What is fermentation process
Beer Production History.
Comment fonctionne réellement le processus de fermentation
This magical transformation is what gives beer its unique flavors, aromas, and .4: Fermentation.
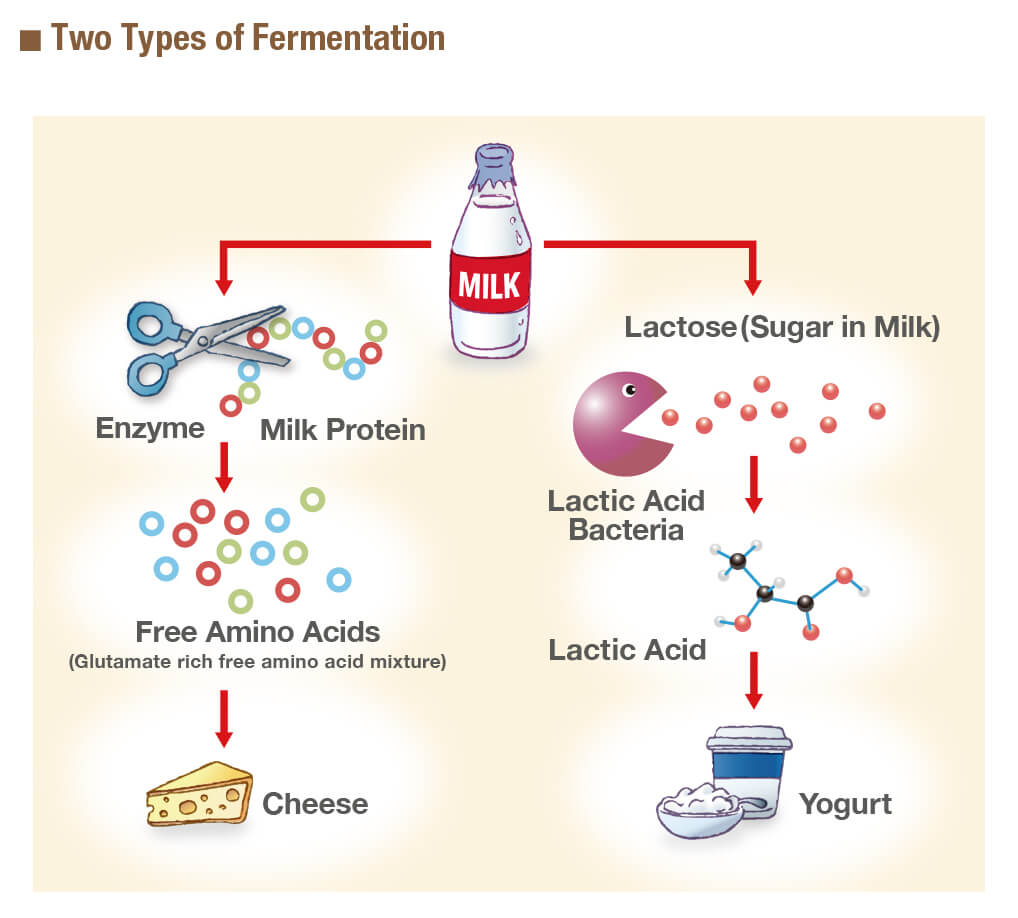
Fermentation of Yogurt and the Chemistry Behind It
Fermentation uses microorganisms to convert raw materials (generally . Fermentation tanks have valves so that .The fermentation process is a biochemical reaction where yeasts, bacteria, and other microorganisms convert sugars into other substances, such as alcohol or lactic acid.The fermentation process is critical for the production of beer, wine, cheese, and a wide range of everyday products that you likely can’t live without.5: Fermentation. Lactic Acid Fermentation. Fermentation uses .When this process is used in baking bread and the creation of dough, the fermentation facilitates the yeast and bacteria changing sugars and starches into carbon dioxide.Fermentation dates back to 10,000 BCE; humans first utilized the fermentation process to preserve dairy products, such as cow, goat, sheep, and camel milk. The study of fermentation is known as Zymology. These chemical changes are brought about by various chemicals called enzymes. Fermenters make very little ATP—only two ATP molecules per glucose molecule during glycolysis.Another familiar fermentation process is alcohol fermentation (Figure 4. For example, yeast performs fermentation to obtain energy by . In the next step, pyruvate is reduced to lactic acid, ethanol or other products. The salt-brine method involves two stages: In stage one of lacto-fermentation, vegetables are submerged in a brine that is salty enough to kill off . Batch fermentation itself clears that it involves batch-wise fermentation of the specific media.Fermentation is a process that involves the breakdown of carbs by bacteria and yeast. Since ancient times, humans have taken .
