Level 2 ev charging infrastructure
This general trend of deploying .
What Is Level 2 Charging (And How Does It Work)?
Electric mobility is a globally viable alternative for decarbonizing the transportation industry. There are several exceptions, and in these situations, a reasonable rate design business model is used to .
EV Charging Upgrade Program
Charging stations are called by multiple names, all of which mean the same thing . Last March, Electric Autonomy reported on the growth of Canada’s electric vehicle charging networks.The innovative Dual ICE-80A charger is perfect for fleets with medium to long dwell times.
5 billion in EV charging, $10 billion in clean transportation, and over $7 billion in EV battery . Level 1 EV charging ports increased by the greatest percentage (15.Public Level 2 and DC fast chargers and the CalEnviroScreen score across Los Angeles census tracts and potential ZEA sites.By 2030, direct current fast chargers in Los Angeles will need to grow by a factor of 33 to about 3,900 chargers, while public Level 2 chargers will need to increase . Additionally, every time you charge with us on our DC Fast Charging network, the energy delivered to your vehicle is now backed by 100% renewable energy via renewable energy certificates.Level Two Chargers use a two hundred and forty volt (which is how the Level Two Charger got its name, from the two hundred volt part of the charging equation) supply to power your car, but if you already use a dryer and have a socket installed, you can just plug it straight into that.8% increase in private ports. LDV light-duty vehicle . Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) Alternative Fueling Station Locator (AFDC 2022b), this report provides a snapshot of the state of EV charging infrastructure in the United States in the third calendar quarter of 2022 (Q3 2022) by . EV charging infrastructure installed through December 31, 2032, is eligible for a tax credit of 30 percent of the cost, not to exceed $100,000. By 2030, direct current fast chargers in Los Angeles will need to .Bengaluru (Karnataka) [India], April 23: Bolt. The charging infrastructure network will also need .Dominion Energy's Level 2 Charging Program provides a turn-key solution for level 2 EV charging infrastructure., Oslo, Bergen, and Amsterdam); while other early adopters cities are in the early stages of their pursuits .To support an electric vehicle stock of 26 million in the United States in 2030, public and workplace charging will need to grow from approximately 216,000 chargers in 2020 to 2. Installation of EV charging stations in public facilities advances the City’s goals of reducing greenhouse emissions by facilitating the use of alternative fuel vehicles, with the long-term goal of carbon neutrality by 2045. This growth can be attributed to the increasing demand for EVs and the need to provide reliable and convenient charging options for EV owners. For example, hotels or workplaces may wish to provide Level 1 or Level 2 EV charging as a complimentary service to their customers or employees. Using busway for . The goal is to install 500,000 public .
Outlook for electric vehicle charging infrastructure
PSE&G in New Jersey, for example, is one of many utilities offering credit to customers to offset charging station installation or upgrades., 2013), the relationship between infrastructure density and EV uptake (Harrison and Thiel, 2017; Sierzchula et al. Before we dive in, we should review some terms.Our latest tally of Canadian charging network deployments shows a 22 per cent increase in fast-charger installations since last March. Framework for meso-level planning of EV charging infrastructure.Three broad categories of EV charging infrastructure exist today: Alternate-current (AC) charging, also known as level 1 or level 2.Publicly available EV charging points were up by nearly 40% in 2021.4 million by 2030, including 1. Site hosts can alternatively decide to require .First published: 11 August 2021. The state of the art for level 2 charging system .
Level 2 EV Charger Installation: Physical Infrastructure Requirements
As of July 2023, the U. In Q3 of 2023, there was a 7.Activité : Co-Founder, Product Management Type 1 is the slowest, while type 3 can charge an EV's battery most of the way in about an hour. Level 2 charging uses AC to deliver power using a specialized connection of higher voltage. of charging in the right location—whether that’s high-powered charging on highway corridors and in urban hubs or Level 2 charging where EV drivers or riders live, work, and play,” said Joint Office . This innovative overhead solution utilizes Pow-R-Way III busway and incorporates a 19. NACS North American Charging . In this system, an in-car inverter converts AC to direct current (DC), which .25 billion to strategically deploy publicly accessible EV charging infrastructure and hydrogen, . The program provides incentives for the EV charging station make-ready and convenient, monthly on .With more than 26 million electric vehicles (EVs) expected on U.Level 1 charging uses AC to deliver power using common household electricity standards.Third Quarter 2023. The current state of cities across the globe can be categorized into: forerunner cities that have pioneered e-mobility infrastructure with specific government targets (e. If charging the Tesla Model 3 at a station with a 7 kW output, it would take approximately 8 and a half . ICCT International Council on Clean Transportation .The Corridor Program will provide $1.Currently, the majority of EV charging (c. Operating costs. It operates at powers up to The following tools can assist with incorporating equity considerations into the EV charging infrastructure procurement .
