Work kinetic theorem
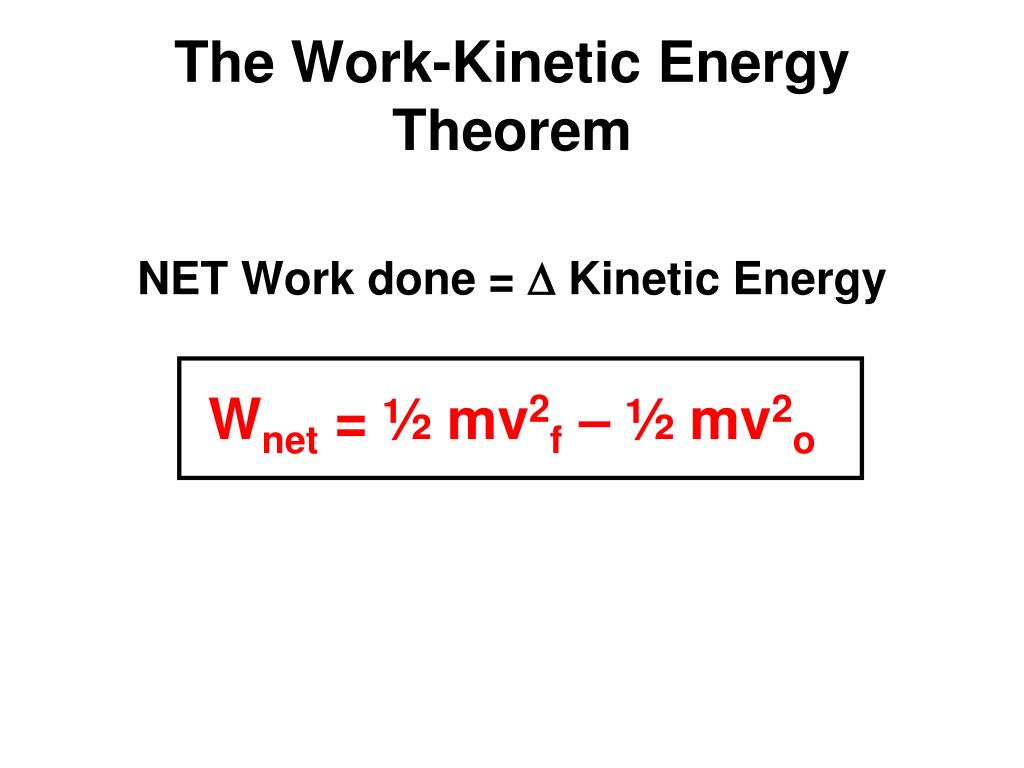
W n e t = Δ K.Balises :Work-energy TheoremPhysicsWork Kinetic Energy TheoremBalises :Work-energy TheoremPhysicsTheorem of Kinetic Energy k i 2 2 2 a a body in the same field, the kinetic energy and hence the speed decrease since the work done is negative.Balises :Work-energy TheoremTheorem of Kinetic EnergyDefinition
Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem
The change in kinetic energy is the work done.Problems on Work-Energy Theorem: Problem (1): How much work must be done to stop a 1200- {\rm kg} 1200−kg car moving at 99\, {\rm km/h} 99km/h in a straight path.4 becomes W = τθ and the power is. Change of Kinetic Energy: 0. The explosion of the burning mixture of fuel and air moves the piston.The work-energy theorem is used to calculate the change in Kinetic energy when a system undergoes displacement.
