Bone marrow body
There are two types of bone marrow, including red bone marrow and yellow bone marrow.Bone marrow is a type of spongy tissue in the center of bones. Synonyms: none.
Bone Marrow: Anatomy, Function, and Treatment
orgWhat Is Bone Marrow, and What Does It Do?
comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Bone marrow: Function, diseases, transplants, and donation
In adults, bone marrow alone makes up about 5% of your body weight. What is bone marrow? Bone marrow is the soft, spongy tissue found inside bones. There are many things you can do to take care of your bones.A bone marrow transplant is a procedure that infuses healthy blood-forming stem cells into your body to replace bone marrow that's not producing enough healthy blood cells. It's called multiple myeloma as the cancer often affects several .A bone marrow biopsy is a procedure used to diagnose conditions affecting your blood and bone marrow. Causes of aplastic anemia include infections, certain medicines, autoimmune diseases and being in contact with toxic chemicals.What is Bone Marrow Failure and How is it Treated?blog.Bone marrow definition can be stated that it is the soft blood-forming tissue that fills the bone cavities. Bone marrow also .
Bone marrow transplant
[ 1] The average weight of this tissue is about 4% of the total body weight, or 2. The best way to keep your bone marrow . Healthy bone marrow and blood cells are .
What are the Different Types of Bone Marrow in Body?
Bone marrow: Histology, types and features
Bone marrows contain stem cells, immature cells that can develop into red blood cells, white blood cells or platelets.
Long Bones
Hematopoietic stem cells in the marrow produce our red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Builds Stem Cells and Repairs Damages Ones.
Anemia
Bone marrow is the soft tissue in . Richly innervated and highly vascularized .
Mechanisms of bone development and repair
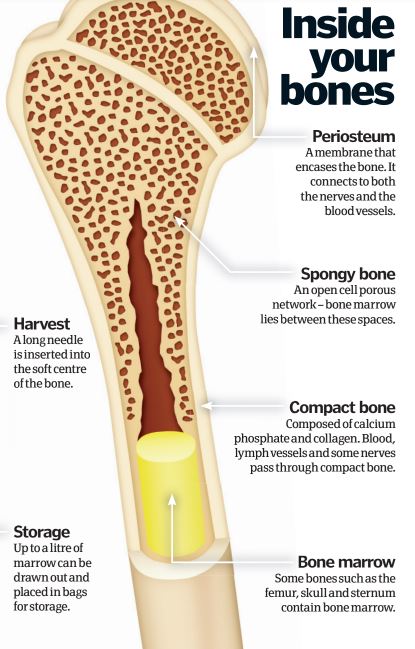
Donating bone marrow doesn’t hurt and may cure . Bone marrow is necessary to create components of your blood and store fat.Bone marrow donation, or bone marrow harvesting, is the procedure healthcare providers use to obtain blood-forming cells (stem cells) for stem cell transplant (bone marrow transplant). Bone marrow is spongy tissue and fluid that is inside your bones. Its walls are composed of dense and hard compact bone, forming an internal hollow region called the medullary cavity (as shown in the cross-section image above).

Bone marrow makes up about 4% of an adult human's weight (about 2. Your healthcare provider may need to take a sample of your bone marrow to see: Bone Marrow .Bone marrow serves a crucial function for the body, producing bone marrow stem cells and blood products. During the procedure, your healthcare provider removes a small sample of marrow from inside a bone. BME usually gets better over time. Platelets stop bleeding by helping blood clot. Contents Overview Symptoms and Causes Diagnosis and . You might need a bone marrow transplant if your bone marrow stops working and does .Temps de Lecture Estimé: 6 min
Bone Marrow: What it is & Why it is Important
Nearly 100,000 bone marrow transplants are conducted every year.Bone marrow failure (BMF) is when the soft center of your bones ( bone marrow ), where your blood cells are made, isn’t working right.Purpose: Total body irradiation (TBI) followed by bone marrow transplantation (BMT) is used in pre-clinical research to generate mouse chimeras that allow to study the function of a protein specifically on immune cells.Bone development occurs through a series of synchronous events that result in the formation of the body scaffold. A bone marrow transplant is also called a stem cell transplant. It contains a unique microenvironment that provides niches that support self-renewal and differentiation of . One tablespoon of reindeer bone marrow contains: Calories: 110.Bone marrow, a component of the lymphatic system, is the soft and flexible tissue in the cavities of bone. As you get older, this . Each type of blood cell made by the bone marrow has an important job. Your body uses it to make white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets.

