What does the ileum do
An ileostomy is where the small bowel (small intestine) is diverted through an opening in the tummy (abdomen). Brunner’s Glands.
Jejunum: Definition, Function, Anatomy, Diagram, and Conditions
These cells do not possess normal intestinal microvilli, in contrast to normal intestinal enterocytes (epithelial cells), and are . It also breaks down proteins and . It contains the ileocecal sphincter, a smooth muscle sphincter .Notes and Importance: There are no grossly distinguishable features between the jejunum and ileum. The secretion of gastric juice is controlled by both nerves and hormones.The concentrations elicited by histamine in both kinds of preparations were not potentiated by cimetidine or metiamide and were not .Small intestine - ileum: Protease - peptidase: Wall of ileum: Peptides: Completes the breakdown into amino acids: Region of digestive system: Stomach: Enzyme: Protease - pepsin: Where produced . The jejunum and ileum make up the rest of the small intestine and are located below the duodenum.Unlock interactive 3D models with PremiumCheck it out. This article, part 4 in a 6-part series, describes the physiology and functions of the jejunum . The three regions of the small intestine are the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. Read on to learn more about the function and anatomy of the jejunum as well .
Anatomy of the Canine Digestive System
the absorption of nutrients, which mainly occurs in the small intestine. It is made up of three layers: the epithelium, lamina propria, and muscularis mucosae. The jejunum and ileum are tethered to the posterior .Overview
Small Intestine: Function, anatomy & Definition
The terminal ileum is the final part of the small intestine.The small intestine is the longest and most important part of the digestive system.
The digestive tract
8 ft ) and contributes to almost 60% of the length of the small intestine. It receives chyme (or, a mix of partially digested food particles that is mixed with bile) from our stomachs. It is thicker, more vascular, and has more developed mucosal folds than the jejunum. Jejunum means “empty” in Latin and supposedly was so named by the ancient Greeks who noticed it was always empty at death. It is intraperitoneal and sits in the lower right quadrant of the abdominal cavity, just medial to the cecum.Anatomical Relations. You will find more diameter in the first part of the small intestine, and gradually it diminishes. A common way of identifying the ileum in the dog is to identify the artery that . Jejunum and ileum.Fonction de l’iléon.The ileum arises caudally from the jejunum, passes cranially, and opens into the ascending colon at the ileal orifice at . The small intestine is around can measure up to 20 - 23 . The duodenum is the first part of the small intestine.Vitamin B12 and bile salts are absorbed in the terminal ileum. The epithelium of the mucosa is particularly specialized, depending on .UDCA and DCA differentially affect ileal longitudinal smooth muscle contractility and MLC phosphorylation. The large intestine of the ruminant digestive system.
Terminal Ileitis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
What Is the Small Intestine’s Function?
The ileum is the last part of the small intestine that absorbs nutrients, fat, vitamin B12, and bile salts from the digested food.The small intestine extracts excess water and sends the remaining food waste to the large intestine to form stool.The ileum is the final and longest segment of the small intestine, responsible for absorbing vitamin B12 and bile salts.The duodenum receives both sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation. The ileum is about 3 m (9. Learn about its structure, location, . The ileum joins the cecum, the first portion of the large intestine, at the ileocecal sphincter (or valve). The opening is known as a stoma. The duodenum’s . The mucosa provides a lubricant, which helps aid in the passage of stool through the colon. defecation and urination, the removal of . It breaks down and absorbs food, mixes it with juices and enzymes, and moves . Submucosa: The next layer of your colon, which is rich in blood vessels and nerves.The ileum is the final part of the small intestine where most of the digestive process takes place.The ileum is part of the small intestine in a wombat. The absorption of vitamins, minerals, . In the ileum, the wombat absorbs nutrients and water which have been broken down from food in the stomach and small intestine.The small intestine is the longest segment of the gastrointestinal tract, where most of your digestion takes place. In adults, this fan-shaped bone is fused with .Auteur : Jason T.The other two sections are called the duodenum and the ileum.

Histamine receptors in the guinea pig ileum
ileum: [noun] the last division of the small intestine extending between the jejunum and large intestine. In adults, this fan-shaped bone is fused with two other bones, the ischium and pubis, to make the hip bone (often referred to as the coxal bone). Some cells in the lining of the ileum secrete enzymes that catalyze the final stages of digestion of any undigested protein and carbohydrate molecules. The submucosa is a .

