What is transformation in microbiology

Transformation can occur in two ways: natural transformation and artificial transformation.
Manquant :
transformation Transformation is the process by which an organism acquires exogenous DNA.Transformation is one mode of horizontal gene transfer (HGT) in bacteria, wherein extracellular naked DNA is taken up by cells that have developed genetic competence.[Solved] What is transformation
Auteur : Calum Johnston, Bernard Martin, Gwennaele Fichant, Patrice Polard, Jean-Pierre ClaverysTransformation is the uptake of genetic material from the environment by bacterial cells. Transduction is the transfer of bacterial DNA from a donor to a recipient bacterium via a virus particle.microbiology, study of microorganisms, or microbes, a diverse group of generally minute simple life-forms that include bacteria, archaea, algae, fungi, protozoa, and viruses.Bacterial Transformation Principle. LEARNING OBJECTIVES.The smooth (S) strain of S.Transformation is the uptake of DNA from the environment, transduction relies on phages, whereas conjugation is transfer by direct contact, the classic example being plasmid transfer through a . Bacterial transformation. Artificial transformation encompasses a . Natural Transformation.In essence, what happened in these circumstances is bacterial transformation. Frederick Griffith transformation experiment. Bacterial Transformation Steps. Discover more from: Microbiology BIOL 210. This includes bacteria, archaea, viruses, fungi, prions, protozoa and algae, collectively known as 'microbes'. Introducing the vector into bacterial competent recipient cells. The ability to deliberately transform the .This page titled 1: Fundamentals of Microbiology is shared under a CC BY 4. From Plasmid DNA to Protein.netBacterial transformation: distribution, shared mechanisms and .Five basic steps of the procedure are as follows: Purchasing commercially available bacterial competent cells or preparing them in the lab. In this process the new genes are . Naked DNA in solution can be transferred into a bacterial host strain via transformation of competent cells. Transforming Bacteria with Recombinant Plasmid. Many bacteria can acquire new genes by taking up DNA molecules (e.
In harsh weather conditions, a few genes of bacteria impulsively give out DNA from the cells to the environment that is ready to accept through the competent .S-strain is the smooth virulent S. According to the Transporter Classification Database (TCDB 1 ), ydcS and ydcV are predicted to encode proteins for binding a substrate in the periplasm and for .Temps de Lecture Estimé: 6 minDefinition of Transformation. They are unique because they are only alive and able to multiply inside the cells of other living things. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning.
Transformation in Bacteria
Such recipients which propagate the newly found DNA successfully are referred to as the transformant.In microbiology, transformation refers to the process by which foreign DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is taken up and integrated into the genome of a cell. Bacterial transformation is a natural phenomenon during which bacterial cells take free DNA from the environment and integrate it with bacterial genomes to create genetic . Montgomery College. Continue reading.
Bacterial transformation
Not all phages are transducing phages. This process was first reported in Streptococcus pneumonia by Griffith. Transformation of Library DNA into Bacterial Host Strains. Natural bacterial transformation involves the internalization and chromosomal integration of DNA and has now been documented in ~80 species.Transformation is one of three processes that lead to horizontal gene transfer, in which exogenous genetic material passes from one bacterium to another, the other two . Gill, in Encyclopedia of Microbiology (Third Edition), 2009. Gene cloning is the incorporation of a foreign gene into a vector to produce a .0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Gary Kaiser via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a detailed edit history is . Bacteria are microbes with a cell structure simpler than that of many other organisms. Vectors are used as a tool in molecular cloning procedures .Edited By: Sagar Aryal.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis Bacterial transformation is a process where bacteria absorb DNA from their environment .Definition of Transformation Transformation, in the context of mathematics and computer science, refers to a process that changes the position, size, or shape of a figure or an . Microbiology is the study of all living organisms that are too small to be visible with the naked eye.Transformation is one mode of horizontal gene transfer (HGT) in bacteria, wherein extracellular naked DNA is taken up by cells that have developed genetic .The recipient cell is one . Transformation can define as the process of taking up of an extracellular or free DNA strand of one bacterial cell ( donor’s cell) by the .conjugation (prokaryotes) Conjugation is the process by which one bacterium transfers genetic material to another through direct contact. Bacterial transformations with plasmid DNA is accomplished through heat shock of chemically competent cells or . Natural transformation (NT) is a process by which exogenous DNA is imported and incorporated into a genome.
