What is a marker gene

TUJ1, neurofilament (NEFL), and .CD163: CD163 is another commonly used marker for identifying M2 macrophages and is also known as a scavenger receptor for the hemoglobin-haptoglobin complex.
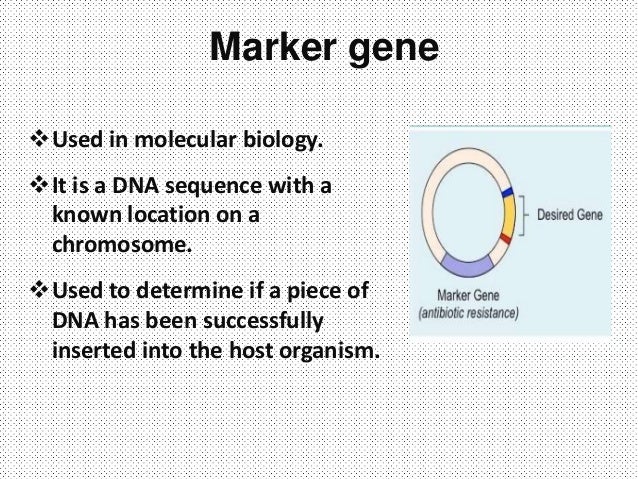
Marker Gene
A marker (largely synonymous with the word “landmark” and often referred to as a genomic marker or a genetic marker) is a DNA .Temps de Lecture Estimé: 6 min
Genetic marker
Exact sequence variants should replace operational taxonomic
CD163 is a transmembrane protein predominantly expressed on the surface of monocytes and macrophages.The growth and development of organism were dependent on the effect of genetic, environment, and their interaction.A biomarker—short for “biological marker”—is something that can be objectively measured and is a sign of a normal or abnormal process, or a condition or disease.Recent advances have made it possible to analyze high-throughput marker-gene sequencing data without resorting to the customary construction of molecular operational taxonomic units (OTUs ., immune cells).In recently published atlases, it is often unclear how strongly and robustly the proposed markers fulfill these . Processes have many more markers.
Neuron markers guide
Each marker is associated with a specific trait of a disease.
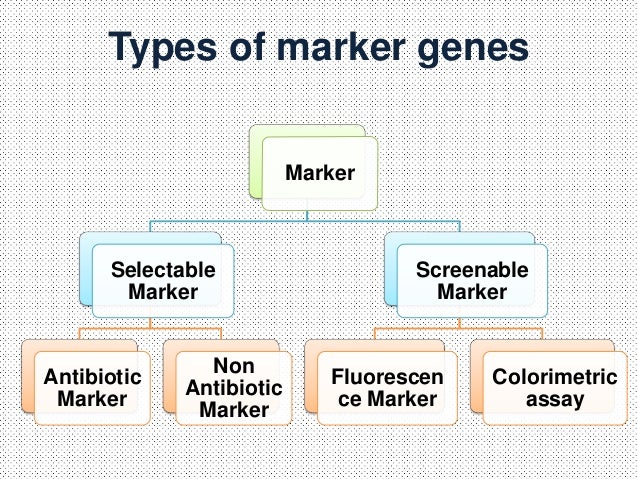
Selectable marker
Selectable marker genes are conditionally dominant genes that confer an ability to grow in the presence of applied selective agents that are normally toxic to plant cells or inhibitory to plant growth, such as antibiotics and herbicides.Selectable Markers.Marker genes are clearly necessary to select for transgenic fungi.Marker genes, defined as genes that are expressed primarily in a single-cell type, can be identified from the single-cell transcriptome; however, such data are not always available for the many uses of marker genes, such as deconvolution of bulk tissue.
What Are Genetic Markers and What Are They For?
PCNA is a DNA clamp that act as a cofactor of DNA polymerase delta . A biomarker can be a molecule found in the blood or other body fluids or tissues. In this technique, the flanking non-repeated regions of the . Another type of biomarker is a genetic signature or “fingerprint”—a pattern of activity in a . The ideal marker gene fulfills two criteria: (1) it is expressed in all cells of the population of interest, providing high coverage; (2) it is not expressed in background cells, providing a high signal-to-noise ratio (Figure 1 A). Thus, it is indispensable to select transformed .

Genetic marker

Macrophages can originate from embryonic precursors and from bone marrow-derived monocytes. It is important for DNA synthesis and is widely expressed during S phase .What is a marker and reporter gene? A marker gene is a gene that is introduced into cells or organisms to identify and select those that have successfully taken up the gene . Recombinant progeny will have the genotype A 1 A 2 B 2 B 2 or A 2 A 2 B 1 B 2.Overview
Genetic Marker
SOX1 is a transcription . Testing whether someone carries a harmful variant in one of these genes can confirm whether a condition is, indeed, the result of an inherited syndrome. Genetic testing is also done to determine whether family members who have not (yet) developed a . HES5 is a transcriptional repressor that acts downstream of the Notch signaling pathway to regulate differentiation of neuroepithelial cells . First, because of the way DNA polymorphisms arise and are retained, they are frequent . Molecular markers are used in .

