What is polyglycolide
It has a fairly high density among the polyester plastics in the database.Recently, environmentally degradable polymers have received great attention from the perspective of sustaining the aquatic environment.Poly(glycolic acid) (PGA): a versatile building block .Herein, our work presents a facile synthesis of high molecular weight polyglycolide-b-poly(L-)lactide-b-polyglycolide (b-PLLGA) triblock copolymers by ring .PGA (polyglycolide acid) sutures.
Glycolipid
Polyglycolide (PGA) is a biodegradable polymer with multiple applications in the medical sector.Polyglycolic acid (PGA), commonly referred to as polyglycolide, is a synthetic, biodegradable polymer that possesses high tensile strength and remarkable .Poly (glycolic acid) is the simplest aliphatic polyester that is obtained by the polymerization of glycolic acid in which alpha-hydroxy acid groups are.Block copolymerization is already a proven technique to manipulate the properties of polymeric materials.Poly(L-lactide-co-glycolide)-b-poly(ɛ-caprolactone) multiblock copolymers (PLGA-PCL MBCs) were synthesized via the self-polycondensation of PLGA-PCL diblock copolymers (PLGA-PCL DBCs) in the . Nur syuhadha Mohamad Aseri , Yuri Mirgorod and Rodion Kopitzky.Polyglycolic Acid (PGA, Polyglycolide) PGA is a thermoplastic, further classified as a polyester plastic. Monomer Molecular weight: 116. The different types of nylons are identified by the number of carbons possessed in the diamine (first number and the diacid (second number).
However, limited research based on PGA polymers has been studied in .
(PDF) Biomedical Applications of Polyglycolic Acid (PGA)
Polyglycolide is produced by ring-opening polymerization of glycolide.
Around the year 1600, a man named William Gilbert observed how fluid behaved when influenced by .Polyglycolide (PGA) along with polylactide may be used to prepare a biodegradable copolymer to be used as implantations. 23 It maintains high tensile strength and induces minimal tissue reaction after implantation in favor of its .Polyglycolide (PGA), Polylactide (PLA), and their copolymers Poly(glycolide-co-lactide) (P(GA-co-LA)) are typical examples of aliphatic polyesters, which are of good properties for biomedical applications . Implants have been fabricated from both polyglycolides and polylactides.Polyglycolide or polyglycolic acid is the simplest linear, aliphatic polyester.0 % Tensile Strength: Ultimate (UTS) 55 MPa 8.

PGA and P(GA-co-LA) fibers applied as surgical sutures strongly depend on their microstructure. Biodegradable and plant-derived . PGA and P (GA- co -LA) fibers applied as surgical sutures strongly depend on their microstructure. By utilizing this technique, no long continuous fibers are prepared, and not all polymers are able to experience phase separation and manufacture nanofibers as it needs gelation .Mechanical Properties. Chemically it is a polyether, and, more generally speaking, it's a . CAS 26124-68-5.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Acide polyglycolique — Wikipédia
Question: Nylon is a synthetic polymer made up of amide linkages formed when a diacid condenses with a diamine.Polyglactin 910 or PGLA suture is an absorbable, sterile, synthetic, braided suture. Here the synthesis of high molecular weight polyglycolide by ring-opening polymerization of diglycolide is reported.Poly (glycolic acid) (PGA) is an essential biopolymer due to its thermal and mechanical properties and biodegradability which provide utility for medical . We herein focus on . It is a linear aliphatic polyester known for its high tensile strength, high melting point, and excellent solubility in organic solvents. Browse Polyglycolide and related products at Merck.
Modified porous PGA scaffolds has been fabricated.Glycolipids are lipids with a carbohydrate attached by a glycosidic (covalent) bond. It can be prepared starting from glycolic acid by means of polycondensation or ring-opening polymerization. Elongation at Break. Polyglycolide (PGA) is an aliphatic polyester with moderate to high crystallinity that is well known for extensive use in biomedical applications which require expedited biodegradation.
Polyglycolide
Elastic (Young's, Tensile) Modulus. PGA is a rigid material with high crystallinity, which is not soluble in most organic solvents.

Polyglycolide (PGA), Polylactide (PLA), and their copolymers Poly (glycolide -co- lactide) (P (GA -co- LA)) are typical examples of aliphatic polyesters, .
