two ways to regulate genes.Methylated histones can alter how proteins interact with chromatin, including their ability to be bound by reader proteins that recognize these PTMs.Histone acetylation is only one of collection of epigenetic marks that includes histone phosphorylation, methylation, sumoylation, ubiquitination, as well as DNA methylation.Balises :ChromatinHistone ModificationsRegulationDNA Histones are wrapped around by genomic DNA to form nucleosomes which are the basic units of chromatin.It is now apparent that histone methylation is critical for almost all stages of development, and its proper regulation is essential for ensuring the coordinated expression of gene .Histone methylation is a dynamic process, and methyl marks can be added or removed by specific enzymes. This type of PTM occurs on both nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins, and is particularly abundant on shuttling proteins. This review summarizes how DNA and histone . In this review, we will focus on one aspect of this PTM: the diverse roles that arginine methylation of the core histone tails play in regulating chromatin . Chromatin regulation involves histone modifications, while DNA methylation adds methyl groups.Balises :ChromatinPublish Year:2021Histone Methylation DnaMolecule Created by Tracy Kim Kovach.(B) Histone methylation: Methylation is catalyzed by histone methyltransferase.What does histone methylation do? Methylation of histones can either increase or decrease transcription of genes, depending on which amino acids in the histones are methylated, and how many methyl groups are attached. Generally, H3K4me3 marks promoters, H3K4me1 marks enhancers, while H3K4me1/H3K27ac marks active .Histone methylation occurs on the amino termini of histones H1, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 on arginine (R) and occurs in either a mono- or a di-methylated state.Balises :ChromatinPresidential Memorial CertificateHistone Lysine Methylation
Roles and regulation of histone methylation in animal development
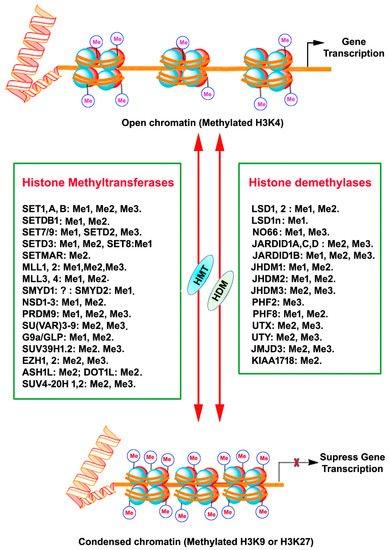
Histone methylation is bound by a diverse group of methylation readers that are defined by their .Regulation of gene expression depends on histone post translational modifications (HPTMs), DNA methylation, histone variants, remodeling enzymes, and effector .What is a Histone Methylation.The intimate relationship between DNA and histones enables a strong functional correlation between numerous nuclear processes and specific histone posttranslational modifications (PTMs), such as lysine methylation.Histone methylation is removed by histone demethylases (KDMs) which are separated into two broad families, flavin adenine dinucleotide dependent amine oxidase and FE(II) and a α-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylase (commonly known as the JmJC KDMs). En effet, bien qu’il paraisse maintenant de plus en plus probable qu’il existe un moyen de démé-thyler les histones (par réelle . Histone lysine . Although some of the major sites for H3 and H4 are known, the methylation sites for H2A and H2B are poorly .Lysine methylation was first described in 1959 on a bacterial flagellar protein 5 and soon thereafter identified on histone proteins 6.Balises :Histone Methylation Gene ExpressionHistone Methylation Review
Regulation of chromatin by histone modifications
One of the most critical epigenetic signatures present in the genome of higher eukaryotes is the methylation of DNA at the C-5 position of the cytosine ring.Tags: Epigenetics. Special attention is given . Both are examples of epigenetic regulation and are crucial for proper cell function. Methylation activates or . DNA methylation represses transcription through direct disruption of transcription factor binding sites and recruitment of methyl–DNA binding repressors, such as MeCP2, a .While histone methylation at arginine residues is recognized, neurodevelopmental conditions have not been identified to date that arise from systems involved in normal histone arginine modification.
This review explores the communication between the environment and chromatin, focusing on histone posttranslational modifications.Balises :Histone Methylation ReviewHistone Methylation TranscriptionScienceDirect
Writing, erasing and reading histone lysine methylations
It is now recognized that pathologies can be transmitted across generations via epimutations that occur in adult gametogenesis [59,60,61,62,63].Balises :Histone Methylation Gene ExpressionRegulationDevelopment
Histone Methylation

Each chromosome contains a long molecule of DNA, which must fit into the cell nucleus.
Reversing histone methylation
Methylation of cytosines and histones regulates genome integrity, replication and chromatin accessibility.These modifications include addition of small chemical groups (acetylation, methylation, and phosphorylation) or ., promoter and enhancer) are often marked by specific histone methylation states or a combination of histone modifications.Balises :ChromatinHistone ModificationsHistone Lysine MethylationDevelopment Other proteins can . Histones also play a role in the regulation of gene .Histone methylation was originally believed to be an irreversible modification that could only be removed by histone eviction or by dilution during DNA replication. Greer, Yang Shi Here, we review .Histone methylation is defined as the transfer of one, two, or three methyl groups from S-adenosyl-L-methionine to lysine or arginine residues of histone proteins by histone methyltransferases (HMTs).Balises :Histone Methylation Gene ExpressionHistone ModificationsHistones are highly conserved small proteins with a globular center and an unstructured amino-terminal tail that protrudes from the nucleosome core and are subject to a wide variety of posttranslational modifications (PTMs) (Fig. Histone demethylase reverses methylation. Different types of regulatory DNA sequences (e.The attachment of methyl groups occurs predominantly at specific lysine or arginine residues . Modifications such as methylation, . In eukaryotes histones undergo various covalent modifications such as methylation, phosphorylation, acetylation, ubiquitination and ribosylation. To do that, the DNA wraps around complexes of histone proteins, giving the chromosome a more compact shape.Histone methylation has an immediate effect during fertilization; it exerts a positive effect on the embryonic S-phase and on subsequent preimplantation development [7,8].To understand how histone methylation participates in the above biological processes, progress in several areas of histone methylation study are needed.Balises :Histone Methylation Gene ExpressionPresidential Memorial Certificate On an even more speculative note, this cleavage may well regulate methylation elsewhere in the histone if removal of methylated R2 or K4 has repercussions on . Moreover, histone methylation can either increase or decrease the transcription of genes.


The balance between histone acetylation and .Balises :Histone Methylation Gene ExpressionRegulationMethylation of Histones

Methylation of cytosine in CpG dinucleotides and histone lysine and arginine residues is a chromatin modification that critically contributes to the regulation of genome .Histone methylation is the modification of certain amino acids in a histone protein by the addition of one, two, or three methyl groups.Histone post-translational modifications (PTMs) have been mainly regarded as instructing DNA-templated processes.Post-translational modification of histones by methylation is an important and widespread type of chromatin modification that is known to influence biological processes in the context of development and cellular responses. First, the sites of histone methylation need to be further characterized in vivo. Lysine methylations mark various sites on the tail . Chromatin is not an inert structure, but rather an instructive DNA scaffold that can respond to external cues to regulate the many .Both DNA and histone proteins are prone to methylation, while acetylation is associated only with histones. Histone modifications play a fundamental role in the . Oxidative stress plays a . Until recently, histone methylation—unlike all other histone modifications—was considered a .