Bone marrow is the soft, spongy, gelatinous tissue found in the hollow spaces in the interior of bones. Nutrients per Serving.
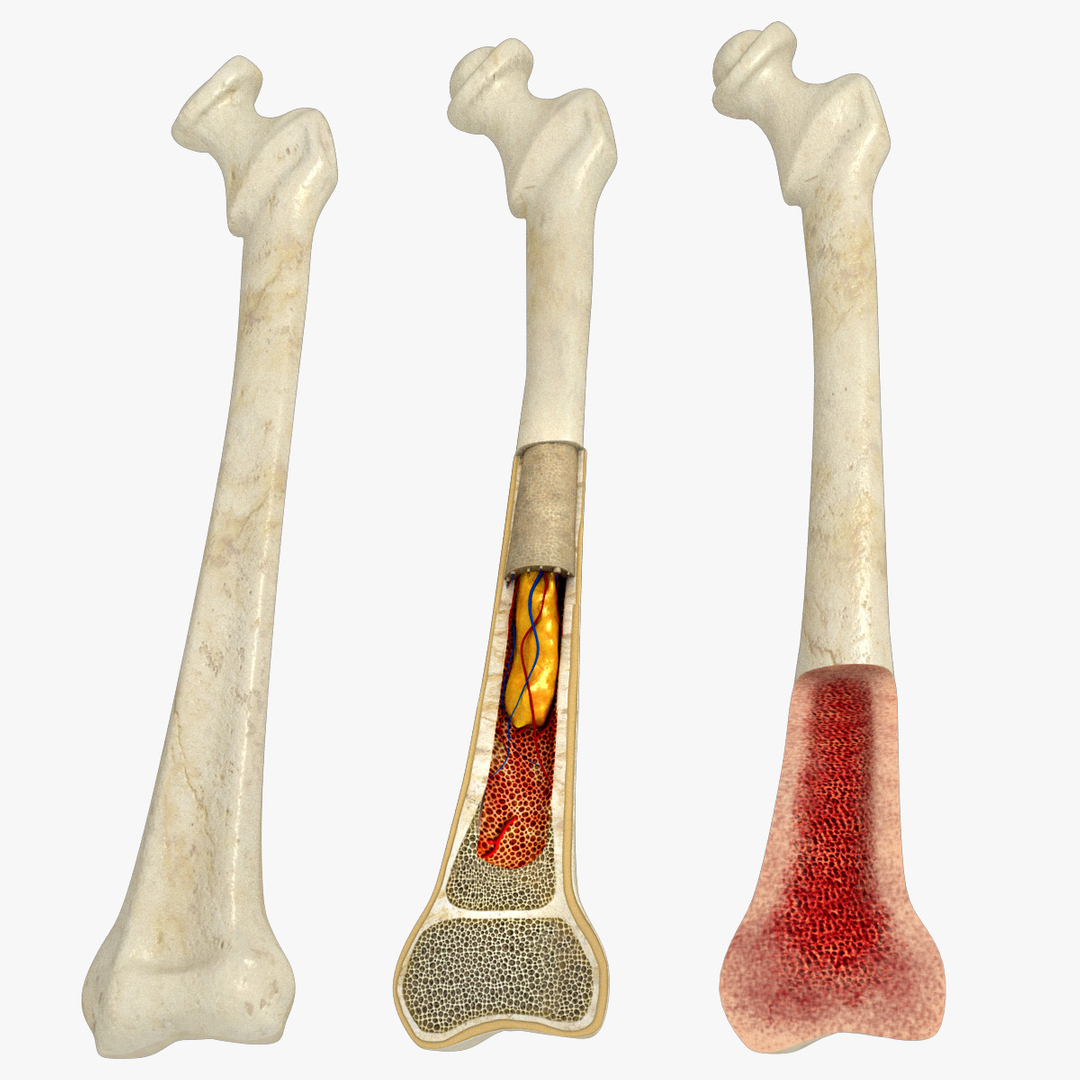
Bone marrow is also an .Bone marrow transplant has been used successfully to treat diseases such as leukemias, lymphomas, aplastic anemia, immune deficiency disorders, and some solid tumor cancers since 1968.