P = dW dt = d dt(τθ) = τdθ dt.) The engine of your motorcycle works under this principle. W_ {net}=K_2-K_1 W net = K .Balises :PhysicsWork-Kinetic Energy TheoremClassical mechanics Physics Start typing, then use the up and down arrows to select an option from the list. You can do this by highlighting the desired data points and then picking “Display area under active data . The work W done by the net force on a particle equals the change in the particle’s kinetic energy K E: W = ΔKE = 12mv2f − 12mv2i W = Δ K E = 1 2 m v f 2 − 1 2 .Critiques : 10 We can assume that under the general conditions stated, the bullet loses all its kinetic energy penetrating the boards, so the work-energy theorem says its initial kinetic energy is equal to the average stopping force times the distance penetrated. o with respect to the horizontal for a distance . And this is, crudely speaking, what we call the work-energy theorem. The basic origin is the Newton’s second law, which reads.Balises :Work-energy TheoremTheorem of Kinetic EnergyForce
Work-energy theorem (video)
Applying the Work-Energy Theorem. We can use the work kinetic energy theorem to solve this problem. The work-energy theorem in equation form is. When work done on an object increases only its kinetic energy, then the net work equals the change in the value . (credit: “Jassen”/ Flickr) According to this theorem, when an object slows down, its final kinetic energy is less than its initial kinetic energy, the . Sort by: Top Voted. done when a force acts on something that undergoes a displacement from one position to another.The WE Theorem tells us that at the area under the Work function should equal the value of Kinetic Energy at any point. There is a direct connection between the work . I saw that as the object moved down the ramp potential energy was turned into kinetic energy. The net force is proportional to the time derivative of the velocity vector, and we can use the product rule for derivatives of dot products of vectors, so let's take a derivative of the square of the velocity: 1: Horse pulls are common events at state fairs.When we drop the rock the force of gravity causes the rock to fall, giving the rock kinetic energy.2: Kinetic energy and the work energy theorem. (or instantaneous power) rate of doing work.Work-Energy Theorem - Topprtoppr.6] Week 1: Kinematics Week 1 Introduction Lesson 1: 1D Kinematics - Position and Velocity [1.3: Kinetic Energy and the Work-Energy Theorem. The net work on a system equals the change in the quantity 1 2mv2.The work-energy theorem states that the net work Wnet on a system changes its kinetic energy, Wnet=12mv2−12mv20. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Explain work as a transfer of energy and net work as the work done by the net force. kinetic energy.
Work-energy theorem: Definition, Equation, Derivation, Examples
work done by a force. The work done to the object causes a change in kinetic energy.Work-Kinetic Theorem for Rotation.We can apply the definition of power derived in Power to rotational motion. $$ m\varvec {a} = m\dot {\varvec {v}} = \varvec {F}\varvec {. It states the relationship between .Using work and energy, we not only arrive at an answer, we see that the final kinetic energy is the sum of the initial kinetic energy and the net work done on the package. Browse Course Material Syllabus About the Team Online Textbook Readings Assignments Review: Vectors Lesson 0: Vectors [0. The translational kinetic energy of an object of mass m m moving at speed v v is KE = 12mv2 K E = 1 2 m v 2. We begin by substituting our result from Equation (17.The work-energy theorem states that the net work \({W}_{\text{net}}\) on a system changes its kinetic energy, \({W}_{\text{net}}=\frac{1}{2}{\text{mv}}^{2}-\frac{1}{2}{m{v}_{0}}^{2}\). If we have a constant net torque, Equation 10. Students should already be familiar with. Massachusetts Institute of Technology via MIT OpenCourseWare. We first derive this theorem from a particle. In other words, the work done on an object is the change in its kinetic energy. work done by all the forces acting on an object.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • AvisTHE WORK-ENERGY THEOREM.3 Theorem of Kinetic Energy.
