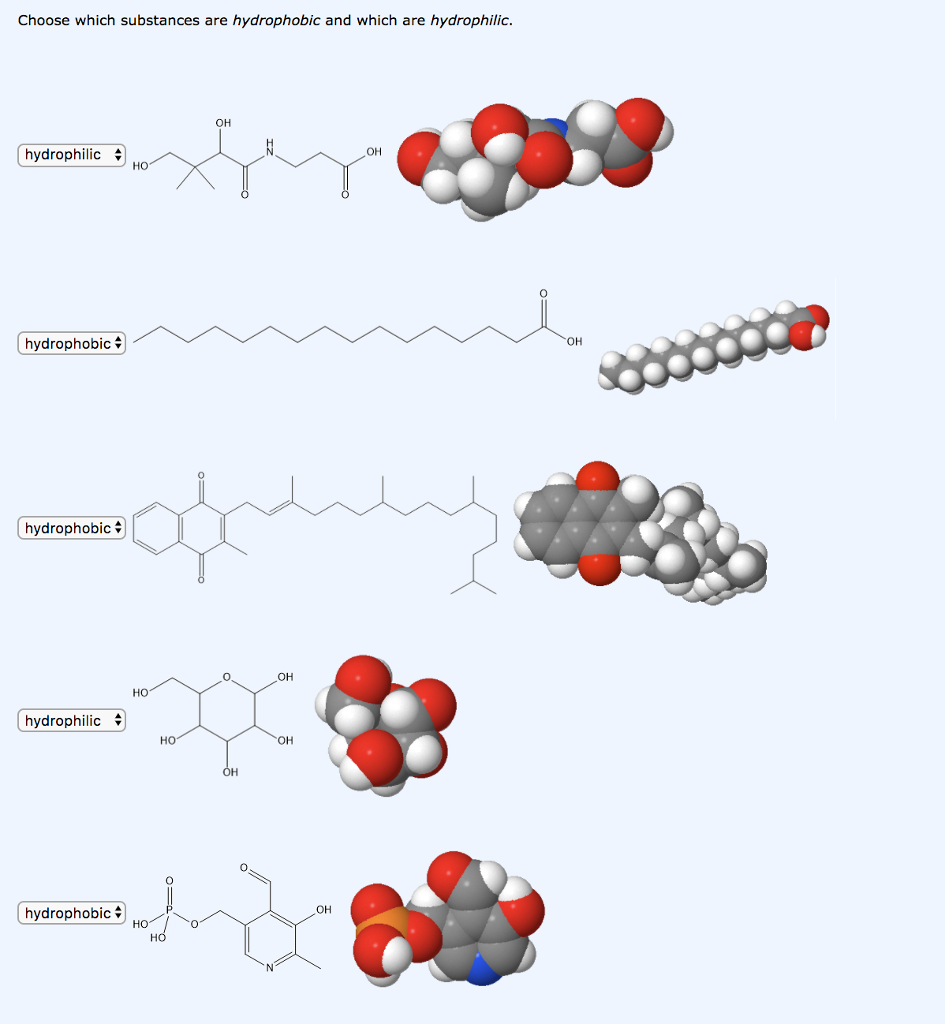
Which substance is hydrophobic
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar molecules that group together to form micelles rather than be exposed to water. It isn't that the substance is repelled by water so much as it .Table of Contents. These terms are often used in the context of biology, chemistry, and materials science, and understanding their differences is crucial in these fields. Figure 3: Magic Sand models hydrophobic effect .
