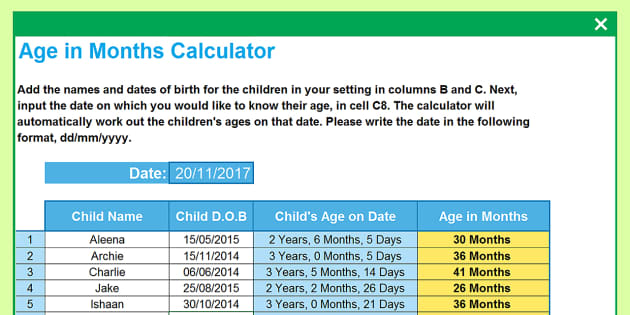
What is hot dipped galvanized

December 20, 2023.The hot-dip galvanizing (HDG) process consists of three basic steps: Surface Preparation.The tell-tale sign of a hot-dipped galvanized material is the presence of a crystalline-like pattern on the surface, sometimes referred to as “spangle.
Hot Dipped Galvanized Steel Coil
The hot-dip galvanized steel body’s hot-dip galvanized surface is robust underneath its hold and difficult to fall off. In fact, an 85 micron galvanized coating can last for nearly a century in many UK atmospheric settings ( click to see corrosion rates in your area). Carbon steel is used in various applications, including bridges, buildings, and automobiles.
STANDARD SPECIFICATION FOR HOT DIP GALVANIZING
Surface preparation is a critical step in the application of . a typically lower cost has galvanized. Therefore, the performance of hot-dip . Hot-dip galvanizing is a common and effective method for protecting steel from corrosion. The hot-dip galvanizing process is a widely used technique in the metallurgical industry for protecting .
Carbon Steel vs Galvanized Steel: What’s the Difference
The HDG Coating.
Galvanized Steel: Everything You Need To Know
Ideal for indoor applications, the EG coating has an average lifespan of 5-10+ years depending on the .
Hot-Dip Galvanizing Cost Calculator
It involves immersing the steel in a bath of molten zinc at a temperature of . Hot dip galvanizing is performed per ASTM A153 or F2329 and is a thicker and longer lasting coating.” The hot-dipped galvanizing method is an economical choice that can be quickly executed on both simple and complex shapes. Apply vinegar and primer.The basic specification for hot dip galvanized coatings on iron and steel articles is defined by a single standard, EN ISO 1461 ‘Hot dip galvanized coatings on iron and steel articles – specifications and test methods’.To clean galvanized steel before painting, rinse with warm or hot soapy water and then allow it to dry completely.Hot-dipped galvanized steel is dipped into a vat of molten zinc, which coats the steel.Environmental Product Declaration (Epd)In Extreme TemperaturesThe HDG CoatingWhy is Steel Chemistry ImportantHealth Product DeclarationFacts About HDG Typically pregalv at 20-25 microns and hot dip at 3-4 times that.Hot dip galvanizing, according to the American Galvanizers Association, is defined as the process of dipping fabricated steel into a kettle or vat containing molten zinc. galvanizing, however, allows you to use various colors, textures, and portability in the process that you don’t get . The origins of the process date back more than 250 years; however, new technologies and creative chemistry contribute to the continued .By Team Xometry.
The HDG Coating
Employing hot-dip galvanizing is innovation.
Is it Galvanized?
Hot-dipped galvanized steel is produced by immersing the steel in a bath of molten zinc.When hot dip galvanizing is specified, the surface of the steel is completely covered with a uniform coating whose thickness is determined principally by the thickness of the steel .90 oz/square foot.
Performance of Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Products
Preparation and pre-treatment of surfaces – Pickling. Hot-dip galvanizing refers to the process of applying a protective zinc coating to a steel sheet or iron sheet, in order to prevent rusting. Main steps within the galvanizing .In its simplest form, galvanizing refers to the application of a zinc coating to the surface of a metal (usually steel or iron). The new coated material can be worked and machined in a similar .The main difference between pregalv (such as you would get that had ultimately come from the likes of Bluescope in Waiuku, NZ), and post fabrication hot dip galvanized is thickness of coating.Hot-Dip Galvanizing (HDG) History Process.What is Hot-Dip Galvanizing? Why Specify Galvanizing? How Long Does HDG Last? Is Galvanizing Sustainable? How Much Does HDG Cost? What is Zinc? Hot .Hot-dipped galvanization involves submerging the steel in molten zinc, whereas galvanized steel is coated with a protective