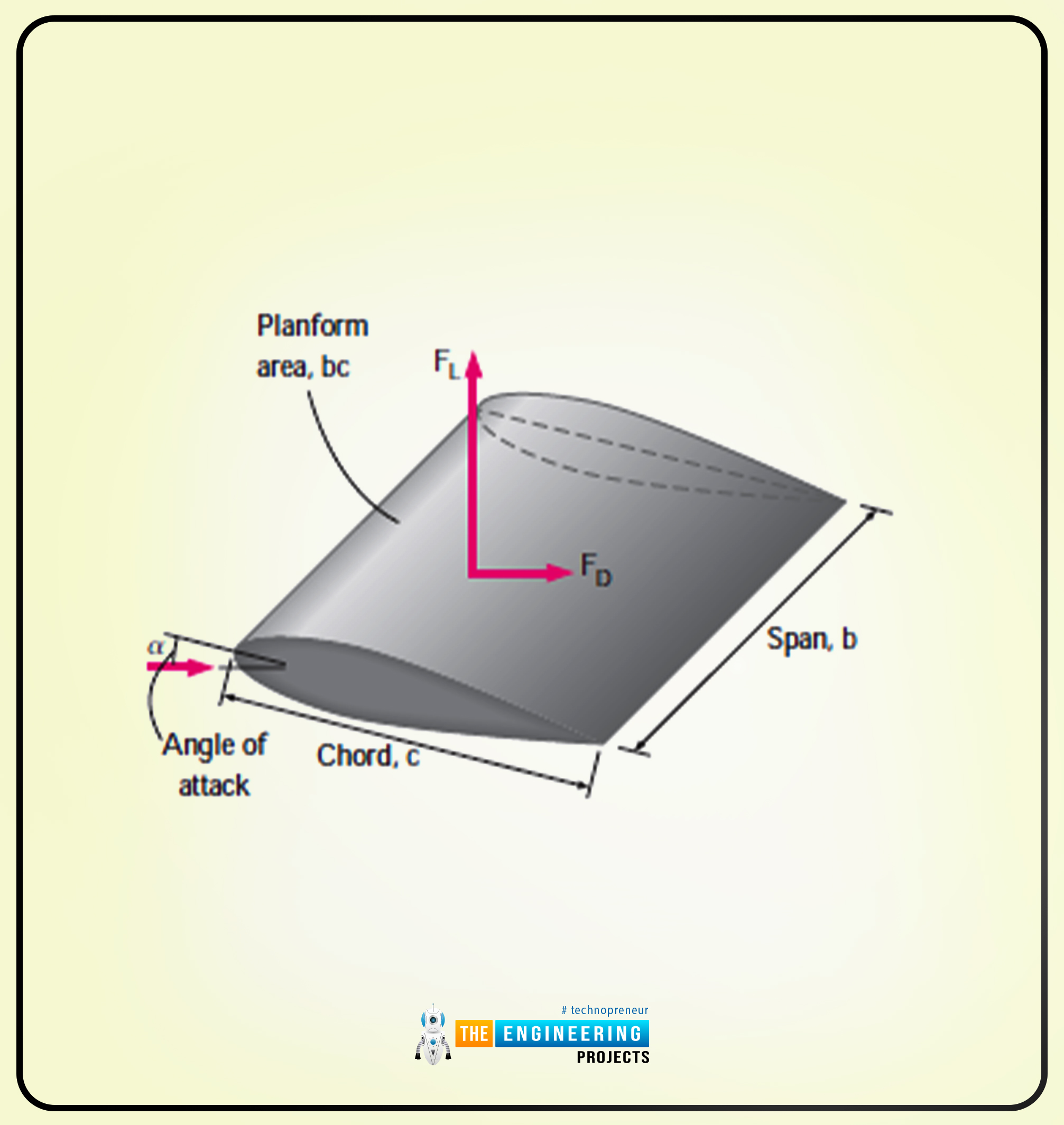
What is drag in fluid

Drag occurs when an object moves through a gas or liquid at high velocity.Drag is generated by the difference in velocity between the solid object and the fluid.Balises :Drag DefinitionDrag Force FormulaDrag Force in Fluid Mechanics+2Application of Drag ForceExample of Drag Force
Fluids
Fluid is any liquid or gas or any material that is unable to withstand a shearing or tangential force, when at rest. It allows aerodynamicists to model the influence of shape, inclination and flow conditions on aerodynamic drag. Definition: Drag Force.In fluid dynamics, the drag coefficient (commonly denoted as: , or ) is a dimensionless quantity that is used to quantify the drag or resistance of an object in a fluid . The drag force always acts in the opposite direction .