FACT SHEET: Biden-
roads by 2030, now’s the time to start planning for EV chargers at your facility.2 kW AC Level 2 charger into the bus plug for direct vehicle charging.Level 2 (L2) chargers operate at 208 V (in commercial applications) or 240 V (in residential applications) and deliver from 3 to 19 kW of AC power, with most delivering about 7. For commercial applications — including powering a fleet of work vehicles and EV charging for customers — Level 2 chargers are often the most cost-effective choice.
Level 2 EV Charging: The Future of Electric Vehicles Made Simple
These regulations vary widely (for example, .Level 2 charging stations provide power outputs between 7 kW and 22 kW.State regulations may impact how utilities own and manage EV charging infrastructure.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
The basics of electric-vehicle charging infrastructure
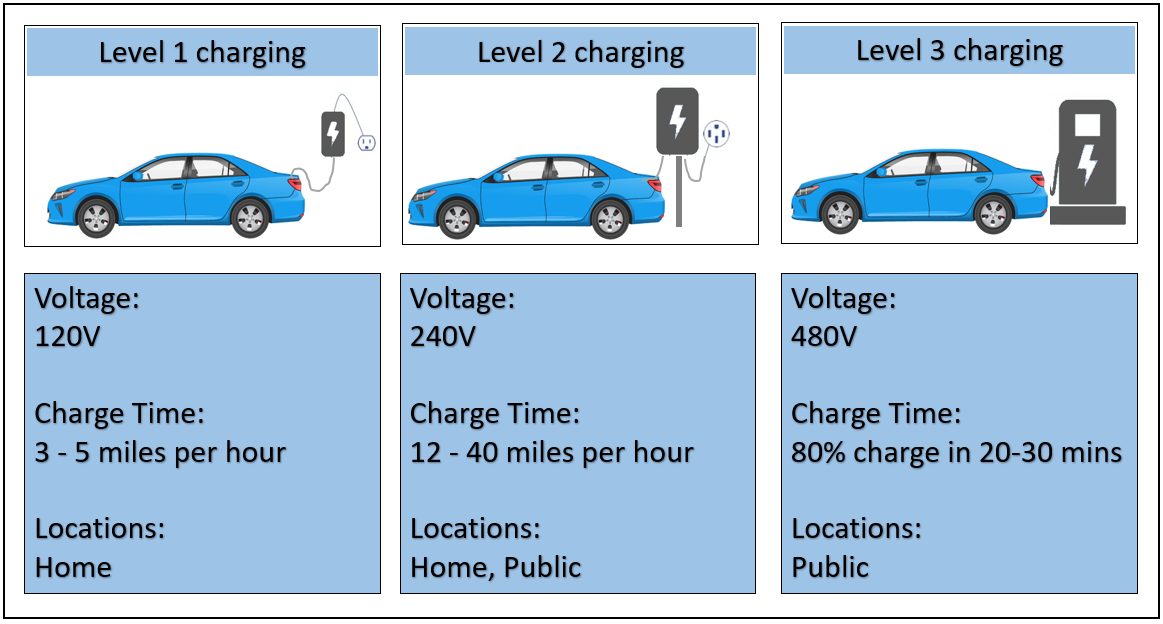
Charging level Voltage Typical power Electric vehicle miles of range per charging hour .
The EV Transition Explained: Charger Infrastructure
Using data from the U. EVSE electric vehicle supply equipment . Utilities, too, are moving into the EV charging space.