Neuronal nuclei can be visualized with NeuN (a transcription factor encoded by RBFOX3). TUJ1, neurofilament (NEFL), and tau (MAPT) mark axons, whereas MAP2 .Genetic markers — heritable polymorphisms that can be measured in one or more populations of individuals — lie at the heart of modern genetics and enable the . These immunological tools . Because marker genes are designed to facilitate the identification and tracking of gene-marked cells in vitro and in vivo, ideally they should be safe, nontoxic, nonimmunogenic, and easily monitored and they should facilitate positive immunoselection if purification of marked cells is desirable. These are known as marker genes.These markers are capable of distinguishing the allele variation of the selected genes, and consequently enhance the accuracy and efficiency of MAS .Selectable marker genes are pivotal for the development of plant transformation technologies because marker genes allow researchers to identify or isolate the cells that are expressing the cloned DNA, to monitor and select the transformed progeny.modifies gene expression .
Genetic Marker
Once stable transformants have been isolated, these marker genes can be used to track transgenic .
Genetic markers are detectable variations of DNA sequence with known chromosome locations.A marker gene is a gene used in molecular biology to determine if a nucleic acid sequence has been successfully inserted into an organism's DNA.Molecular markers have three-fold applications in gene mapping: (1) A marker allows the direct identification of the gene of interest instead of the gene product, and .
Genetic Testing Fact Sheet
Reporter Genes.Neuronal nuclei can be visualized with NeuN (a transcription factor encoded by RBFOX3).
What is the main difference between marker and reporter gene
They are a type of reporter gene used in laboratory microbiology, molecular biology, and genetic engineering to indicate the success of a transfection or other procedure .It is a highly polymorphic marker and is used in genetic diversity studies, gene tagging, evolutionary study and phylogenetic studies. Genes that are frequently used to select transformed plant tissues include npt II, hpt . M2 macrophages express high levels of CD163 and other M2-associated .A genetic marker is a fragment of DNA whose exact position in the genome scientists are aware of. Different colours indicate the different class contributions which that particular gene explains. A genetic marker may or may not have a biological function.Neuron-specific enolase (NSE, encoded by ENO2), for example, is a neuron-specific marker that labels neuronal cell bodies. A different pair of primers is used to amplify DNA from either parent (P) and 15 of the F 2 offspring from the cross shown.Marker genes have many applications and enormous utility in downstream scRNA-seq data analysis, so further developing methods for their selection is essential. [0:15] can use that to deliver the transgene into a new plant. The presence of a prophage or of plasmids is not usually referred to as a “marker.They are categorized by their human NCBI gene symbol (Gene), common names (Synonyms), expression in human or mouse (Species), type of macrophage marker (Marker Type), protein type, cellular localization, and protein size.Marker genes play an essential role for experimental validation and computational analyses such as physiological characterization, annotation, and . “Association Plots (APL)”, a new statistical method for visualizing gene activity within a cell cluster makes it easier to find its marker genes. When Agrobacterium is used to insert a transgene into a plant, one or two extra genes can be added to help simplify the transformation process. Each possible . A The mean |Shapley value| for the top 30 ranked marker genes across all broad cell types of the mouse brain, before additional filtering and sorting, using SMaSH ’s network mode. Marker genes for a cell type, however, are highly correlated in bulk data, because their . In recent decades, lots of candidate additive .The marker gene of C5 was identified using differential expression analysis (DEA).

To be successful, the marker gene or gene set (a collection of marker genes) should be specifically and consistently expressed in a given cell, cluster or class of cells (e.
Marker Genes
“A marker gene is a known DNA sequence located nearer to the target gene with detectable and inherited properties. The antibiotic-resistant gene which is a type of selectable marker gene is one of the examples of the marker gene that is used in genetic transformation experiments.Markers in the monocyte-macrophage transition.2 Genetic Engineering | CIE A Level Biology Revision . CD56 is the archetypal phenotypic marker of natural killer cells but can . A marker can be a gene mutation or a phenotype. Individuals #3, #8, #13 are recombinant . Real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), bulk RNA-sequencing dataset .A genetic marker is a DNA sequence with a known physical location on a chromosome.Thus, marker genes that are specific to or highly expressed in a particular cluster will appear as large, dark dots in the corresponding column for that cluster.Molecular markers have three-fold applications in gene mapping: (1) A marker allows the direct identification of the gene of interest instead of the gene product, and consequently, it serves as a useful tool for screening somatic cell hybrids; (2) Use in several DNA probes and easy-to-screen techniques, a marker also helps in the physical mapping of the . In this respect, CD56 (also known as neural cell adhesion molecule) is a very good example. 2: CMeasuring recombination frequency between two molecular marker loci, A and B.The general principles of molecular marker techniques have been elucidated with detailed explanation of some notable basic concepts associated with .Alternatively, novel marker genes could be proposed to enhance the resolution for identifying more diverse immune cell types.ADVERTISEMENTS: Depending on the nature of selection, marker genes are divided into two types: 1.
Types of Marker Genes
Most likely, the strain that you are working with contains the mutations that you desire: recA, endA, lac ΔM15, rps L and ton A. As only a very small portion of cells are transformed in most experiments, the . Selectable Marker Genes 2.Here we present a standard developed by the Genomic Standards Consortium (GSC) for reporting marker gene sequences—the minimum information about a marker gene sequence (MIMARKS). Genetic markers can help link an inherited disease with the responsible .
Genes involved in many of the known inherited cancer susceptibility syndromes have been identified. Selectable Marker Genes: One of the constraints in plant transformation technique is the obtaining of transformed plants with less frequency.The selectable markers are the marker genes used to screen transformants in the corresponding selectable medium while the reporter genes are marker genes to measure the amount of expression.

Jha, Nandkishor.