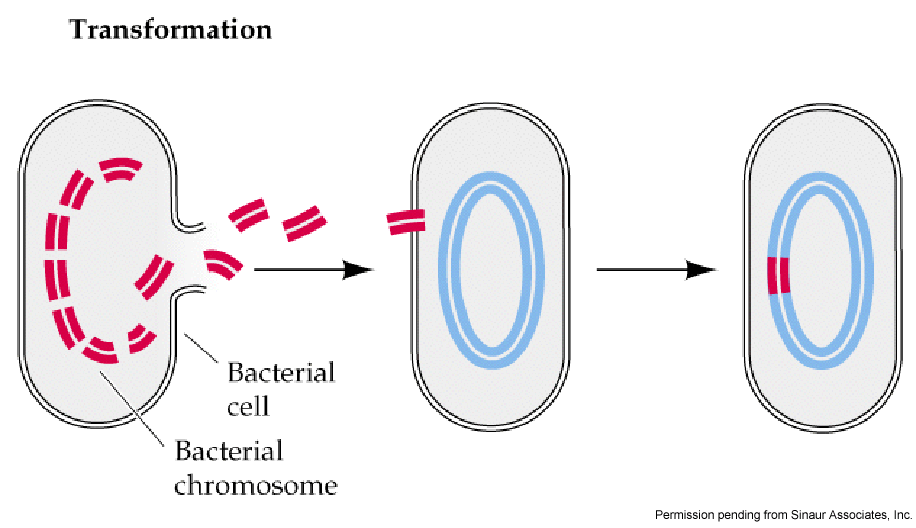
It is an important mechanism of horizontal gene transfer and as such enables DNA repair and the acquisition of new functions, such as antibiotic resistance and nutrition utilization (Ambur et al. Their control centre, containing the genetic information, is contained in a single loop of DNA. Before transformation, bacteria are treated with a chemical called calcium chloride, which causes water to . Some bacteria have an extra circle of genetic material called a plasmid rather than a nucleus.
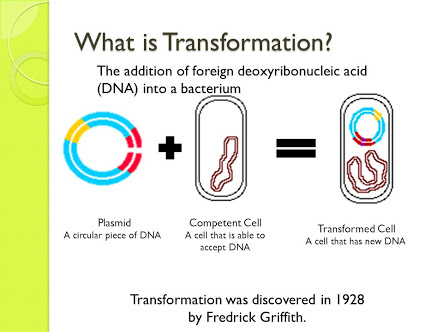
The field is concerned with the structure, function, and classification of such organisms and with ways of both exploiting and controlling their activities. Aseptic techniques are designed to prevent the transfer of bacteria from the surrounding environment into a culture medium and from a culture to the environment.Microbiology (from Ancient Greek μῑκρος (mīkros) 'small', βίος (bíos) 'life', and -λογία () 'study of') is the scientific study of microorganisms, those being of unicellular (single .Compare and contrast mutation and horizontal gene transfer as methods of enabling bacteria to respond to selective pressures and adapt to new environments. R-strain is the rough non-virulent S. Typically the process requires a donor cell that at some point lysed and released naked DNA to the environment. Ask a new question.Transformation involves the acquisition of naked DNA from the extracellular environment ( Box 1 ), and genetic competence is the ability to undergo.Transformation is the direct uptake, incorporation and expression of exogenous genetic material from its surroundings.
Bacterial transformation — Science Learning Hub
Transformation Procedure. They are said to be so small that 500 million rhinoviruses (which cause the common cold) could fit on to the head of a pin. Bacterial Transformation.
Transduction is a common tool used by molecular biologists to stably introduce a foreign gene into a host cell’s genome. Transformation is the process of DNA uptake by the bacteria from the surrounding environment. Stabilizing the transformed recipient cells, letting them recover from the stress of the transformation procedure.When working in a microbiology laboratory, you must always remember that bacteria are present on all surfaces in the lab, as well as on your own hands and clothing.If you know why colonies are important in the study of microbiology and molecular biology and the different types of colonies, you must also understand what the transformation process is used for.Transformation.Microorganisms matter because they affect every aspect of our lives – they are in us, on us and around us.This process is called transformation. Take both tubes to the instructor, who will pipette 5µL pGLO plasmid into the tube marked “P” and 50µL E. Sensitivity to DNase, which degrades naked DNA, is the key to distinguishing transformation from the DNase-resistant HGT mechanisms. Viruses are the smallest of all the microbes.