Fermentation Definition, Process & Examples
Upon a strictly biochemical point of view, fermentation is a process of central metabolism in which an organism converts a carbohydrate, such as . The fermentation process typically involves the use of bacteria, yeast, or fungi to produce a specific active ingredient or intermediate, which is then extracted .
Types of Fermentation: Definition, Process, Advantages
17 The reaction resulting in alcohol fermentation is shown.Fermentation uses an organic molecule as a final electron acceptor to regenerate NAD + from NADH so that glycolysis can continue. Microorganisms like yeasts, anaerobic bacteria , . It results in a distinctive tart flavor and is used to make foods like yogurt, cheese, and sauerkraut. This is what gives red wine such high tannins.Lacto-Fermentation Process. The enzymes are taken from or released by microorganisms. Les organismes utilisent la fermentation pour vivre, . Fermentation is a natural process that has been used for centuries to transform raw ingredients into a wide array of products.What process is shared between aerobic cellular respiration and fermentation? Describe the process briefly.
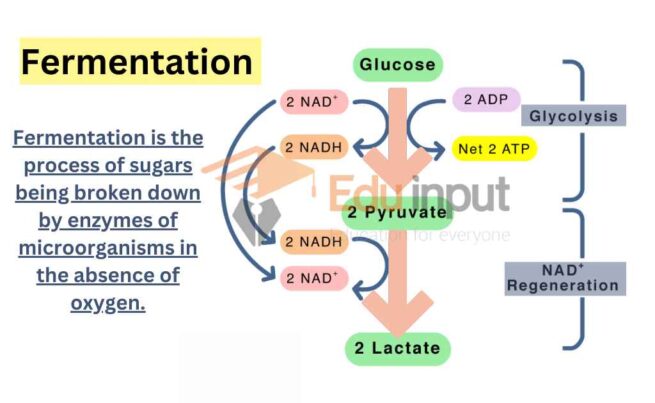
Fermentation is an anaerobic biochemical process.

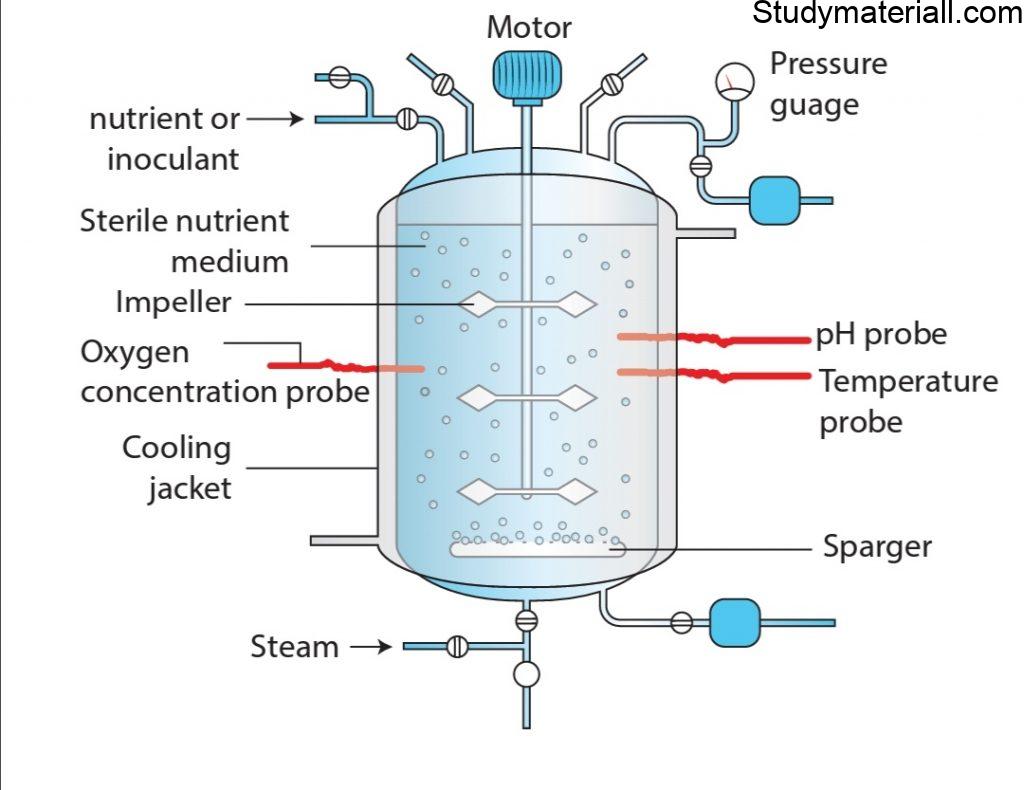
is aerated stirred tank batch fermentor because mos t industrial fermentation process are aerobic. It is also a critical component in many industrial processes, from the production of biofuels to waste .Fermentation is a biochemical process in which carbohydrates like glucose or starch are converted to alcohol or acid without oxygen. But the fermentation process is not just about food and drink. What you’ll learn to do: Illustrate the basic components and steps of fermentation. Today, following the scientific discoveries of French microbiologist Louis Pasteur, who showed that living organisms initiate fermentation, we know why fermentation not only makes food like sourdough .

Fermentation defined.
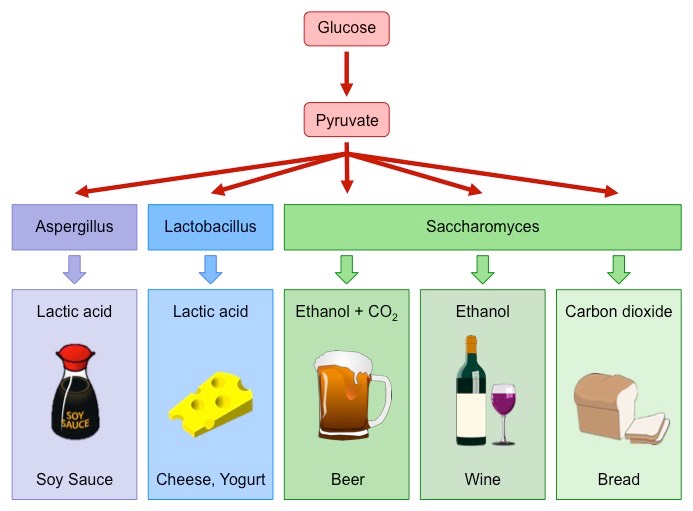