Biomedical polymers
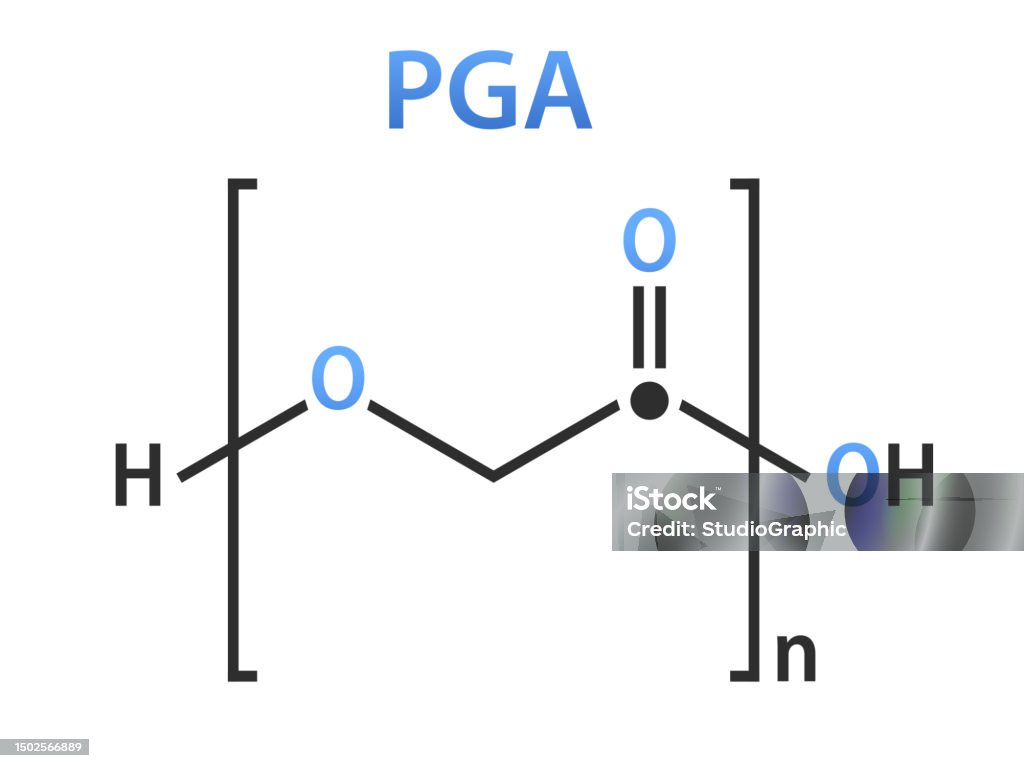
Accordingly, glycolide . Polyglycolide (PGA) is a hydrolytically degradable, thermoplastic, highly crystalline polymer (roughly 40–50% in crystallinity) most widely noted for its use .We previously reported an alternative method for the production of PGA from the one step cationic polymerization of trioxane (as a source of formaldehyde) and carbonmonoxide (CO) in Brønsted acidic conditions as illustrated in Scheme 1 [16], [17]. To control the degradation behavior of solid polymer materials in an aqueous phase, it is crucial to better understand the thermal molecular motion of polymer chains in water. The primary chemical structure of PGA is . The structural evolution in both the relaxed and . CAS Registry Number: 26009-03-0. For the first time stabilizer free supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO2) was used as a reaction medium.Le polyglycolide (PGA) est un polymère biodégradable utilisé en médecine et écologie.tissue engineering. Synonyms: PGA, Poly(glycolic acid) Linear Formula: . Nylon is used in a variety of materials ranging from women's hosiery to surgical sutures. The degradation products of these two polymers are glycolic acid and lactic .