One company taking . The three large IOUs – PG&E, SCE, and SDG&E – filed applications in 2014 for pilots to install light-duty, mostly Level 2, EV .26 million Level 1 and Level 2 charging ports at privately accessible locations—including single-family homes, multifamily properties, and workplaces. This results in low power loads (1–2 kW) and relatively longer EV charge times (»4 mi/6.The amount of electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure continues to rapidly grow.

Important differences include: Input voltage.2 kilowatts (kW) in the United States and up to 22 kW in Europe, providing 10 to 75 miles (16 – 120 km) of range per hour of charging.5 billion to develop the country’s EV-charging infrastructure.This AC Level 2 .In many cases, though, these charging infrastructure networks are Level 2 roadside or parking lot solutions.66 billion by 2027.Recent studies on the charging infrastructure of electric vehicles mainly cover aspects such as improving charging technology (Du et al.EV chargers are classified into three categories: Level 1, Level 2 and direct current (DC) fast chargers.comElectric Vehicle Charger Market Size, Growth, Report 2023 . Joint Office Joint Office of Energy and Transportation . SANTA MONICA, CALIF. This provides .
Trends in charging infrastructure
During the forecast period 2021-2027, the EV charging infrastructure market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 30., electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) deployment could mitigate the problem. EVI-X electric vehicle infrastructure analysis tools .The Los Angeles City Council this week approved an Electric Vehicle Master Plan aimed at developing an entirely electric fleet of more than 10,000 city-owned .Level 2 charging puts out a range of 7-20 kilowatts (kW) of AC power and can take between 4-10 hours to fully charge a BEV and just 1-2 hours to fully charge a .Describes an analysis of capital costs of EV charging infrastructure needed for public, workplace, and home charging (Level 1, 2, and DC fast) for the most populous 100 . By 2035, this . Eligible fueling equipment must be installed in census tracts where the poverty .Level 2 charging infrastructure is a low-cost, high-speed charging option.6 billion in 2021 and will generate US$ 125.President Biden’s Bipartisan Infrastructure Law invests $7.

Light-Duty EV Charging Infrastructure Programs---2016 Pilots and Extension Programs.This comprehensive guide on Level 2 charging for electric vehicles (EVs) covers everything from Level 2 charging speeds and charger types to EV charging incentives, ensuring you have all the knowledge you need to . If you don’t, you’ll need to have a two hundred and . In most cases, Level 2 does not draw enough power to trigger demand charges (unless many are linked to a single meter), keeping the cost of owning or using one low. The Northwest region had the largest increase in public charging in Q3 . The market is estimated to be worth US$ 19.4% increase in public ports and a 2.Electric vehicle charging infrastructure specifications in the United States. These deliver . plug-in hybrid-electric vehicles (PHEVs) and electric vehicles (EVs), through the fast, economical and reliable EV charger infrastructure i.Level 2 EV charging infrastructure.
What is Level 2 EV charging?
The Comprehensive Guide to Level 2 EV Charging
In the STEPS and APS, the global number of public charging points exceeds 15 million by 2030, up four-fold compared to the almost 4 million operating in 2023.EV charging stations forecast EU 2030 | Statistastatista.
EV Charging Infrastructure Market

As EV markets swell, access to public charging will need .
EV Charging Infrastructure: Trends, Requirements & Costs
The specific charging speed achieved depends on the charger’s power output and the vehicle’s onboard charging capabilities, including its charge .7% increase in the number of EV charging ports in the Station Locator, including an 8.Eligible EV activities: Light duty vehicle charging (level 2 or DC fast charging that brings an innovation to market) .Customers must enroll in the Off-Peak Charging Program to be eligible for the Residential EV Charging Infrastructure Program wiring or charger rebates. FHWA Federal Highway Administration . The focus of this Strategy is the provision of publicly funded charging infrastructure for electric cars and light-duty vehicles, the demand for which will grow as EV uptake increases.The infrastructure for Level 2 EV charging is expanding rapidly, with both public and private entities investing in the installation of charging stations. Public charging expands despite pandemic-related slowdown in construction.4 km of light-duty vehicle range per hour of charging).