Fermentation can begin with wild yeast found in the environment but usually winemakers will add reliable, predictable commercial yeast.La fermentation est une réaction biochimique qui extrait l'énergie des glucides sans utiliser d'oxygène.Processes that use an organic molecule to regenerate NAD + from NADH are collectively referred to as fermentation. While white wine is created by just fermenting grape juice, red wine is made using the whole grape, grape skins and all. As a fermented food, yoghurt results from the bacterial transformation of milk.Store your finished kombucha in the refrigerator to slow the fermentation process. In aerobic conditions, the final receptor is oxygen (respiration), andin anaerobic conditions, the final receptors are other organic molecules, such as pyruvate or acetyl CoA (fermentation). Alcohol, carbon .Fermentation is a biochemical process in which complex organic substances are converted into simple substances with the help of bacteria yeasts and other microorganisms known as fermentation. The alcohol fermentation reaction is the following: Figure 2 The reaction resulting in alcohol fermentation is shown. Why is this process able to occur in fermentation as well as aerobic . The fermentation occurs naturally . During fermentation, the .Types of Fermentation: Definition, Process, Advantages - . It is also used to make dairy items, including cheese and yogurt .The process of carbohydrate decomposition creates a flow of protons and electrons.Fermented foods are a mainstay of Japanese cuisine. The alcohol fermentation reaction is the following: Figure 4.
How Does Bread Fermentation Work?
Define fermentation and explain why it does not require oxygen; Describe the fermentation pathways and their end products and give examples of microorganisms .
Fermentation — Wikipédia
Vue d’ensemble
Fermentation
Since any sugar (starch) containing substance can undergo alcoholic fermentation, many cultures quickly adopted and invented beer as a .orgRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Fermentation
It occurs in certain types of .