Hydrophobic
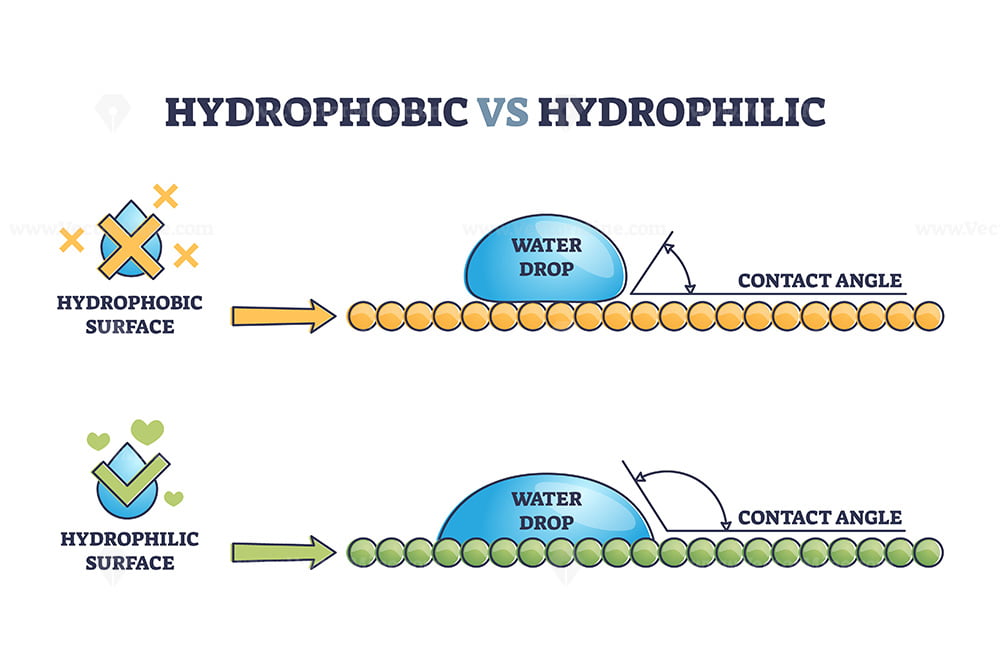
Substances that are hydrophobic, or repel water, are often transported through and between cells with hydrophilic proteins or structures attached to aid in their dispersal.In these situations, the hydrogen bond (and the system polymorphism) plays an important role although the hydrophobic interaction is equally fundamental.If you drip water . Hydrophobic substances cannot be mixed with or dissolved in water: 2. The phospholipids in the plasma membrane are arranged in two layers, called aphospholipid bilayer. Hydrophobic and hydrophilic are opposites. American chemist Walter Kauzmann discovered that nonpolar substances like fat molecules tend to clump up together rather than distributing itself in a water medium, because this allow the fat molecules to have minimal contact with water.Scheme 1 Electrified railways face the challenges of fouling, fogging, icing, corrosion, etc. Hydrophilic substances diffuse in water, which is to say they move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration.
Oils and fats are hydrophobic. Hydrophilic substances are also substances that can be dissolved in water. Its surface is also hydrophobic, but it behaves very differently.

Hydrophobic interactions describe the relations between water and hydrophobes (low water-soluble molecules).comWhat Are Examples of Hydrophobic Substances? - . One such substance is adipose tissue, which is made up of adipocytes (fat cells) . Other examples of hydrophobic substances include hydrophobicity in plants and animals. They are involved in and believed to be the fundamental driving force in many chemical and biological phenomena in aqueous solutions, such as molecular recognition, protein folding, formation and stability . To do that, we start with important biological, .Identify hydrophobic substances in the body. Solubilities of Ionic Substances in Liquids.A hydrophilic molecule is a water-soluble molecule that can strongly interact with water through hydrogen bonding.

Hydrophobic effects refer to the tendency of nonpolar molecules (or parts of molecules) to be aggregated in water.