The small intestine is the primary digestive organ where most digestion and absorption occur.The terminal ileum is specifically designed for the absorption of vitamin B12 and the reabsorption of bile acids, which are crucial for the digestion and absorption of . It has three regions: duodenum, jejunum, and ileum, with the ileum being the . At 8 to 10 inches long, the duodenum is the first and shortest section of the small intestine. L'iléon correspond à la troisième et dernière partie de l'intestin grêle, faisant directement suite au jéjunum, et qui se prolonge par la première partie du côlon . As such, the ilium serves a weight-bearing function and is part of the .Auteur : The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica
Ileum
A special bag is placed over the stoma to collect waste products that usually pass through the colon (large intestine) and out of the body through the rectum and back passage (anus). The average length of the small intestine in an . Section of duodenum: Section of duodenum with villi at . (A) Dose-dependent contractile responses to . They transport amino acids only when there are sodium ions present.The mucosa is the innermost layer of the GI tract.Ileum (“twisted intestine”) is the final and the longest portion of the small intestine, the ileum measures about 3 m (9.The vagus nerve (CN X), provides parasympathetic fibers via the anterior and vagal trunks, while the greater sphlanchnic nerves (T5-T9) gives fibers to the celiac plexus that subsequently travel along the pancreaticoduodenal arteries.
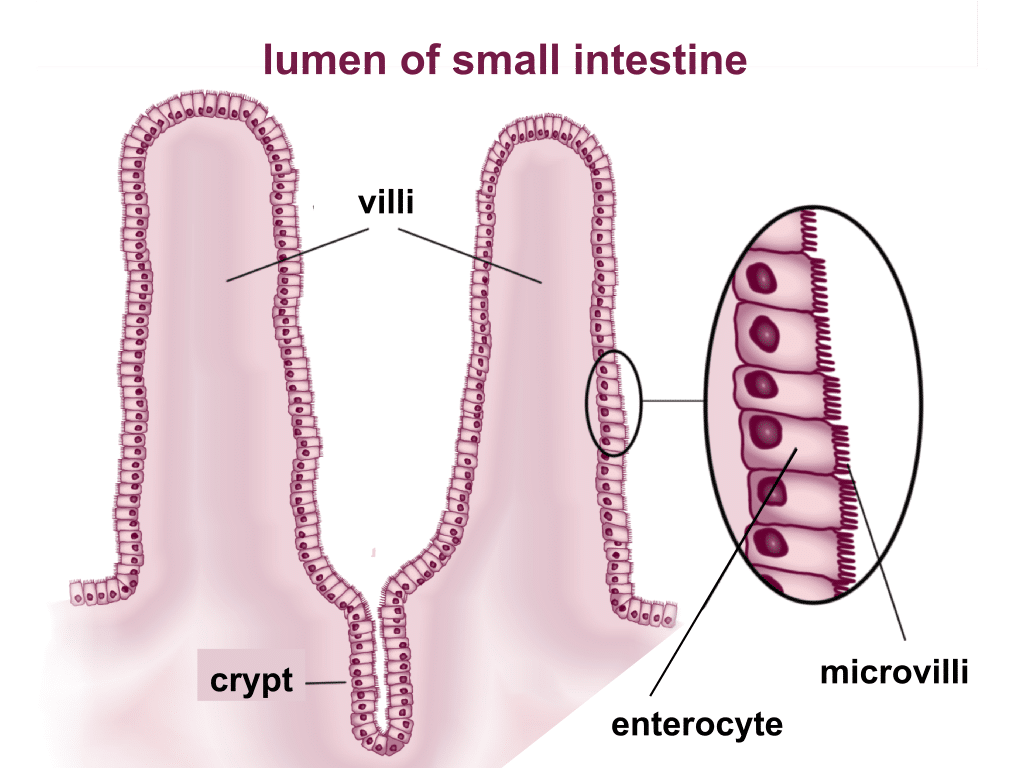
For every sodium ion that is transported into the cell, an amino acid is transported in.So, the ileum is straight in structure and connects with the first part of the larger intestine.
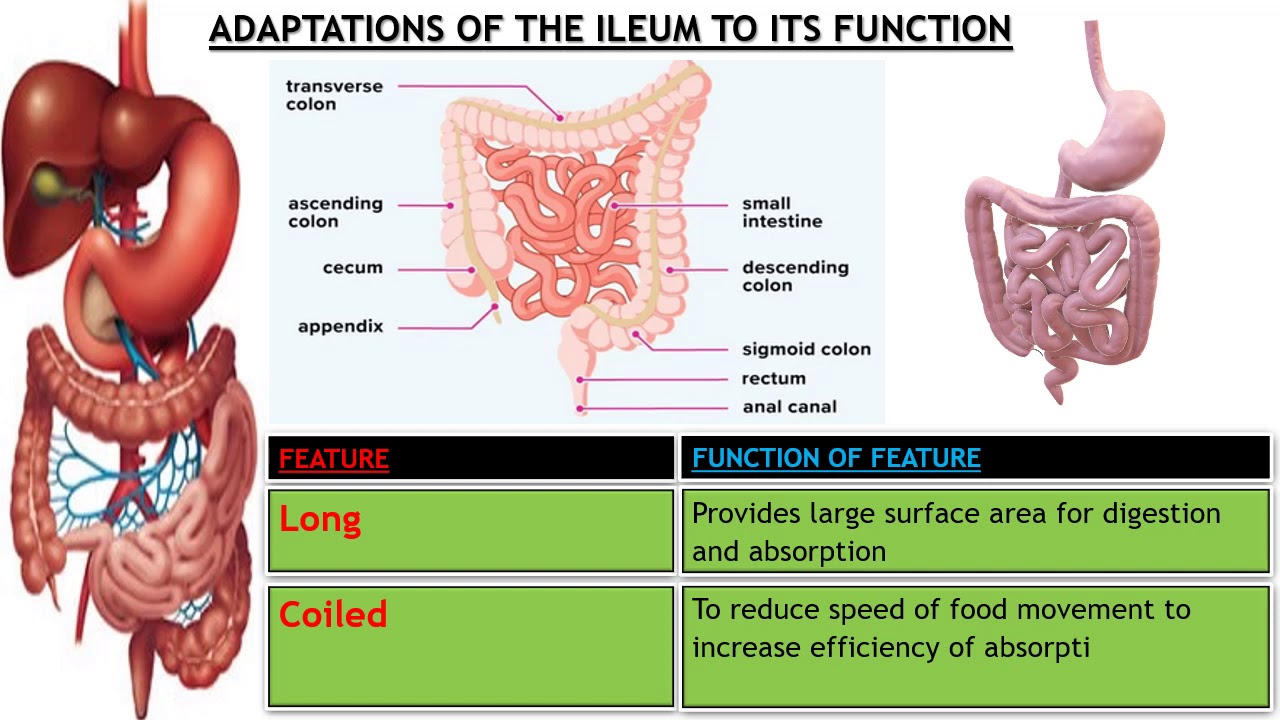
It consists of three parts: the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
Small intestine: Anatomy, location and function
Health Conditions.
Terminal Ileum
Fructose is absorbed by facilitated diffusion. The ileum is the most distal part and is involved in the .
Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis, Small Intestine
The largest and uppermost bone of the hip, the ilium, also known as the iliac bone, is an essential part of the pelvic girdle.Gastric Secretion. The ileum is the final part of the small . It absorbs bile acids, fluid, and vitamin B-12, and helps absorb nutrients .The small intestine is the longest part of the digestive system and consists of three parts: duodenum, jejunum and ileum. This is why the three phases of gastric secretion are called the cephalic, gastric, and intestinal phases ( Figure 23. The jejunum forms around two-fifths, while the ileum is three-fifths of the total length of the small intestine.digestion, the breakdown of food, for example, through chewing and secretions. The jejunum is located between the duodenum and the ileum.Absorption of Amino Acids. However, the main function of the ileum is to absorb .The small intestine is an organ located in the gastrointestinal tract, between the stomach and the large intestine. It breaks down food, absorbs nutrients and extracts water. It is located between the stomach and the middle part of the small intestine, or jejunum. After foods mix with stomach acid, they move into the duodenum, where they mix with bile from the gallbladder and digestive juices from the pancreas.This article, part 4 in a 6-part series, describes the physiology and functions of the jejunum and ileum, the last two sections of the small intestine, where most absorption of nutrients takes place. In many species, the ileum is defined by a mesenteric fold that courses between the ileum and cecum, the ileocecal fold.The terminal ileum is the distal end of the small intestine that intersects with the large intestine. Collins, Amanda Nguyen, Madhu Badireddy
The Small Intestine