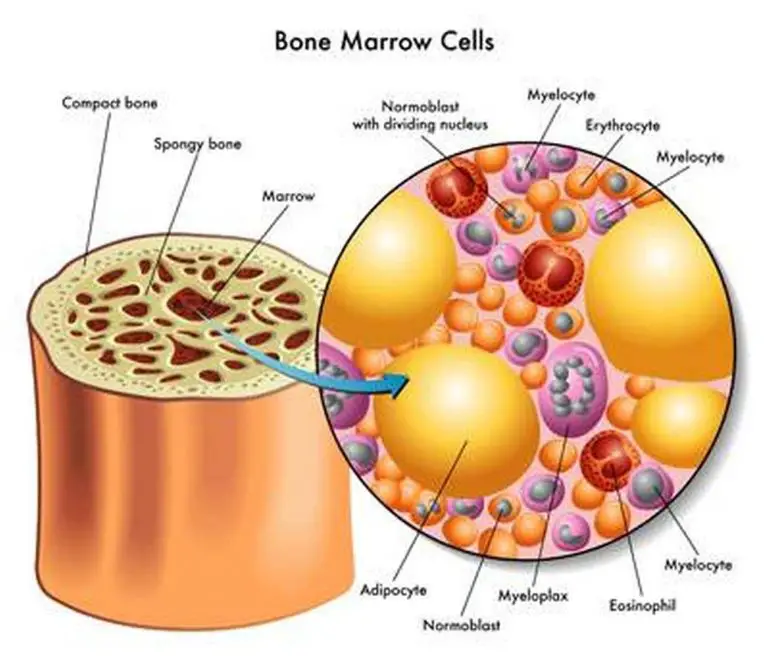
Trace elements are essential micronutrients for the human body.The bony skeleton that supports the human body and facilitates locomotion has an intricate microarchitecture of its own. This tissue contains fat and immature blood cells and is responsible for producing mature blood cells, white blood cells, that helps fight diseases and build immunity, helps to form red blood cells and platelets.They produce some of the specialized cells that our body requires.Your bone marrow may also be affected by problems that involve your entire body such as deficits in nutrients like iron or vitamin B12, infections, and renal disease.Bone marrow is a spongy substance found in the center of the bones.
Bone marrow biopsy and aspiration
Types of Bone Marrow. Red blood cells carry oxygen to tissues in the body.
Red bone marrow: Histology and function
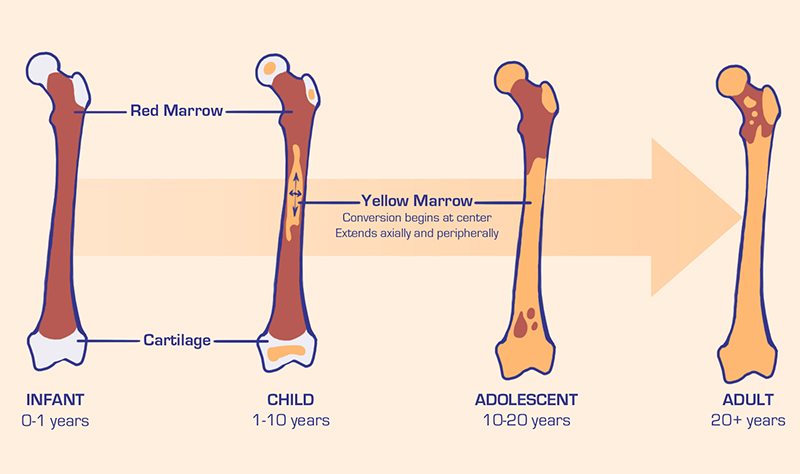
Bone marrow is the soft, spongy, gelatinous tissue found in the hollow spaces in the interior of bones.Bone marrow is ubiquitous throughout the skeleton, primarily composed of hematopoietic cells and fat cells between bony trabeculae and fibrous retinacula. Brio Medical is a . Over time, the red bone marrow in long bones is replaced by yellow bone marrow.The marrow in your bones serves as the primary site to produce red blood cells (RBCs) and white blood cells (WBCs). This cavity contains yellow bone marrow, helps in fat storage, and is internally lined by a delicate membrane called . Let's discuss each of these in detail below. Although bone marrow is an excellent . The bone marrow is a soft tissue with many .A component of the lymphatic system.Medulla ossium rubra.The bone marrow is the spongy tissue on the inside of your bones. Bone marrow scarring can also cause you to have a low number of blood-clotting cells called . The average weight of this tissue is about .Bone marrow edema (BME) occurs when fluid builds up in your bone marrow.Bone marrow is one of your body’s largest organs. Red bone marrow is a jelly-like substance that represents the hematopoietically active unit of bone marrow. It is where most of the body's blood cells develop and are stored.Mesenchymal stem cells are cells that can develop into cartilage, bone, fat or muscle cells, if needed.Bone marrow is found in the medullary cavities – the centres of bones. Apparent Diffusion Coefficient of Normal Abdominal Organs and Bone Marrow From Whole-Body DWI at 1. The marrow's mesenchymal stem cells produce bone, cartilage, and fat cells (adipocytes).The ADCs of bone marrow in women are significantly higher than those of men and correlate strongly with FF.Yellow bone marrow is a type of fatty tissue that plays a vital role in your body's immune system, energy production, and blood cell formation. The bone marrow donation process begins when someone agrees to donate bone marrow.Red bone marrow produces blood cells (red and white) and platelets while the main function of yellow bone marrow is adipose (fat) storage for energy production. Platelets, which stop you from bleeding and help your wounds heal. It makes your blood cells. Bone marrow is either red or yellow, depending upon the preponderance of . Progenitor cell (stem cell) lines in the bone marrow produce new blood cells and stromal cells. Underlying health conditions, injury or infection cause it. The central tubular shaft connects the two