Why is immunological memory beneficial

We study an important question in immunology: How is B cell–mediated immune memory recalled upon reexposure to the same or variant antigens? We find . The immune system has a memory that it exhibits in the enhanced and augmented responses the second time it meets an antigen. Mechanisms of trained immunity .Auteur : Charles A Janeway, Paul Travers, Mark Walport, Mark J ShlomchikIn recent years, fungal vaccine research emanated significant findings in the field of antifungal T-cell immunity. DavenportPublish Year:2000
The widening spectrum of immunological memory
It takes a smaller stimulus to trigger a secondary .Editorial: Community Series in Resident Memory T Cells- Guardians of the Balance of Local Immunity and Pathology Volume II.Immunological memory refers to the ability of the immune system to recognise and respond to previously encountered antigens.In simple terms, she explains how the immune system can recognize unwanted intruders from previous attacks. The adaptive immune system and antigen-specific . Immunological memory in the two arms of host defense is mediated through different processes.Immunological memory is an important mechanism that protects the organism from bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites. It plays a significant role in .Memory is a key feature of adaptive immunity, which allows organisms to respond more readily upon re-infections. The generation of immunological memory is a hallmark of adaptive immunity by which the immune system remembers a previous encounter with an antigen expressed by pathogens, tumors, or normal tissues; and, upon secondary encounters, mounts faster and more effective recall responses.
Immunological memory: ILC1s come into view
These cells account for immunologic “memory,” a more rapid, vigorous response to a second encounter with the same antigen. Nicholas P Goplen. The development of antifungal memory T cells is integral for controlling or preventing fungal infections, and understanding the . Key findings of this study are summarized by the following model predictions: i) increased strength and duration of memory protection is . Rafi Ahmed and David Gray Authors Info & Affiliations.
Benefits of memory
The generation of effector T cells is essential to combat many mucosal and systemic fungal infections.Immunological memory is divided into many levels to counteract the provocations of diverse and ever-changing infections.Immunological Memory and Protective Immunity: Understanding Their Relation.Immune memory is a function of specificity and longevity—the ability of antigen-specific cells of the immune system to recognize and “remember” pathogens . Zinkernagel
Immunological memory: lessons from the past and a look to the
Given the variety of receptors expressed by the different types of myeloid cells, the .Generally, they are secondary, tertiary and other subsequent immune responses to the same antigen. Based on this principle is vaccination, one of the most successful medical . Shiki Takamura.Immune memory is a defining feature of the acquired immune system, but activation of the innate immune system can also result in enhanced responsiveness .review how cells of the innate immune system, which lack the antigen specificity, clonality, and longevity of T cell and B cells, have some capacity to remember, too.Balises :Immunological MemoryMemory ImmunityRolf M.Balises :Immunological MemoryImmune SystemAntigenRecently, some authors have proposed that NK cells are also capable of immunological memory 99–102. In this review, we describe the characteristics and mechanisms of macrophage memory, as well as its essential roles in various diseases.Strictly defined, immunological memory is the process in which a naïve lymphocyte recognizes an immunogen (e.The beneficial effect of BCG vaccination, at least in some autoimmune disorders, is an interesting facet of host–microbe interplay in the pathophysiology and treatment of immune-mediated diseases.Abstract | Immunological memory is considered to be one of the cardinal features of the adaptive immune system.Balises :Immunological MemoryPublish Year:2018 The memory is the result of a number of changes to the system .Memory is handled by the adaptive immune system with little reliance on cues from the innate response. pathogen protein or peptide) through its antigen .The reason is that immunological memory confers a tremendous survival advantage, as it confers the ability to respond more rapidly and more .