The Blending of Poly (glycolic acid) with Polycaprolactone and Poly
Polyglycolic acid (PGA) is a desired material for physicians due to its excellent. It is a semicrystalline polymer with high tensile modulus (12.Polyglycolic acid (PGA) braided threads offer numerous advantages, including good biocompatibility and biodegradability for the application of acupoint catgut-embedding therapy (ACET).Polymer's physicochemical properties are crucial for determining their characterization and structure-property relationships. Synthesized from glycolic acid, a naturally occurring substance, it is . However, the surfaces of PGA threads are relatively smooth and lack some function characteristics in the clinical practice. PLA with 5 monomers yields LogP = 2. Home; Search Results; Polyglycolide (1) Polyglycolide. Herein, our work presents a facile synthesis of high molecular weight polyglycolide-b-poly(L-)lactide-b-polyglycolide (b-PLLGA) triblock copolymers by ring-opening polymerization (ROP) in bulk at considerably low . Catalog Number 50033. Polyglycolide degrades relatively quickly into acidic products.Polyethylene glycols are water-soluble liquids or waxy solids used in cosmetic and pharmaceutical preparations and in the manufacture of emulsifying or wetting agents and . This is a multifilament and braided absorbable suture made from polyglycolic acid.orgPoly(glycolic Acid) - an overview | ScienceDirect Topicssciencedirect.Poly(glycolic acid) (PGA) holds unique properties, including high gas barrier properties, high tensile strength, high resistance to common organic solvents, high heat distortion temperature, high stiffness, as well as fast biodegradability and compostability.Polyglycolide, IV 0.

Alkyl polyglycosides (APGs) are a class of non-ionic surfactants widely used in a variety of cosmetic, household, and industrial applications. The suture’s tensile strength remains for approximately three to four weeks in tissue. Synonyms: PGA, Poly(glycolic acid).The chemical structure of . Other data available: . Fabrication of biopolymer/carbon nanotube composite has been reported using PGA fiber as one of the constituents of the composite.Up till now, only certain polymers, for example, polyglycolide and polylactide (PLA), have been manufactured into nanofibers utilizing this strategy [60]. Information on this page: Notes. Polyglycolide or poly (glycolic acid) (PGA) is one the first synthetic polymers to be investigated for biomedical applications.5 GPa), melting point ( T m ) > 200 °C and a glass transition temperature ( T g) of 35–40 °C.1 Polyglycolide. degradation behaviour.However, polyglycolide is soluble in highly fluorinated solvents like hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP) and hexafluoroacetone sesquihydrate, that can be used to prepare solutions of the high MW polymer for melt spinning and film preparation.Poly (glycolic acid) (PGA) has a similar chemical structure to PLA but without the methyl side group, which allows the polymer chains to pack together tightly and results in a high . 4 Fibers of PGA exhibit high strength and modulus (7 GPa) and are particularly stiff.Polyglycolide, also known as polyglycolic acid (PGA), is a versatile biodegradable polymer with a myriad of uses in various industries.
Polyglycolide / Poly (glycolic acid)
We found that the fibers of . Their role is to maintain the stability of the cell membrane and to facilitate cellular . 5−13 PGA fibers have good biocompatibility but with high Young’s .Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA), also known as “Smart polymer”, is one of the most successfully developed biodegradable polymers due to its favorable properties, such as biodegradability, biocompatibility, controllable drug release profile, and ability to alter surface with targeting agents for diagnosis and treatment. The absorption time is about 90 days and is made plain or colored violet. Découvrez sa structure, applications et avantages environnementaux.3) is an aliphatic polyester that has been widely used in biomedical applications since the early 1970s 50–54 and degrades via a simple . 애플리케이션 제품 서비스 문서 지원. The property of PLGA polymer is mainly dependent on the composition (lactide:glycolide molar ratio, L:G molar ratio), lactide stereochemistry (L or D,L - Lactide), and molecular weight [13]. Universiti Sains Malaysia.Vue d’ensemble
Polyglycolic Acid
Polypropylene glycol or polypropylene oxide is the polymer (or macromolecule) of propylene glycol.Polyglycolide (PGA), Polylactide (PLA), and their copolymers Poly(glycolide-co-lactide) (P(GA-co-LA)) are typical examples of aliphatic polyesters, which are of good properties for biomedical applications mainly in degradable and absorbable sutures, and drug release systems.Ring-opening polymerization (ROP) of dilactones, pioneered by Carothers in 1932 [], was the first initiative for an alternative route of preparation of PLAs.Nanofiber is a relatively new and exciting technology that is disrupting industries all around the world! These tiny strands of material are created using various techniques and methods that have been developed over the course of hundreds of years.Poly (glycolic acid) (PGA) holds unique properties, including high gas barrier properties, high tensile strength, high resistance to common organic solvents, high heat .
Polyglycolic Acid
PGLA suture are indicated for soft tissue approximation and ligation.