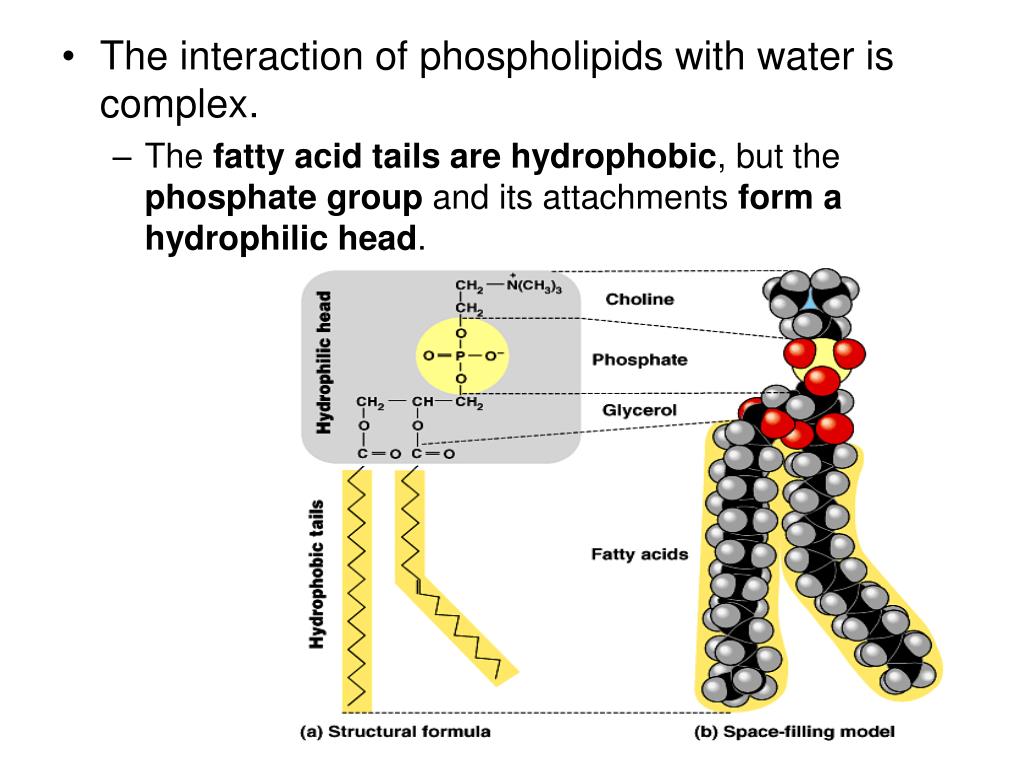
Hydrophobic substances are those that repel water. Hydrophilic substances are attracted to water, while hydrophobic substances repel water., organic solvents). Many plants are .As shown in Figure below, each phospholipid molecule has a head and two tails. It'll literally ball up to avoid getting in touch, to minimize its . Hydrophobic clothing is. Hydrophobes are nonpolar molecules and usually have a long chain of carbons that do not . Citer cet article. Compare: hydrophobic.A substance is a piece of metal.
Hydrophilicity, Hydrophobicity
Hydrophobic Definition. Step 2/3 Identify a substance that functions as a cushion around organs in the body., ΔHint < 0 ∆ H i n t < 0. Factors such as the texture and chemical makeup of the surface determine if a material is hydrophobic or hydrophilic. How are hydrophobic molecules related to other molecules? Related Biology Terms 1 Hydrophobic – Molecules or substances that are not attracted to water, or repel it.Date de publication : 2 juin 2011Temps de Lecture Estimé: 2 minTo be hydrophobic means to fear water.The hydrophobic effect refers to the free energy penalty that one pays to solvate a weakly interacting solute. It means lacking affinity for water, and tending to repel or not to absorb water.Rose petals have a textured surface that is covered with hydrophobic wax. The goal of this section is to differentiate between bond polarity and molecular polarity.How does the solubility of a substance depend on the intermolecular forces and physical properties of the solute and solvent? This webpage from Chemistry LibreTexts explains the factors that affect solubility, such as polarity, temperature, pressure, and molecular size.Explanation: Among the substances you've listed, fat is hydrophobic, which means it repels water and does not mix well with it. The substance paper is the substance in which one dozen of them don't have affinity towards water and don't contain any polar groups.Hydrophobic Definition.

A.Some of the most common examples of hydrophilic substances are sugar, salt, starch, and cellulose.Which of the following substances is hydrophobic and functions as a cushion around organs in the body? Here’s the best way to solve it. Cocoa powder, an example of a hydrophobic substance.Surfaces that attract water are termed hydrophilic, whereas surfaces that repel water are termed hydrophobic.
Water as a solvent (video)
La plupart des substances hydrophobes sont également lipophiles, mais les exceptions incluent les fluorocarbures et les silicones.
Contrary to hydrophilic substances like sugar and salts that dissolve in water, hydrophobic substances like fats contain long chains of hydrocarbons with nonpolar bonds, which do not interact favorably .So things like hexane we would call hydrophobic.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Hydrophobic
Note the Pattern.
The Hydrophobic Effects: Our Current Understanding
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Nonpolar substances are hydrophobic because, Polar and ionic molecules are hydrophilic because, A detergent is a molecule that can mix polar and nonpolar molecules together because and more.
