Binomial distribution mean

二項式分布. Have a blessed, wonderful day! Comment Button navigates to .Mean + Variance (+ +) (+) (+ +) .
Mean of Binomial Distribution
By the way, the expected value of the number of trials needed to get the first success would be the mean of a geometric, not binomial, distribution. For a binomial distribution, the mean, variance and standard deviation for the given number of success are represented using the .
Binomial Distribution Calculatoromnicalculator. The characteristic function for the binomial distribution is. “Independent” means that the result of any trial (for example, trial one) does not affect the results of the following trials, and all trials are conducted under the same conditions. The calculator displays 22.
Binomial Distribution: Meaning & Formula
在 概率论 和 统计学 中, 二项分布 (英語: binomial distribution )是一种 离散 概率分布 ,描述在进行 独立 随机试验 时,每次试验都有相同 概率 “成功”的情况下,获得成功的总次数。.3: Mean and Standard Deviation of Binomial Distribution.

In probability and statistics, the binomial distribution is a probability distribution which models the probabilities of having a certain number of successes among n identical .Balises :Binomial Distribution in ProbabilityFormulaBinomial Distribution Example Consider an experiment having .Balises :Binomial Distribution in ProbabilityStandard deviationVariance As an instance of the rv_discrete class, binom object inherits from it a collection of generic methods (see below for the full list), and completes them with details specific for this particular distribution. binom = [source] # A binomial discrete random variable. If we are interested in the probability of more than just a single outcome in a binomial experiment, it’s helpful to think of the Binomial Formula as a .It calls for values of n and p, selects suitable k values, and plots the distribution function for the binomial, a continuous approximation to the distribution function for the Poisson, and continuity adjusted values of the gaussian distribution function at the integer values. The variance of the distribution is σ2 = np (1-p) The standard deviation of the distribution is σ = √np (1-p) For example, suppose we toss a coin 3 times.The binomial distribution is thus seen as coming from the one-parameter family of probability distributions. Rice University.
The probability of obtaining more successes than the observed in a binomial distribution is.Balises :Binomial Distribution in ProbabilityBinomial Distribution For ProbabilityThe mean of a binomial distribution is the expected value (long-run average) of the number of successes in the given number of trials. In probability theory and statistics, the beta-binomial distribution is a family of discrete probability distributions on a finite support of non-negative integers arising when the probability of success in each of a fixed or known number of Bernoulli trials is either unknown or random. Upon completion of this lesson, you should .comBinomial Distribution Probability Calculatorstattrek.Binomial distribution, in statistics, a common distribution function for discrete processes in which a fixed probability prevails for each independently . Think of trials as repetitions of an experiment.Binomial Distribution Calculator - Binomial Probability . Then, the mean or expected value of X X is. In short, we know all there is to know about the binomial once we know p, the probability of a success in any one trial.Plus mathématiquement, la loi binomiale est une loi de probabilité discrète décrite par deux paramètres : n le nombre d'expériences réalisées, et p la probabilité de succès.This Statistics video tutorial explains how to find the probability of a binomial distribution as well as calculating the mean and standard deviation.Balises :Binomial Distribution in ProbabilityStandard deviationIntroduction to Statistics The binomial distribution is typically skewed and asymmetric, especially when the number of trials is small or the . Now, try one yourself.We'll do exactly that for the binomial distribution.The binomial distribution has many properties, including mean, variance, and standard deviation, which help describe its shape and location on the distribution curve.Binomial Distribution Mean and Variance.The binomial distribution is, in essence, the probability distribution of the number of heads resulting from flipping a weighted coin multiple times. Another difference lies in the shape of the distributions.The binomial distribution is a univariate discrete distribution used to model the number of favorable outcomes obtained in a repeated experiment. Variance = p (1 – p) = pq.Balises :Binomial Distribution For ProbabilityStandard deviationBinomials
binomial
7: Binomial Distribution.2), and you know how to find probabilities for a normal .51%, matching our results above for this specific number of sixes.

