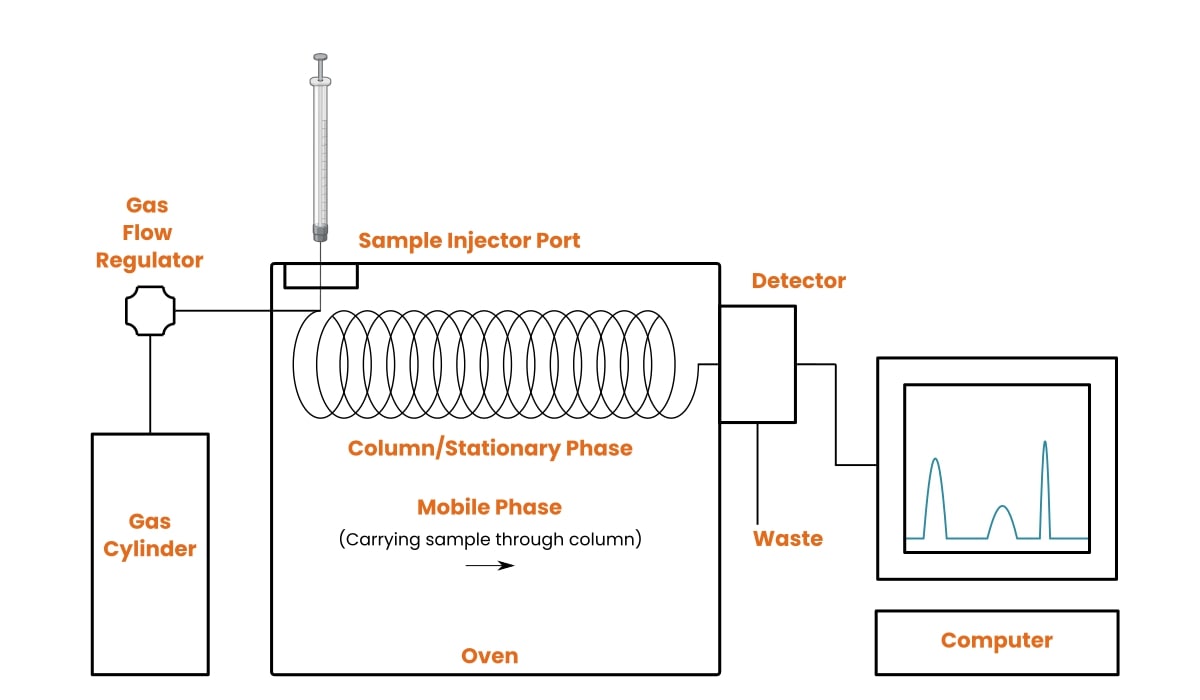
Electroretinogram amplitude is measured in

Amplitudes of a- and b-waves were approximately 3 % lower in the inferior quadrant than in the superior quadrant of the cornea. The electroretinogram, or ERG, provides an objective, quantitative . The pattern electroretinogram amplitude in multiple sclerosis . Carr The standard clinical electroretinogram (ERG) is a recording of the electrical discharges from certain outer retinal layers elicited by a flash of light.This method of performing ERGs allows for the calculation of amplitude and time-to-peak of two major waves, the a-wave and b-wave.0 30-Hz flicker: This is a more sensitive measure of cone function; both time and amplitude are important. The present results comprise the start of the first .An electrical sensor (electrode) is placed on each eye. On the basis of response amplitude and . Electroretinography is a mainstay of clinical ophthalmic diagnostic testing.Electroretinography measures the electrical responses of various cell types in the retina, including the photoreceptors ( rods and cones ), inner retinal cells ( bipolar and amacrine .Background: The retina has gained increasing attention in non-ophthalmological research in recent years.The PhNR amplitude is measured from the baseline of the ERG to the negative trough of the PhNR.
Selner • Amani Al . Because OPs measured to a bright white flash reflect both rod and cone system activity, it is important to compare OP amplitudes to photopic ERG measures as well as scotopic . Electroretinography (ERG) responses are described as photopic (light adapted) or scotopic (dark adapted).The amplitude and timing of N1 may also be measured.The amplitude of the a-wave is measured from a baseline that is monitored before the light stimulus, to the trough of the negative wave. Although the rods outnumber the cones 13 to 1 in the normal human retina, the cones account for 20% to 25% of the ERG response amplitude. A blue background light and red flashes were then used to elicit the .Hippocampal theta–gamma phase–amplitude coupling integrates cognitive control and workingmemory storage across brain areasin humans.