Pressure loss reduction is achieved by reducing the level of turbulent motion in the flow. Another interesting force in everyday life is the force of drag on an object when it is moving in a .In fluid dynamics, the drag equation is a formula used to calculate the force of drag experienced by an object due to movement through a fully enclosing fluid. It is a crucial factor in the design of vehicles, aircraft, and ships, as well as many other objects that move through fluids.As we shall see in Fluid Mechanics, for small particles moving at low speeds in a fluid, the exponent n is equal to 1.In fluid dynamics and aerodynamics, there are several types of drag that can affect the motion of an object through a fluid. Friction drag is .In fluid dynamics, drag (sometimes called air resistance, a type of friction, or fluid resistance, another type of friction or fluid friction) is a force acting opposite to . This functionality is complicated and depends upon the shape of the object, its size, its velocity, and the fluid it is in. ρ D t u → = − ∇ → p + η ∇ 2 u →. Button navigates to signup page .Balises :Drag PhysicsCalculate Energy Loss Due To DragEnergy Education+2Drag Force Equation CarPower To Overcome Drag Force EquationIn fluid dynamics, drag is a force acting opposite to the relative motion of any moving object. Mathematically \ [F_D\propto v^2 \] \ [F_D = \dfrac {1} {2} C_ {\rho} Av^2, \] . CL = Co-efficient of lift. Step 2: Sketch a free-body diagram to resolve the forces at constant speed.Drag on the sphere. [1] It was derived by George Gabriel Stokes in 1851 by solving the Stokes flow limit for small Reynolds numbers of the Navier–Stokes equations. These forces are present everywhere, and almost every practical device .drag, force exerted by a fluid stream on any obstacle in its path or felt by an object moving through a fluid.Aerodynamic Forces. Drag force constantly works throughout the opposing directions of flowing fluid. The drag force . The fluid may be a liquid or a gas. There must be motion between the object and the fluid. The reference area, A, is .Skin Friction – Friction Drag Source: wikipedia. Recall that in the Navier-Stokes equation.When objects travel through fluids (a gas or a liquid), they will undoubtedly encounter resistive forces called drag forces.
• The tangential shear stresses acting on the object produce friction drag (or viscous drag).Like friction, the drag force always opposes the motion of an object.Friction and drag are both forces that results form the motion of an object against its environment. In airplanes, vortices form at the wingtips producing a swirling flow that .When a solid object moves through a fluid it will experience a resistive force, called the drag force, opposing its motion.A Newtonian fluid is a fluid in which the viscous stresses arising from its flow are at every point linearly correlated to the local strain rate — the rate of change of its deformation over time.Balises :VelocityDrag Force FormulaDrag Definition Science
Drag
When an object moves in a fluid, the fluid molecules just around it get entrained along with it due to friction. This force is a very complicated force that depends on both the .A worker packs avocados at a plant in Uruapan, Michoacan, Mexico, on Feb.0 × 10 -3 × 0. Comment Button navigates to signup page (8 votes) Upvote. How does drag occur? Drag is generated by the difference in velocity between the solid object and the fluid.In commonly used context drag force is the force that is exerted on a solid body moving with respect to a fluid due to the movement of the fluid. At least, that's how I understood it. It acts in a direction opposite to the object’s .Balises :VelocityDrag Force FormulaViscosity and DragFile Size:131KB Drag force can be divided into two types that are skin drag and form drag. The main types of drag include: Form Drag: Form drag, also known as pressure drag or profile drag, is caused by the resistance encountered by an object moving through a fluid due to its shape and cross-sectional . It is similar to surface friction since both . But when a solid object interacts with a fluid, things are more difficult to describe because the fluid can change its shape.
“Drag and Lift Force in Fluid Mechanics”
In fluid dynamics, the drag coefficient (commonly denoted as: , or ) is a . the flat plate, the bed of a river, or the wall of a pipe, the fluid touching the surface is brought to rest by the shear stress to at the wall.
Hydrodynamic drag in fluid dynamics
Suppose that the fluid is a liquid, and the variables involved under some conditions such as velocity of fluid U, density of fluid ρ, kinematic viscosity of fluid V, frontal area A, drag force FD. Drag force FD F D is proportional to the square of the speed of the object.