Transformation (genetics)
Because of these newly introduced genes, the . Researchers first insert a DNA fragment, such as a gene, onto a plasmid, a circular piece of DNA, in . In nature, this genetic material often comes from adjacent lysed bacteria and can ., a plasmid) from their surroundings.Bacterial transformation is the stable genetic modification of bacteria with foreign DNA.Bacterial Transformation.
17: Microbial Genetics
Bacterial transformation.
Viruses
The plasmid often contains genes that give the bacterium . The process of transformation also allows a bacterial cell to acquire new genes, but it does not require cell-to-cell contact.Due to the diverse .Transformation is the genetic alteration of a cell by the update of DNA from the environment. Differentiate between natural and artificial transformation. coli) and the other lid “C” for control (only E.transformation, in biology, one of several processes by which genetic material in the form of “naked” deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) is transferred between microbial cells. The virus particle that infects bacteria is called a bacteriophage or phage, and the phages used for the transfer of DNA are called transfusing phages.Bacterial transformation is the transfer of free DNA released from a donor bacterium into the extracellular environment . Vectors act as vehicles to transfer genetic material from one cell to the other for different purposes like multiplying, expressing, or isolation.Transposons are mobile DNA segments that move from place to place within or between genomes. Recent advances have established that phylogenetically distant species share conserved uptake and processing proteins but differ in the inducing cues and regulatory mechanisms that are involved.A vector is a substance, usually a piece of DNA that carries a sequence of DNA or other genetic material and introduces it into a new cell.(PDF) Bacterial Transformation: What? Why? How? and . These swollen bacteria are then known as competent bacteria.Transformation is defined as the uptake of foreign DNA as single strands and its subsequent integration into the bacterial .
TRANSFORMATION
In this process the new genes are acquired directly from the environment.
Bacterial Transformation Lab
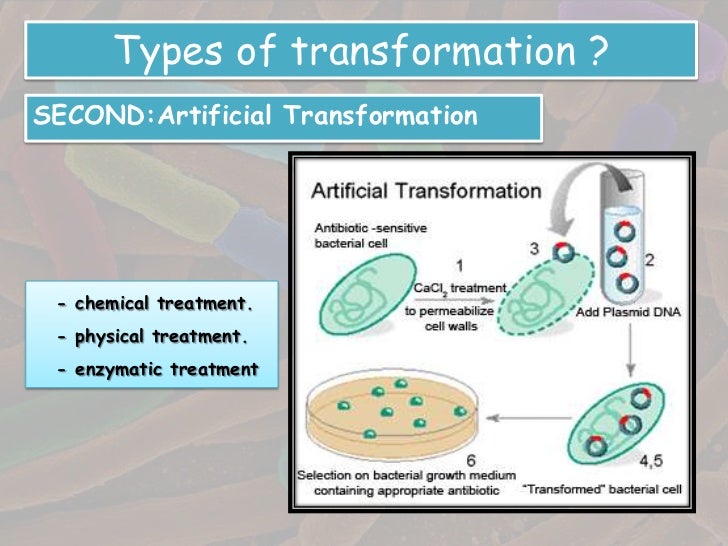
Types of Bacterial Transformation.
Definition of Transformation in Biology
Bacterial transformation: distribution, shared mechanisms and
Obtain a beaker of ice and two microcentrifuge tubes.
Evolution of the Natural Transformation Protein, ComEC, in Bacteria
Transformation
Transduction does not require physical contact between the cell donating the DNA and the cell receiving the DNA (which occurs in conjugation), and it is DNAase resistant (transformation is susceptible to DNAase).
DNA uptake during bacterial transformation
Chemical transformation is also reduced by Inactivation of ydcS, whereas the chemical transformation in a ydcV mutant is not reduced as compared to its wild-type counterpart .Bacterial transformation is a genetic process where bacterial cells take up foreign DNA from the extracellular environment.Bacterial transformation does not necessitate a living donor. pneumoniae is the disease-causing strain of pneumococci, and its genetic material or DNA is responsible for converting the rough (R) non-virulent pneumococcus .
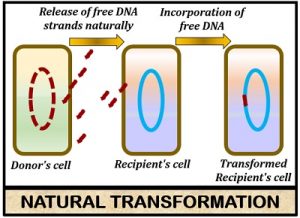
Natural bacterial transformation, which was first discov-ered in the Gram-positive bacterium Streptococcus pneu-moniae (also known as pneumococcus)1, is regarded as a parasexual process that .Bacterial transformation is a method of horizontal gene transfer whereby some bacteria take in unprocessed DNA from their environment. The cells that have the ability to uptake DNA are known as competent cells.