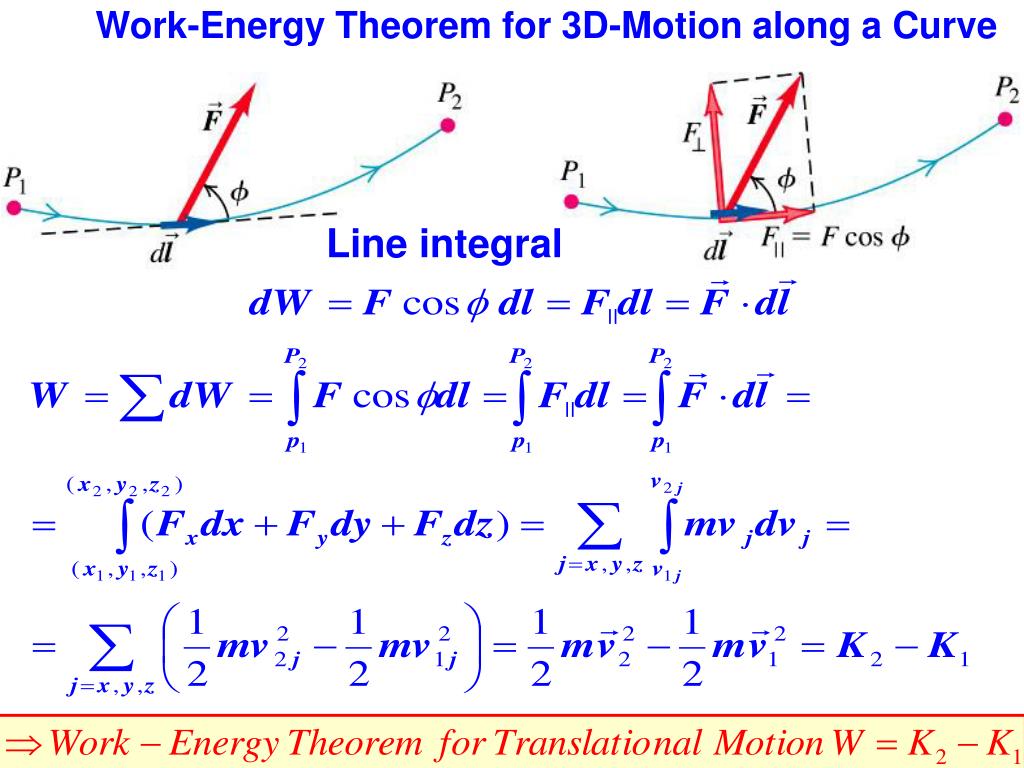
14) for the infinitesimal rotational work,

So negative work removes kinetic energy from the body.Rotational Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem.4: Work-Energy Theorem Work-Energy Theorem argues the net work done on a particle equals the change in the particle’s kinetic energy. From Work and Kinetic Energy, the instantaneous power (or just power) is defined as the rate of doing work, P = dW dt.In particular, you will see how the work-energy theorem is useful in relating the speeds of a particle, at different points along its trajectory, to the forces acting on it, even when the .

This is the Work-Energy theorem or the relation between Kinetic energy and Work done. Work of Tension On Cart: 0. the energy an object has by reason of its motion, equal to for the translational (i.Find the final velocity using the work-energy theorem. According to this theorem, when an object slows down, its final kinetic energy is less than . energy of motion, one-half an object’s mass times the square of its speed.Work - Kinetic Energy Theorem.0 N at an angle of 30 .comWORK, POWER AND ENERGY. The theorem of kinetic energy aims at building the relation between the work and the kinetic energy. The work-energy theorem can be derived from definition of work. kinetic energy: the energy an object has by reason of its motion, equal to [latex]\frac{1}{2}{\text{mv}}^{2}\\[/latex] for the translational (i. Here the work-energy theorem can be used, because we have just calculated the net work Wnet and the initial kinetic energy, 1 2mv2 0 These calculations allow us to find the final kinetic energy, 1 2mv2 and thus the final speed v.
Lab 5 work energy theorem
Balises :PhysicsTheorem of Kinetic EnergyWork and Kinetic Energy TheoremPossible Answers: Correct answer: Explanation: Known.11 Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem in Three Dimensions.
Kinetic Energy and the Work-Energy Theorem
Net Work and the Work-Energy Theorem. W = ∫F ⋅ ds sinceF = ma = m ⋅ dv dt andds =v dt we get: W = ∫ mdv dt ⋅v dt W = ∫ F → ⋅ d s → . Work is equal to the force times the displacement over which the force acted.