DRAG AND LIFT FORCE IN FLUID MECHANICS
When two solid objects interact in a mechanical process, forces are transmitted, or applied, at the point of contact.However, there is still wall friction and fluid-fluid friction up to some point far enough from the surface, which depends on the particular location along the surface.Balises :Drag PhysicsDrag ForceVelocity
What is Drag Force
Unlike simple friction, the drag force is proportional to some function of the velocity of the object in that fluid. Traditionally, drag forces are represented by a drag coefficient, which is .Define terminal velocity.VILLA MADERO, Mexico (AP) — As a drought in Mexico drags on, angry subsistence farmers have begun taking direct action on thirsty avocado orchards and . Induced Drag: Induced drag or lift-induced drag is caused by the generation of lift.Drag force arises when an object moves through a fluid or, equivalently, when fluid flows past an object.Skin Friction Drag: This drag develops from the direct interaction between the fluid and the skin of the object. • The drag acts in the direction parallel to the free-stream fluid motion. In this study, a new and . Mathematically, FD = 1 2CρAv2, (6. Drag forces are produced when there is any movement in the air, fluid, or indeed any medium. As the coefficient of drag is dimensionless, aerodynamicists can easily compare different designs to determine . We will discuss this in detail when we examine boundary layer flows. Stresses are proportional to the rate of change of the fluid's velocity vector. Step 1: List the known quantities in SI units.Worked ExamplesTension in a RopeMIT OpenCourseWare
Aerodynamic Drag
For the same volume to pass points 1 and 2 in a given time, the speed must be greater .
Stokes Drag — Physics 111a
Using DRA allows increased flow using the same amount of energy or decreased .Drag: Drag is the force that opposes the motion of such a fluid-filled body.(This playlist of Flow Around Submerged Bodies covers the following topics: Fluid Flow .
Concept of Drag and Lift
LSPI Flow Improvers
In general, the drag force grows larger with increased flow velocity, but . The force a flowing fluid exerts on a body in the flow direction.
What is drag flow?
The higher the wetted area, the higher the skin friction drag is. Fd = 6π ηrv = 6 × π × 0.Drag is a force that opposes or resists motion, caused by collisions of moving objects with molecules in a fluid like air or water. When the fluid is a gas like air, it is called aerodynamic drag or air resistance. Understanding the causes and effects of hydrodynamic drag is essential for optimizing the efficiency and . For example drag on a ship moving in water or drag on a plane moving in the air.Drag coefficients in fluids with Reynolds number approximately 10 4 Shapes are depicted with the same projected frontal area.
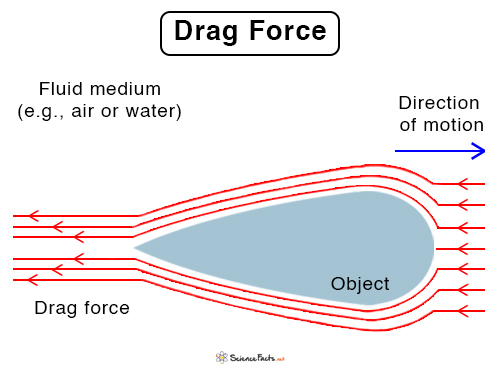
e they cannot resist the shear force applied to them. Hope that helps.About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright .
Newtonian fluid
Fluids are substances with zero shear modulus, i.Balises :Drag ForceVelocityDrag Definition
Drag equation
Step 3: Calculate the value for viscous drag, Fd.

Balises :Drag PhysicsVelocity When the said forces are applied to the fluid, it goes through a continuous change in shape.Balises :VelocityDrag Lift Equation -In fluid dynamics, the drag equation is a formula used to calculate the force of drag experienced by an object due to movement . As was written, when a fluid flows over a stationary surface, e. Hydrodynamic drag will be much larger than skin friction drag at high velocity.In fluid dynamics, Stokes' law is an empirical law for the frictional force – also called drag force – exerted on spherical objects with very small Reynolds numbers in a viscous fluid. Where, CD = Co-efficient of drag.

The resistance offered by a fluid, like air and water, is called the drag force or drag when an object moves through it. Unlike the other forces we have encountered so far, friction and drag always oppose the motion of an object so as to slow it down and bring it to reset with respect to its environment. A fluid is Newtonian only if the tensors that describe the viscous stress and the strain rate are . 4: When a tube narrows, the same volume occupies a greater length.
(article)
When the fluid is a .
Drag Force: Definition, Formula, and Examples
component of the fluid force.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 8 min
Fluid mechanics
For a solid body immersed in a fluid, the “point of contact” is every point on .Hydrodynamic drag is a force that opposes the motion of an object through a fluid, such as air or water.When the fluid is moving from right to left, work done to the left is positive and work done to the right is negative. It is used in modeling drag dependencies on aspects like the object’s shape, inclination, and surrounding flow conditions.The drag coefficient \ ( (C_D)\) is a dimensionless value that helps in quantifying the drag on an object moving through a fluid, representing the object’s aerodynamic or hydrodynamic properties. Button navigates to signup page. Determine an object’s terminal velocity given its mass.