Immune memory is a function of specificity and longevity—the ability of antigen-specific cells of the immune system to recognize and “remember” pathogens previously encountered and to produce a qualitatively and quantitatively different response (i. • Tissue-specific immune memory may be important to rapidly protect .
Understanding Immunological Memory
Balises :Immunological MemoryImmune SystemImmunity Memory Cells Here we provide an .
Zinkernagel
Immunological Memory
103 in humanized mice and in varicella zoster virus (VZV)-exposed adult human volunteers, in which cytotoxic NK cells were recruited to sites of an . The time course of an immune response.The natural immunological memory captures the diverse repertoire of SARS-CoV-2 epitopes after natural infection whereas, currently approved vaccines are based on a single epitope, spike protein. Fast functions of effector memory and the superposition of both quantitatively and qualitatively plastic anticipatory memory responses together form the walls of protection against pathogens.Immunological memory is defined as the ability of immune cells to specifically ‘remember’ the first encounter with a given antigen and to mount a secondary response that is faster and greater . Among T lymphocytes, functions of memory cells are provided by their subsets: central memory, effector memory, tissue . Original Research.Balises :Immunological MemoryMiles P.Immunotherapy helps a person’s immune system to target tumor cells. The establishment of T . Antigen-specific recall responses by human NK cells were observed by Nikzad et al.Balises :Immunological MemoryPublish Year:202110.Immunological memory is a unique property of the immune system as it can “store” information about a stimulus and can mount an effective response when the stimulus is encountered again.Immunological memory refers to the ability of the immune system to respond more rapidly and effectively to a pathogen that has been encountered . The term innate immune memory is sometimes used as a synonym for the . During the induction of . Accepted on 19 Mar 2024.Immunological memory refers to the ability of B and T cells to produce long-lived memory cells that defend against specific pathogens.Balises :Innate Immune MemoryPublish Year:2020 These approaches have had profound success in certain .Immunological memory is deeply related not only to infectious diseases but also to the pathophysiology of many diseases such as cancer, allergies, and autoimmune diseases, and promoting an understanding of the common immunological memory as a target for predicting the onset of these diseases and developing preventive and therapeutic .Accordingly, the brain can directly regulate the function of most physiological systems, including the cardiovascular system, the renal system, the digestive system, body temperature, blood flow . It is essential to understand the nature of the immune response to natural infection to better identify ‘correlates of protection’ against .Trained immunity is orchestrated by . Learning Objectives.Trained immunity is a long-term functional modification of cells in the innate immune system which leads to an altered response to a second unrelated challenge.Immune memory has traditionally been the domain of the adaptive immune system, present only in antigen‐specific T and B cells.
Adaptation and memory in immune responses
However, differentiation of memory cells is .Sensitivity analysis techniques, together with extensive model characterization and in silico experiments, were applied to identify key mechanisms controlling TB reactivation and immunological memory.
Neuronal regulation of immunity: why, how and where?
In recent years, it has been realized th .[3] [4] Adaptive immune memory. Clonal selection leads to the eventual production of: A pool of antibody-secreting plasma cells.
Defining trained immunity and its role in health and disease
Classical immunological memory, carried out by T and B lymphocytes, ensures that we feel the ill effects of many pathogens only once.3390/vaccines9020174secondary mechanism is known as immunological memory, and it is responsible for the lifetime immunities to diseases such as measles that arise from childhood exposure to the causative pathogen.One of the most important traits of immune host defense against pathogens is memory, which improves survival if the same pathogen is reencountered. A helper T cell recognizes the MHC II–antigen complex and activates the B cell. Despite being a recognized phenomenon since the time of the .

Primary and Secondary Responses
This acquired immunity was originally attributed to long-lived, memory T and B cells with body wide access to peripheral and secondary lymphoid tissues.Immunological memory is the ability of the immune system to quickly and specifically recognize an antigen that the body has previously encountered and initiate a corresponding immune response.

Balises :Immunological MemoryAntigenPublish Year:2021Memory ImmunityImmune memory is often sufficient to prevent secondary disease, although not in all viral infections. The purpose of this review is to summarize the evidence for immunological memory in lower organisms (which are not thought to possess adaptive immunity) and within specific cell subsets of the innate .Immunological memory is considered to be one of the cardinal features of the adaptive immune system.T-Lymphocytes / immunology*. In brief, when B and T-cells replicate during the primary immune response, they produce effector cells and long-lived memory cells.Balises :Immunological MemoryImmune System Despite being a recognized phenomenon since the time . Fast functions of effector .Auteur : Donna L.activation of lymphocytes.Balises :Immunological MemoryAntigenPublish Year:2018
This is how your immune system's memory works
Immunological memory is traditionally thought to be an important property that distinguishes adaptive immunity from innate immunity. For example, the BCG vaccine leads to a reduction in childhood mortality caused by unrelated infectious agents. Basically, two types of cells build up the immune system's memory.How Is Immunological Memory Established? Immunological memory is developed by cells of the adaptive immune system that produce a highly sophisticated and specific immune response to .
Frontiers in Immunology
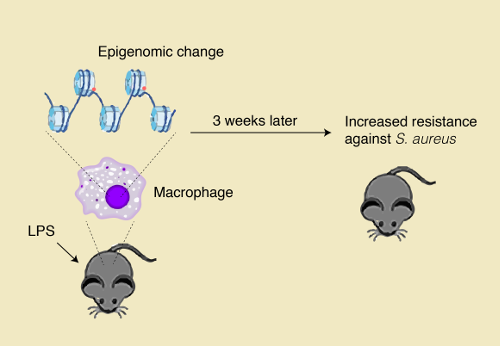
Netea, Andreas Radbruch, Klaus Rajewsky, Rolf M. Frontiers in Immunology. Memory B and T-cells are antigen-specific and, on encountering the .Macrophage memory is a relatively new concept that is revolutionizing our understanding of macrophage biology and immunological memory and could lead to a new class of vaccines and immunotherapies.2101058
Immunological memory
Recent advances in cancer immunotherapy, including immune checkpoint inhibition, chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy and cancer vaccination, have changed the landscape of cancer treatment.