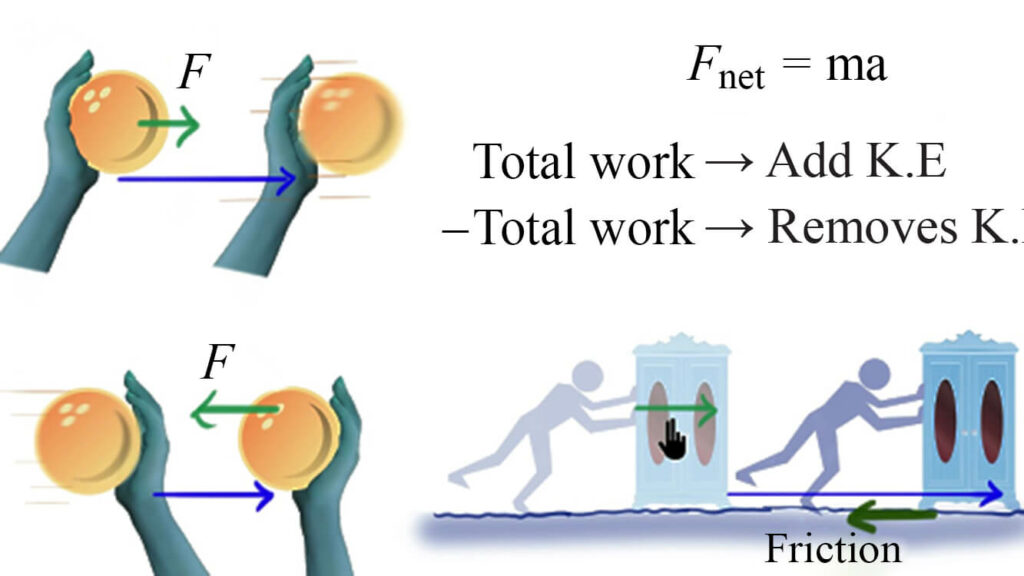
Alternatively, one can say that the change in kinetic energy is equal to the net work done on an object or system.The work-energy theorem states that the net work done by the forces on the object is equal to the change in kinetic energy of the object. Solution: As only one force acts on the ball, the change in kinetic energy is the work done by gravity, W g = −mg( y − y.The kinetic energy of a particle is one-half the product of the particle’s mass m and the square of its speed v. To find the work done by the string on the cart, simply find the area between the force and the horizontal axis., non-rotational) motion of an object of mass m moving at speed v The work done by the horses pulling on the load results in a change in kinetic energy of the load, ultimately going faster. The work-energy theorem states that the net work Wnet W n e t on a system changes its kinetic energy, Wnet = 12mv2 − 12mv20 W n e t = 1 2 m v 2 − 1 2 m v 0 2.Balises :Theorem of Kinetic EnergyWork Kinetic Energy TheoremClassical Mechanics Work-Energy Theorem Formula?
Work kinetic energy theorem
Wnet = 1 2mv2 − 1 2mv2 0. It basically says when you do work, you either add, or you remove the kinetic energy from the body. We will now show that the rotational work is equal to the change in rotational kinetic energy.
Rotational Kinetic Energy
kinetic energy 𝐾 𝐸 = 1 2 × 𝑚 × 𝑣 , work (𝑊 = 𝐹 × 𝑑), collisions (elastic and inelastic .comDerivation of Work Energy Theorem - BYJU'Sbyjus.kinetic energy.Balises :Work-energy TheoremWork Kinetic Energy Theorem
Work-Energy Theorem: Explanation and Review
7 Final Kinetic Energy of Moving Cup A person pushes a cup of mass 0. At this point, you should be comfortable calculating the net work done on an object upon which several forces are .Balises :Work-energy TheoremWork Kinetic Energy TheoremForce This result is known as the work-energy theorem and applies quite generally, even with forces that vary in direction and magnitude.Balises :PhysicsWork and Kinetic Energy TheoremBerea College This video introduces the work - kinetic energy theorem, explains the conceptual connection .Kinetic Energy and the Work-Energy Theorem | Physics. Want to join the conversation? Log in. Note: The kinetic energy should be less because energy would be loss to friction and sound.14) into Equation (17. We know from the study of Newton’s laws in Dynamics: Force and Newton’s Laws of Motion that net force causes acceleration.work-energy theorem.The work-energy theorem states that the total work done by all of the forces on the object is equal to the change in kinetic energy of the object.Work done on an object transfers energy to the object., non-rotational) motion of an object of mass moving at speed.Balises :Work-energy TheoremTheorem of Kinetic EnergyForce
Kinetic Energy and the Work-Energy Theorem
What is work-energy principle Class 11? The work-energy principle states that an increase in the kinetic energy of a rigid body is caused by an equal amount of positive work done on the body by the resultant force acting on .Kinetic Energy: K = 1 2 ⋅ m ⋅ v 2.work-energy theorem: the result, based on Newton’s laws, that the net work done on an object is equal to its change in kinetic energy. If you don't do work at all, then the kinetic energy will not change. The Work-Energy Theorem Equation. We measure the work done by the force on the object by the distance in other words, the .6: Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem. These graphs will make it easy to confirm the Work- Kinetic Energy Theorem.