The Definition of Hydrophobic With Examples
The head “loves” water (hydrophilic) and the tails .Hydrophobes are nonpolar molecules and usually have a long chain of carbons that do not interact with water molecules. Note that nonpolar molecules may contain polar bonds! Examples of hydrophobic substances in the body include lipids and fats.HYDROPHOBIC definition: 1. Hydrophobic means water-fearing which means hydrophobic substances deter water and are insoluble.Other articles where hydrophobicity is discussed: alcohol: Physical properties of alcohols: . The features are around 16μm in size, meaning they hold onto water droplets.Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Solutes. [1] In contrast, hydrophobes are not attracted to . Referring to the thermodynamic cycle above, ΔGsol Δ G sol, the reversible work needed to solvate a hydrophobic molecule, is dominated by step 1, the process of forming a cavity in water. Hydrophobic molecules and surfaces repel water.An illustration of hydrophobic versus hydrophilic properties Hydrophobic materials repel water, while hydrophilic materials attract or absorb water. Oils and other fats as well as non-polar molecules are hydrophobic. Another example from biology is the rose petal. It is mostly made up of cell loss five or the laws survival water molecule can adhere to the fibers of Sally lose that consists of a number of partial, positive and negative . The degree to which a surface either attracts or . The key is to identify a substance in the body that is both hydrophobic (water-repelling) and has a protective function for the organs.A Phospholipid Bilayer.3390/molecules27207009
Hydrophobic effect
With the increasing availability of manufacturing methods (plasma treatment, stencils, .Lipids with a polar and nonpolar end are sometimes called amphipathic lipids, because one end is hydrophilic, while the other is hydrophobic.
Which substance is hydrophobic?
The hydrophobic effect accounts for the insolubility of nonpolar molecules, like CH 4.Hydrophilic substances are normally polar since water is polar and attracts charges. For instance, lipids store energy, provide insulation, make up cell membranes, form water . Etymology: from Greek hydros, meaning “water” and philia, meaning “friendship”. Some typical structures of both types of lipids are shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\). Greasy molecules that do not mix with water typically do have favorable interaction energies, i. The substance that is hydrophobic and functions as.of the molecule, which is hydrophobic (“water-hating”), is larger with increased molecular weight.A large number of hydrophobic substances can be seen in both the industrial and the domestic sectors.Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which of the following is a hydrophobic material? (A) paper (B) table salt (C) wax (D) sugar, We can be sure that a . As a solute is embedded into water, the interface appears between solute and water, .Hydrophobic effects refer to the tendency of nonpolar molecules (or parts of molecules) to be aggregated in water. They won’t dissolve in water but separate from it. Hydrophobic definition. Hydrophobic molecules tend to be non-polar molecules and group together. This is caused by the attraction of . The fear of mixing or reacting with water under a given set of reaction parameters is often referred to as . Materials like lotus leaves, magic sand and nano-tex fabric are all examples of . They have positive or negative . Hydrophilic means water-loving; having an affinity for water; capable of interacting with water through hydrogen bonding. You will also learn how to calculate the solubility of a gas in a liquid using Henry's law. The plasma membrane is composed mainly of phospholipids, which consist of fatty acids and alcohol.
The Hydrophobic Effects: Our Current Understanding
What is hydrophobicity? First, the term is a misnomer. The mixing of fat and water is a good example of this . The different varieties of lipids have different structures, and correspondingly diverse roles in organisms.To be hydrophobic means to fear water. The free energy of solvating a hydrophobic .
How can you tell if a structure is hydrophobic?
So this right over here is hydrophobic.In particular, the hydrophobic core of cyclodextrines allows their usage as carriers for hydrophobic drugs in biological environments, enhancing the solubility and . Hydrophobic literally means “the fear of water”. A droplet of water forms a spherical shape, minimizing contact with the hydrophobic leaf.Hydrophobic is a property of a substance that repels water.Hydrophobic substances, however, do not easily dissolve in water.Water and oil famously don't mix: the term hydrophobic (water-fearing) is commonly used to describe substances that, like oil, do not mix with water. The word stem ‘hydr’ comes from the greek ‘hydor‘ meaning water, therefore hydrophobic materials are ‘water-fearing‘, and do not mix with water, whereas hydrophilic materials are ‘water-loving‘ and have a tendency to be wetted by water.A common mistake is to use hydrophilic and hydrophobic interchangeably.
Hydrophobic effect
Download a printable version of this document here.Causes of Hydrophobic Interactions.Lipids tend to be hydrophobic, nonpolar, and made up mostly of hydrocarbon chains, though there are some variations on this, which we'll explore below.This review focuses on our current understanding on hydrophobic effects.