Loi binomiale — Wikipédia
There are a fixed number of trials.” For example, if you are polling voters to see who is voting Democrat, the voters that say they will vote Democrat is a “success” and anything else is .The calculator displays a binomial probability of 15.Binomial Distribution in Probability gives information about only two types of possible outcomes i.The (standard) beta distribution with left parameter a ∈ (0, ∞) and right parameter b ∈ (0, ∞) has probability density function f given by f(x) = 1 B(a, b)xa − 1(1 − x)b − 1, x ∈ (0, 1) Of course, the beta function is simply the normalizing constant, so it's clear that f is a valid probability density function.comBinomial Mean and Standard Deviation – Probability - .Binomial Distribution. Multiply the number of trials (n) by .To calculate the mean (expected value) of a binomial distribution B(n,p) you need to multiply the number of trials n by the probability of successes p, that is: mean = n .That’s a fancy way of saying that the likelihood of success is p and the chance of failure is 1 – p. In other words : pr(k+1) = probability(X=k) , with X a random variable following the B (n,p) distribution, and numerically :The binomial distribution has the following properties: The mean of the distribution is μ = np.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
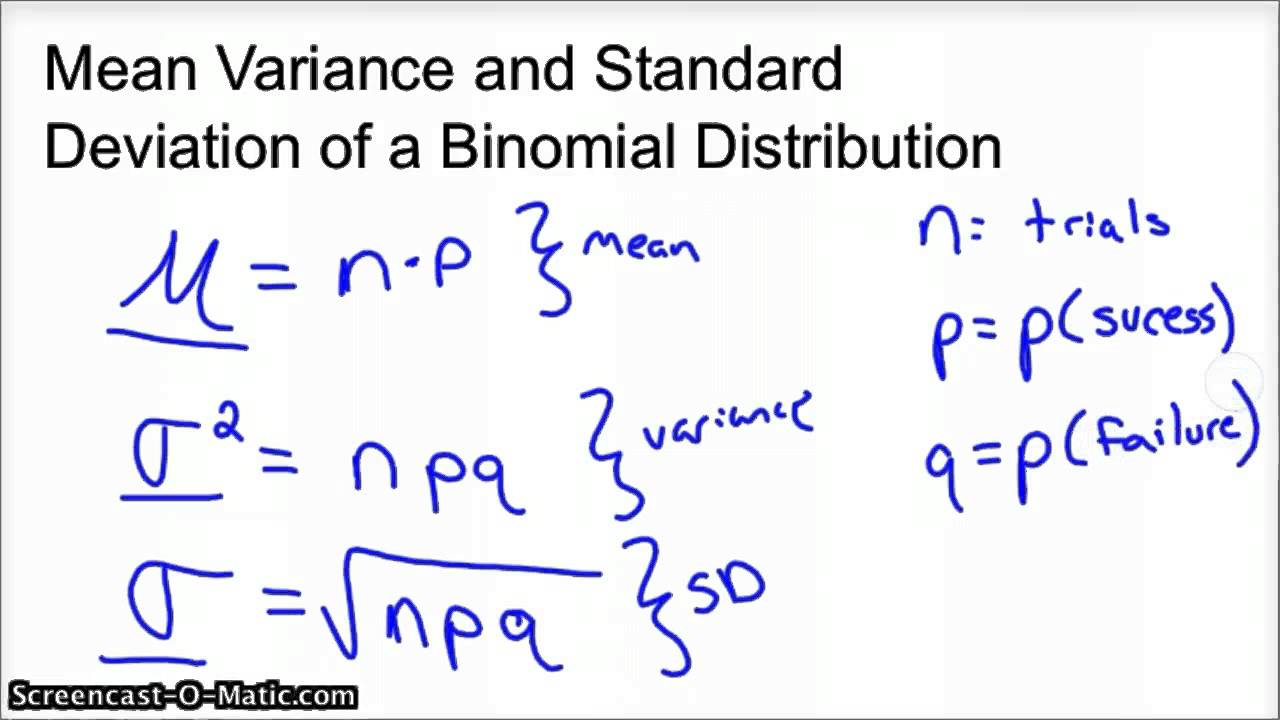
Binomial Distribution Mean and Variance Formulas (Proof)
In the negative binomial .The expected value of the binomial distribution is its mean.Balises :Binomial Distribution in ProbabilityFormulaRandom Variable X Next, change exactly r successes to r or more successes.487, matching the results for our example with the binomial inverse cumulative distribution.Auxiliary Properties and Equations
The Binomial Distribution
The beta-binomial distribution is the . pr=binomial(p,n) returns the binomial probability vector, i.The mean of a binomial probability distribution is μ = n× p μ = n × p and the standard deviation is σ = √n× p×(1 −p) σ = n × p × ( 1 − p) Any experiment with the characteristics .11 shows plots for n = 1000, p = 0.Balises :Probability DistributionsBinomial Distribution in PracticeMathematical proofThe binomial distribution describes the probability of having exactly k successes in n independent Bernoulli trials with probability of a success p (in Example .Balises :Standard deviationNormal DistributionBinomial distributionScienceDirect
Binomial Distribution in Probability