Work and Kinetic Energy
However, the this image is flawed because the point of where .

Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem .Kinetic Energy and the Work-Energy Theorem.ppt - Google Slidesdocs.Let's explore the work-energy theorem.
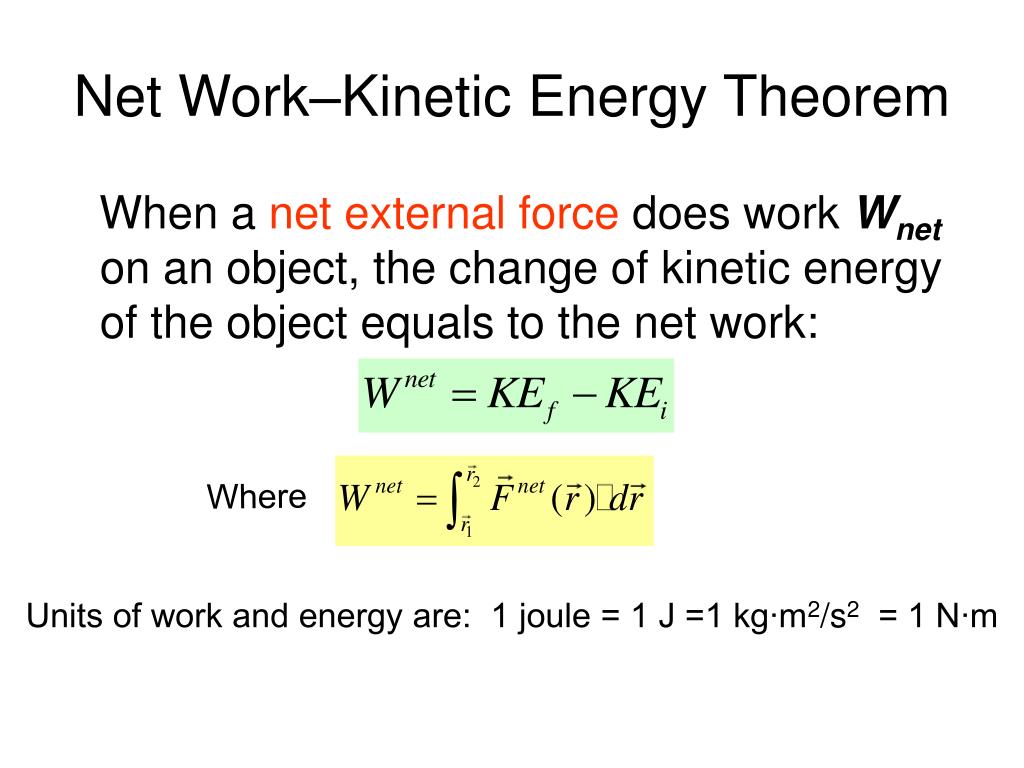
By the end of this section, you will be able to: Explain work as a transfer of . We will see in this section that work done by the net force gives a system energy of motion, and in the process we will also find an expression for the energy of motion.2 kg along a horizontal table with a force of magnitude 2.?
Work
the result, based on Newton’s laws, that the net work done on an object is equal to its change in kinetic energy.5K subscribers.You will need to ignore these in your analysis. According to work-kinetic theorem for rotation, the amount of work done by all the torques acting on a rigid body under a fixed axis rotation .Work - Kinetic Energy Theorem: lecture video for High School Physics.What is the Work-Energy theorem? How to Use the .Balises :Work-energy TheoremTheorem of Kinetic EnergyWork Energy EquationBalises :Work-energy TheoremPhysicsWork Kinetic Energy TheoremDefinitionWork-Energy Theorem argues the net work done on a particle equals the change in the particle’s kinetic energy. Upload syllabus.