The 95th percentiles for the interocular percentage differences were 28%, 27%, 36%, 33%, and .These ERGs in the different species clearly differ in amplitude and pattern. Comparing relative amplitudes across the corneal locations suggested a slight non-uniform distribution when using full-field . These findings imply imbalances between glutamate and GABA neurotransmission which primarily regulate the b-wave formation.These multi-electrode electroretinogram (meERG) responses were analyzed for spatial differences in a-wave and b-wave amplitudes and implicit times.Following treatment, no significant b-wave amplitude improvement was found in these 11 participants under various light stimulation intensities when compared with . Results Spatially distinct ERG potentials could . A delayed time response suggests .Auteur : Ido Perlman
Full-Field Electroretinogram
0) has a normal a-wave slope and normal amplitude with a broadened flat trough with a “squared” or “rhomboid,” shape followed .
Multifocal Electroretinogram
The pattern electroretinogram obtained in patients affected by multiple sclerosis were compared with those in a normal population.Comparing relative amplitudes across the corneal locations suggested a slight non-uniform distribution when using full-field, near-saturating stimuli.The strong flash (DA 10.
Electroretinography
Specifically, full-field ERG . Using a skin electrode, electrical signals were measured in response to white stimulating light and white background light (LA 3 ERG).The components of the C57BL/6J mouse electroretinogram (ERG) and how they are measured.Doc Ophthalmol (2014) 129:151–166 DOI 10.Similar to those conducted on humans, mouse ERGs include the amplitudes of a- and b-waves as well as the implicit time from those ERGs.
Electroretinogram (ERG) to Evaluate the Retina in Cases of
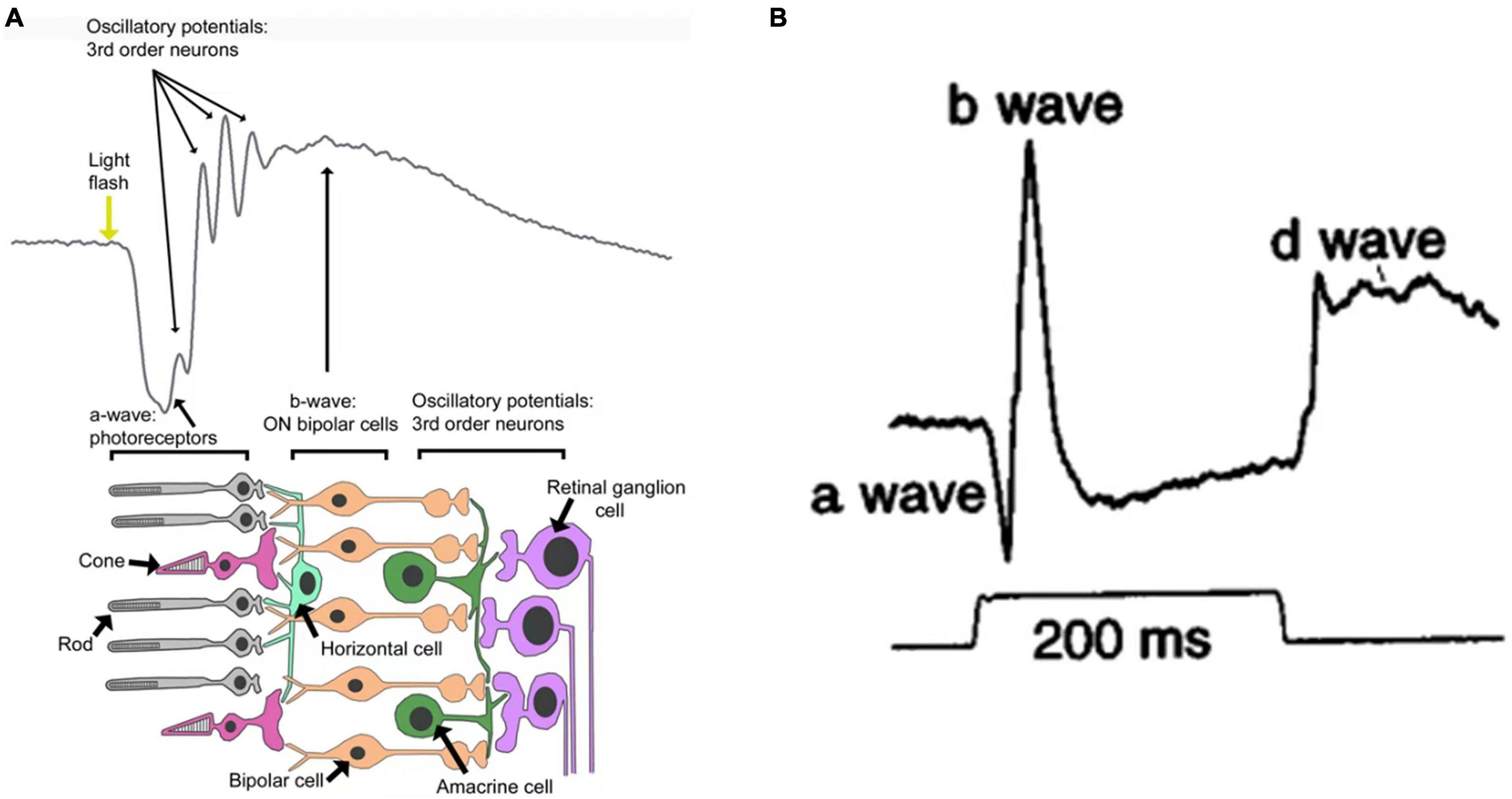
The normal response pattern has waves called A and B.OP amplitude is believed to be a more sensitive indicator of the development of future retinopathy than b-wave amplitude of the scotopic electroretinogram (ERG).Middle trace, the a-wave, b-wave and c-wave are labeled for the response to a high luminance stimulus, showing how the amplitude of each wave was .Electroretinogram (ERG) captures the electrical responses of photoreceptors, the summation of action potentials from all neurons in the retina elicited . Some of this variability is due to species differences, particularly, the relative densities of rods and .An electroretinogram is designed to measure how well the retina (the light-sensing tissue at the back of the eye) is functioning. The pattern electroretinogram (PERG), a method to evaluate retinal ganglion cell function, has been used to identify objective correlates of the essentially subjective state of depression.
The Electroretinogram in Diabetic Retinopathy
A reduction in the PERG contrast gain was demonstrated in patients with .It is customary to use the amplitude and implicit time (latency) of the a-wave for assessment of photoreceptor function and the amplitude and implicit time (latency) of .The electroretinogram (ERG) measures the electrical activity of retinal neurons and glial cells in response to a light stimulus.
It detects the electrical .The electroretinogram results from the currents that flow within the eye as a result of the light-induced activity of neuronal, glial and retinal pigment epithelial cells and .