layer of zinc through electroplating.A hot-dip galvanized coating may show a high zinc content near the outside of the coating with an increased iron content near the metal substrate. In industry parlance, regular HDG is referred to as “GI.What is Hot Dip Galvanized? Hot dip galvanization is the process of coating a zinc layer on a metal in order to protect that metal from corrosion.Cling film comes in at 10-12 microns thick and a typical bacterium is 1-10 microns long.Hot Dip Galvanized. Can you weld hot-dip galvanizing? Yes, you can weld hot-dip galvanized steel, but it’s important to follow proper welding procedures to avoid . This is the most common method of galvanization and provides the thickest and most durable zinc coating. The purpose of hot-dip galvanizing is to protect the material from corrosion by creating a layer of zinc that acts as a . It involves immersing pieces in molten zinc, ensuring a coated and protected surface. Corrosion Protection. There are lighter and thicker coating as well, like G30 and G140, however, G60 and G90 tend to be the most commonly used.Hot dip galvanizing is just that, dipped into hot molten zinc. However, the zinc coating makes galvanized steel more resistant to corrosion.The zinc of the hot-dip galvanized coating is more corrosion resistant than bare iron and steel. Carbon steel is stronger than galvanized steel. Zinc plating is less expensive than hot dip galvanizing. However, there are some exceptions to this standard (see thicker coatings below). The most common method for galvanization occurs on continuous galvanizing lines, where coils are welded together end-to-end and run through a bath of molten zinc. We have been using it for over 100 years because it’s one of the most effective ways to protect steel from corrosion. Surface Preparation. Preparation and pre-treatment of surfaces – Abrasive blast cleaning of steel.
What is Hot Dip Galvanizing
Sizing — The hot-dip process can be used for all product sizes.
Difference Between Galvanized and Hot Dip Galvanized
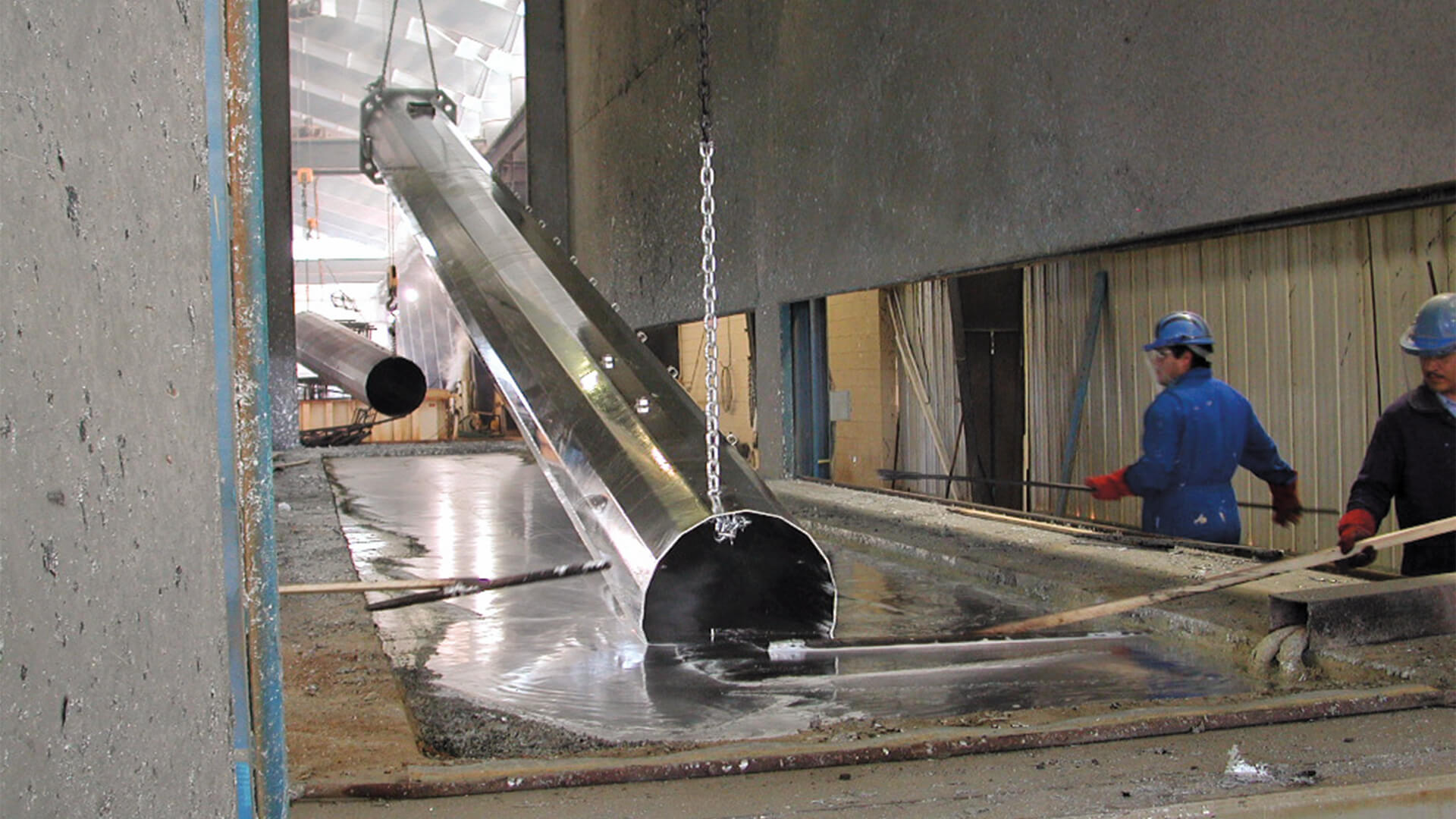
Abrasion Resistance Uniform .For hot dipped galvanized products, there are two main aspects you should inspect after galvanizing, the smoothness and thickness of the zinc coating. The batch hot-dip galvanization process involves immersing the entire finished steel product, or “steelwork”, in a bath of pure liquid zinc. Advancements in metallurgy and furnace technology improve process efficiency and sustainability. Barrier, Cathodic, Zinc Patina. Furthermore, zinc solidifies upon withdrawal from the bath, so there are no delays for curing when . Quality of zinc layer is assessed readily by eye, and the thickness is easy to test with magnetic thickness gauges according to the ISO1461 and the requirement of clients. Hot dip galvanizing is a more involved process compared to galvanizing.What is Hot-dipped galvanization?
Hot-Dip Galvanizing: Purpose, Process, and Uses
60 oz/square foot while G90 has a designated coating of 0. Hot-dip galvanization yields a strong, thick coating but generally has a dull gray finish.Hot dip galvanizing protects steel from corrosion by providing a tough metallurgically bonded zinc envelope, which completely covers the steel surface and seals it from the .Hot dip galvanizing is a technique that forms a coating of zinc-iron alloy on the surface of steel by submerging it in a bath of molten zinc and allowing a. While they share several similarities, there are a few differences between these types of steel which means galvanized steel tends to be inferior to galvannealed steel.
Step-by-Step Explanation of the Hot Dip Galvanizing Process
Hot dipped G60 galvanized steel is . Galvanizers are found throughout North America, and thanks to the factory-controlled process, a wide variety of steel shapes and sizes can be hot-dip galvanized 24/7/365 - rain or shine. This results in a protective zinc coating that helps prevent corrosion and increases the steel’s lifespan.
It involves cleaning steel and immersing it in molten zinc to obtain a coating. This is the total weight of Zinc on both sides of the sheet.