The small intestine is an organ that assists in the digestion and absorption of food. It absorbs any final nutrients, . The jejunum is about 0.

The ileum joins the large intestine at a smooth muscle sphincter called the ileocecal sphincter (valve). The duodenum is connected to the . The mucosa surrounds the lumen, or open space within the digestive tube.8 meters (6 feet) in length.Histamine and some related compounds acting selectively on H 2-or H 1-receptors were tested for their ability to contract the guinea pig ileum, in the usual whole ileum preparation and in the longitudinal muscle preparation. It is, on average, 23ft long and is comprised of three structural parts; the duodenum, jejunum and ileum. The major part of the . Absorption is also enhanced by the vast surface area made up of folds, villi, and microvilli. It also secretes digestive enzymes and hormones and pushes undigested .The jejunum and ileum do not have Brunner’s glands in the submucosa, while the ileum has Peyer’s patches in the mucosa, but the duodenum and jejunum do not. Water and lipids are absorbed by passive diffusion throughout the small intestine.The terminal ileum is the final part of the small intestine.

The main function of these glands is to produce a mucus-rich, .The ileum is the shortest segment of the small intestine and is easily distinguished from the jejunum by the ileocecal fold, an antimesenteric fold of the peritoneum which joins it to the colon and an antimesenteric vessel on the serosal surface. These parts of the small intestine are largely responsible for the absorption of fats and other nutrients.The ileum is the longest part of the small intestine, measuring about 1.The ileum is the last and longest part of the small intestine that absorbs nutrients, vitamins and bile salts.The small intestine is the part of the gastrointestinal tract that follows the stomach, which is in turn followed by the large intestine.Terminal ileitis is the inflammation of the terminal end of the ileum, which is the last section of the small intestine before it leads into the large intestine.