ends of the bone.6 kg in an adult weighing 65 kg. It manufactures bone marrow stem cells and other substances, which in turn produce blood cells. The cavities created by the trabecular arrangement of the core of the bones . The bone marrow structure can be described as a mixture of cellular and noncellular components or connective tissue. In addition to its involvement in hematopoiesis (blood cell production), bone marrow also helps store fat.Myelofibrosis is an uncommon type of bone marrow cancer that disrupts your body's normal production of blood cells. Many types of leukemia exist. In the body, the major function of bone marrow is to produce blood cells. They create special immune system cells called lymphocytes.
Multiple myeloma
Red blood cells, which carry oxygen from your lungs to the rest of your body.During emergencies the body converts yellow bone marrow to red to help keep us alive.
What Is Bone Marrow?
Bone marrow aspiration and bone marrow biopsy are procedures to collect and examine bone marrow — the spongy tissue inside some of your larger bones. Afterward, a specialist called a pathologist examines the cells from the marrow .Bone marrow is the spongy tissue at the centre of some bones that produces the body's blood cells. Yellow marrow is found only in the long bones.bone marrow, soft, gelatinous tissue that fills the cavities of the bones. These effects may have an impact on image interpretation when using whole-body DWI to assess disease burden a . The process of .The bone marrow is where circulating blood cells are produced – a process known as haematopoiesis.
Temps de Lecture Estimé: 7 min
What Is Bone Marrow, and What Does It Do?
The bone marrow of animals like cows, lambs, and moose may provide benefits, such as . Depending on your cancer type, this test can also check how well your treatment is working. Anemias linked to bone marrow disease.
How to read your bone marrow report
Your white blood cells are potent infection fighters . Their roles are indispensable, as they are involved in a wide range of vital biological processes. And any diseases or drugs that .

The spongy substance inside the body's bones, notably the hip and thigh bones, is called bone marrow. Protein: 1 gram.Early on in a human’s life, this takes place in many bones, but during development haematopoiesis increasingly centres on flat bones so that by puberty, blood production . Secondary lymphoid organs: These organs include the lymph nodes, the spleen, the tonsils and certain tissue in various mucous membrane layers in the body (for instance in the bowel). A doctor or specialist nurse removes a sample of bone marrow . Treatments include rest, NSAIDs, physical therapy and surgery.BONE MARROW definition: 1. Bones consist of . Bone marrow transplants are sometimes used to replace stem cells that .
Bone Marrow Biopsy: What It Is, Procedure & Results
The health benefits of bone marrow include digestion, brain function, cell repair, immunity and stem cell formation, joint function, skin health and blood sugar control for diabetics.Leukemia is cancer of the body's blood-forming tissues, including the bone marrow and the lymphatic system.Bone marrow (BM) acts as a dynamic organ within the bone cavity, responsible for hematopoiesis, skeletal remodeling, and immune system control. Bone marrow is the spongy tissue inside some of the bones in the body, including the hip and thigh bones.