The Fermentation Process Explained
What Is Fermentation?
Fermentation for APIs (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients) refers to the use of microbial fermentation to produce pharmaceutical products such as antibiotics, vaccines, and other drugs.
The Science Behind Fermentation: Beer’s Magical Transformation
comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Fermentation
So, I recommend making a scoby hotel to keep some of these extra scobys for . In fermentation, . The initial stage of fermentation is intermittent operation, in which many cells are produced. It refers to a technique in which microbial cells grow and multiply to convert substrates into products. - Definition, Types, Anaerobic .Indeed, although modern science recognizes more than one type of fermentation, a general definition should define fermentation as a biochemical process . Fermentation goes beyond simply puffing up bread. Learning Objectives. La fermentation permet de produire de l' énergie (sous. Define fermentation and explain why it does not require oxygen.Wine Fermentation Process.Fermentation and microorganisms that are used to produce products .
FERMENTATION, TYPES OF FERMENTERS, DESIGN & USES OF
Fermentation is a metabolic process where living organisms consume carbohydrates (such as starch or sugar) and produce alcohol or acid.

While fermentation has existed for hundreds of years, it wasn’t until the latter years of the 19th century that it was finally understood. It’s the carbon dioxide that makes the dough rise. Yeast is everywhere. The name came from the observation that mixtures of crushed grapes kept in large vessels produced bubbles . Fermentation does not involve an electron transport system, and no ATP is made by the fermentation process directly. From soy-based food to condiments, pickles, and beverages, fermented foods (known in Japanese as Hakko shokuhin) are everywhere you look. Table of contents. The process of fermentation was used in making beverages .Simply put, fermentation in winemaking is what converts grapes into alcohol. Microorganisms in fermented foods . Let's discover more about the fermentation of yoghurt and the microbiology that turns milk into yoghurt. Your scoby will inevitably end up making lots of scoby “babies,” which appear as new layers on the bottom of the “mother” scoby. Describe the fermentation pathways and their . For the wine to ferment, winemakers add yeast to the grape juice.Fermentation is a metabolic process in which an organism converts a carbohydrate, such as starch or a sugar, into an alcohol or an acid. In addition to ethanol, other products of alcoholic fermentation include higher alcohols, esters, glycerol, succinic acid, diacetyl, acetoin, and 2,3-butanediol.Another familiar fermentation process is alcohol fermentation (Figure 2), which produces ethanol, an alcohol. This happens when the yeast begins to eat the sugar.Penicillin fermentation process is a typical batch process.com5 Main Types of Fermentations - Biology Discussionbiologydiscussion. In the context of brewing beer, fermentation is the conversion of sugars into alcohol and carbon dioxide by yeast. Beer is considered to be one of the oldest alcoholic drinks, as the evidence presents.The process was named fermentation, from the Latin word fervere, which means to boil.17), which produces ethanol, an alcohol.The production process of beer making is so simple that it led to its invention and popularization.Fermentation is another anaerobic (non-oxygen-requiring) pathway for breaking down glucose, one that's performed by many types of organisms and cells. Here NAD+ is formed which is re-utilized back . In this article, we take a deep dive into all things fermented, looking at what happens during the fermentation process, why fermented .Upon a strictly biochemical point of view, fermentation is a process of central metabolism in which an organism converts a carbohydrate, such as starch or sugar, into .Fermentation is the metabolic process by which organic molecules are converted into acids, gases, or alcohol in the absence of oxygen or any electron transport chain. The word fermentation is derived from the Latin verb serve, which means to boil.Fermentation is a well-known natural process used by humanity for thousands of years with the fundamental purpose of making alcoholic beverages, as well as bread and by-products. Several types of fermenter are further grouped base on di fferent concept of function and designs: 1.Batch Fermentation Definition. After the glucose substrate is consumed by the cells, it comes into semi-intermittent feeding stage where glucose is continuously added into the fermentation cylinder.Fermentation biology is an energy releasing process that brings about chemical changes in raw food.
Fermentation- Principle, Types, Applications, Limitations
Traditional lacto-fermentation involves submerging vegetables in a brine solution— salt and water.La fermentation est un processus biologique se déroulant dans un milieu privé d'oxygène. In contrast, in some living systems, the electron . Microbial cells harness the added nutrients. Many foods come from .