Not bad for a coating which, in cross section, is barely visible to the naked eye.RELEVANT STANDARDS.
Know your Microns
The galvanized steel is removed and allowed to cool.

Hot-dip galvanization is known to have a . As the full hard steel has undergone acid washing followed by a rolling process through the zinc pot, a layer of zinc film is applied to the sheet’s surface .Hot dip galvanizing is a very simple process that provides long term corrosion protection to steelwork.
What is the HDG Process?
Similar to steel, zinc corrodes when exposed to the atmosphere; however, zinc corrodes at a rate approximately 1/30 of that for steel. It is mainly used as a protective .

Hot-dip galvanized (HDG) steel is versatile and readily available.At the time, the steel was hand dipped in the zinc bath.Hot dipped galvanized steel coils are steel coils that have been zinc-coated using the hot dipped galvanizing process. Building materials designed for structural support are commonly hot .Overview of Hot Dipped Galvanized Steel Coil. The process is inherently simple which provides a distinct . So life expectancy is 3-4 times in hot dip than in pregalv. Preparation and pre-treatment of surfaces – Removal of oil, grease and related contamination. It involves immersing the cleaned and prepped steel or iron articles into a .Home » Hot-Dip Galvanizing (HDG) » What is Galvanizing? » The HDG Coating.Hot-dipped galvanized steel. BS 729 was the old British galvanizing . Electro-galvanized steel.hot dip galvanizing are the design’s impact on: • Safety during the process • Quality of the coating • Aesthetics This guide provides general information on basic design and .Thickness — Several times thicker than other galvanized coating methods.

Hot-dip galvanizing is a process used to apply a protective coating of zinc to steel or iron surfaces.Galvanized steel is made by coating the iron with zinc in a process called hot-dip galvanizing. Firstly, galvannealed steel offers a slightly higher degree of rust and corrosion resistance than .
HOT-DIP GALVANIZING FOR CORROSION PROTECTION
Hot dip galvanizing process steps. Applied in construction, automotive, and white goods industries.

During the process, a metallurgically . It is ideal in situations when the galvanized part is predicted to operate for so many years without maintenance owing to its durability and reliability. The coating that develops during the galvanizing process is metallurgically . Hot dip galvanizing is the process of coating iron or steel with a layer of zinc by immersing the metal in a bath of molten zinc at a temperature of around 450 °C (842 °F).
Hot-Dip Galvanizing (HDG)
Steel coils are immersed in a molten zinc bath, which establishes a metallurgical bond with the steel substrate. Hot dip galvanized coatings on threaded fasteners.