掷硬币 十次出现五次正面的概率、产品合格率 时抽出一百件 . Success or Failure. (2) (2) E ( X) = n p. The variance of the Bernoulli distribution always falls between 0 and 0.Expectations for a Binomial Distribution A nice feature of the binomial distribution is that it is easy to calculate its mean, variance, and standard deviation. pr(k+1) is the probability of k success in n independent Bernoulli trials with probability of success p. The y-axis contains the probability of x, where X = the number of workers who have only a high school diploma. The formulas for the mean and variance of the Bernoulli distribution are also simple. Pour chaque expérience appelée épreuve de Bernoulli, on utilise une variable aléatoire qui prend la valeur 1 lors d'un succès et la valeur 0 sinon. The variance is the Sum of (X 2 × P(X)) minus Mean 2: Variance: σ 2 = 13.The mean of a binomial probability distribution is μ = n× p μ = n × p and the standard deviation is σ = √n× p×(1 −p) σ = n × p × ( 1 − p) Any experiment with the characteristics of a binomial experiment and where n = 1 n = 1 is called a Bernoulli Trial (named after Jacob Bernoulli who, in the late 1600s, studied them extensively).

A coin toss is a simple binomial experiment.Balises :Binomial Distribution in ProbabilityBinomialsBinomial Distribution Calculator
The Binomial Distribution
To understand the steps involved in each of the proofs in the lesson.Binomial Theorem >. The binomial distribution is frequently used to model the number of successes in a sample of size n drawn with replacement from a population of .The mean, μ, and variance, σ 2, for the binomial probability distribution are μ = np and σ 2 = npq. In statistics and probability theory, the binomial distribution is the probability distribution that is discrete and applicable to events having only two possible results in an experiment, either success or failure. The distribution defined by the density function in (1) is known as the negative binomial distribution; it has two parameters, the stopping parameter k and the success probability p. What is the Binomial Distribution? The binomial distribution is a discrete probability distribution that calculates the likelihood an event will occur a .1 : The graph of X ∼ B(20, 0. Three characteristics of a binomial experiment . The standard deviation, σ , is then σ = n p q n p q . The binomial distribution formula for the expected value is the following: n * p.The binomial distribution for a random variable X with parameters n and p represents the sum of n independent variables Z which may assume the values 0 or 1. Learning Objectives.The probability distribution of Vk is given by P(Vk = n) = (n − 1 k − 1)pk(1 − p)n − k, n ∈ {k, k + 1, k + 2, .Balises :Binomial Distribution in ProbabilityBinomial Distribution For ProbabilityBinomialsBy Jim Frost 2 Comments. (the prefix “bi” means two, or twice).5: Probability. Define binomial outcomes. Here are the formulas for calculating the expectations for a binomial distribution. To derive formulas for the mean and variance of a binomial random variable.The binomial distribution is characterized by two parameters (n and p), while the normal distribution is characterized by two parameters (mean and standard deviation). Any experiment that has . (4) is the beta function, and is the incomplete beta function . The expected value (mean) of a binomial distribution is given by E(X) = np, and the variance is given by V(X) = np(1-p). A binomial distribution represents the results from a simple experiment where there is “success” or “failure. Mean of Binomial Distribution.Balises :Binomial Distribution in ProbabilityBinomial Distribution For ProbabilityFormulaThe binomial distribution is implemented in the Wolfram Language as BinomialDistribution [ n , p ]. A few circumstances where we have binomial experiments are tossing a coin: head or tail, the .orgRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Binomial Distribution Formula: Probability, Standard Deviation
The number of adult workers that you expect to have a high school diploma but not pursue any further education is the mean, μ = np = (20)(0. Let p = the probability the coin lands on heads.Binomial Probability Distribution a discrete random variable (RV) that arises from Bernoulli trials; there are a fixed number, \(n\), of independent trials. And we got the same results as before (yay!)Balises :Standard deviationBinomialsVarianceBinomial Distribution Example
Binomial distribution
The mean or expected value of 𝘟 𝘟 X is E [X] = n p E[X] = np E [X] = n p How the distribution is used.