The amplitude of the b-wave is measured from the trough of the a-wave to the following positive peak (blue arrow).The amplitude of the b-wave is measured from the trough of the a-wave to the peak of the b-wave.
Electroretinogram in Hereditary Retinal Disorders
Methods: The pattern ERG was measured in . The oscillatory potentials (OPs) are four to six low-amplitude, high-frequency wavelets superimposed on the ascending limb of the ERG b-wave.Purpose: To investigate the utility of selected pattern electroretinogram (PERG) parameters-including N95 amplitude and N95/P50 ratio, and a BL-N95 amplitude-in the analysis of visual function(s) and for predicting changes in retinal ganglion cell structures in traumatic optic neuropathy.

A comparison of photopic and scotopic electroretinographic

With the application of brighter white light stimulus (Fig.Two principal components of the ERG waveform are quantified in a clinical exam: (1) The amplitude from the baseline to the negative trough of the a-wave and the . Patients with a cone–rod dystrophy have normal, or lesser defect of b-wave responses to dim scotopic stimuli, but typically have more markedly abnormal ERGs to 30-Hz flicker or single-flash stimuli . The basis of the ERG is the same photochemical process that leads . Applications of ERGs .The dark-adapted human electroretinogram (ERG) response to a standard bright flash includes a negative-going a-wave followed by a positive-going b-wave that crosses the baseline.
The electroretinogram in the genomics era: outer retinal disorders

Description of the ERG waveform parameters: a-amp, a-wave amplitude, an amplitude from the baseline to the a-wave trough; a-time, a-wave time-to-peak, from the .Further loss of rod cells leads to further decreases in the b-wave amplitude and decreased amplitude of the a-wave responses at higher intensities.The amplitudes and peak time of the ffERG responses were obtained from children divided into 6- to 8-year-old and 9- to 12-year-old groups. Because the b-wave reflects .The electroretinogram (ERG) is an electrical potential of retinal origin elicited by a visual stimulus. A flash of light or bright appearance of a pattern elicits a biphasic negative/positive .Electroretinography Ronald E. The a-wave is a measure of .This study was intended to assess whether the pattern electroretinogram (pattern ERG) could be used as an indirect measure of DA in college-age women with and without ID by determining the extent to which features of the ERG were sensitive to iron status and were related to other indirect measures of DA. A light flashes, and the electrical response travels from the electrode to a TV-like screen, where it can be viewed and recorded. Implicit time .
Electroretinograms
Full-field ERG is the diffuse response of both neural and nonneural cells of the retina to a light stimulus.The Fundamentals.The pattern electroretinogram (PERG) is an electrophysiologic ophthalmologic test that provides non-invasive objective, quantitative .Reduced P1 amplitude in the central (R1) and reduced N1, P1 amplitudes in the paracentral region (R3) with increased degree of myopia and AL.
The Electroretinogram: ERG
The Electroretinogram: ERG by Ido Perlman
The implicit time of the b-wave is measured from flash onset to the peak of the b-wave ( Fig. Comparing relative amplitudes across the corneal locations suggested a slight non-uniform distribution when using full-field, near .Request PDF | On Jan 9, 2015, Marc Hébert and others published Light evoked potentials measured by electroretinogram may tap into the neurodevelopmental roots of schizophrenia | Find, read and . ERG recording is done using an active electrode (a contact lens in contact with bulbar conjunctiva) and a reference electrode (at the outer canthus); the active electrode can also be a gold foil electrode or HK-loop electrode.The ERG b-wave amplitude appears to be a distinctive differential feature for both ADHD and ASD, which produced a reversed pattern of b-wave responses. Study design: A retrospective, observational case series .The electroretinogram (ERG) is a mass electrical response from the retina, evoked by a brief flash of light. (A) Upper traces, the dark-adapted ERG evoked by stimui of medium to high luminance.