Official language of bhutan
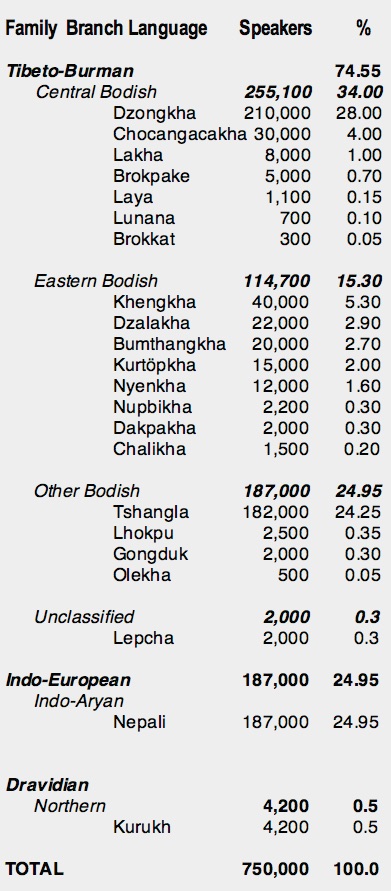
The government classifies 19 related Tibetan languages as dialects of Dzongkha.After the unification of Bhutan, Ngalongkha became the dominant language for official transactions as political offices were mainly based in areas where it was spoken. Ngalongkha slowly came to be known as Dzongkha, the languguage of the Dzong. Most languages spoken in the country belong to the Tibeto-Burman . The origins of the Bhutanese language can be traced back . Definitions Official language A language designated as having a unique legal status in the state: typically, . Hindi is the official language of India, but it was previously . English has official status. While Dzongkha is the official national language, Bhutan is home to an array of other regional languages and dialects. Among the power centres of medieval Bhutan, only Trongsa was not part of the Ngalongkha speaking area.Languages of Bhutan.Dzongkha or Bhutanese ( རྫོང་ཁ་, [dzoŋkʰa] ), is the national language of Bhutan . Dzongkha is the only written local language so far and it is written using Tibetan .Bhutan is a multilingual country where approximately 20 languages are commonly spoken.Factbook > Countries > Bhutan > Demographics. Dzongkha is the official language of Bhutan and it is also the most common language spoken all over the country. Due to the mountainous terrain that separates settlements, around 20 different . Top Selling Bhutan .Bhutan ( / buːˈtɑːn / ⓘ boo-TAHN; Dzongkha: འབྲུག་ཡུལ་, romanized :Druk Yul [ʈuk̚˩.From Wikimedia Commons, the free media repository. Other Languages Spoken in Bhutan.The Tibetic languages form a well-defined group of languages descended from Old Tibetan (7th to 9th centuries)., 2015) Laya at Ethnologue (18th ed.Bhutan Languages.
What Languages are Spoken in Bhutan
↑ Dzongkha at Ethnologue (18th ed.Dzongkha, the official language of Bhutan, holds the key to understanding the culture and traditions of this Himalayan kingdom. Dzongkha is the national language of Bhutan, and the Tibetan alphabet is used for writing. It has its roots in the ancient Tibetan script and has evolved over centuries to become the distinct language it is today. Embracing the Melting Pot.
List of official languages by country
Whether you’re planning a visit to Bhutan or simply .Bhutan’s heart beats in Dzongkha, an age-old language that tells tales of its past, narrates its present, and whispers hope for its future. This category has the following 8 subcategories, out of 8 total.The official language of Bhutan is Dzon (g) kha, one of the 53 languages of the Tibetan language family, but it is mainly spoken in the western part of Bhutan.Auteur : Oishimaya Sen Nag
Spoken by half a million Bhutanese people, Dzongkha is a Sino-Tibetan language.
Dzongkha
Bhutanese languages and dialects contribute to the country’s rich .Dzongkha, the national language of Bhutan, belongs to the Tibeto-Burman language family.
What Language Do They Speak in Bhutan?
When data is available, .Dzongkha is the official language of Bhutan.It was declared the national and official language of Bhutan in 1971. As the world becomes more globalized , the importance of preserving and understanding such linguistic treasures only grows, ensuring that the voice of Bhutan continues to resonate through the Himalayas . Sharchopkha comes in as a major regional language spoken . The script, locally called Chhokey (literally, . Bhutan adopted Ngalongkha as the national language in the 1960s.Language Distribution.
Bhutan
Bhutan Language
Dzongkha
Tibetic languages
National & Regional Status.
Language Policy and Planning in Bhutan Pema Wangdi
In addition, 23 other languages are spoken in Bhutan, all of which belong to the Tibeto-Burmese language family, except Nepali, which belongs to the Indo-Aryan languages. It evolved from Old Tibetan and shares linguistic similarities with other .What languages are spoken in Bhutan? Some of the major languages include Dzongkha and Nepalese, as well as others, some of which have an official status. From ancient indigenous dialects to .
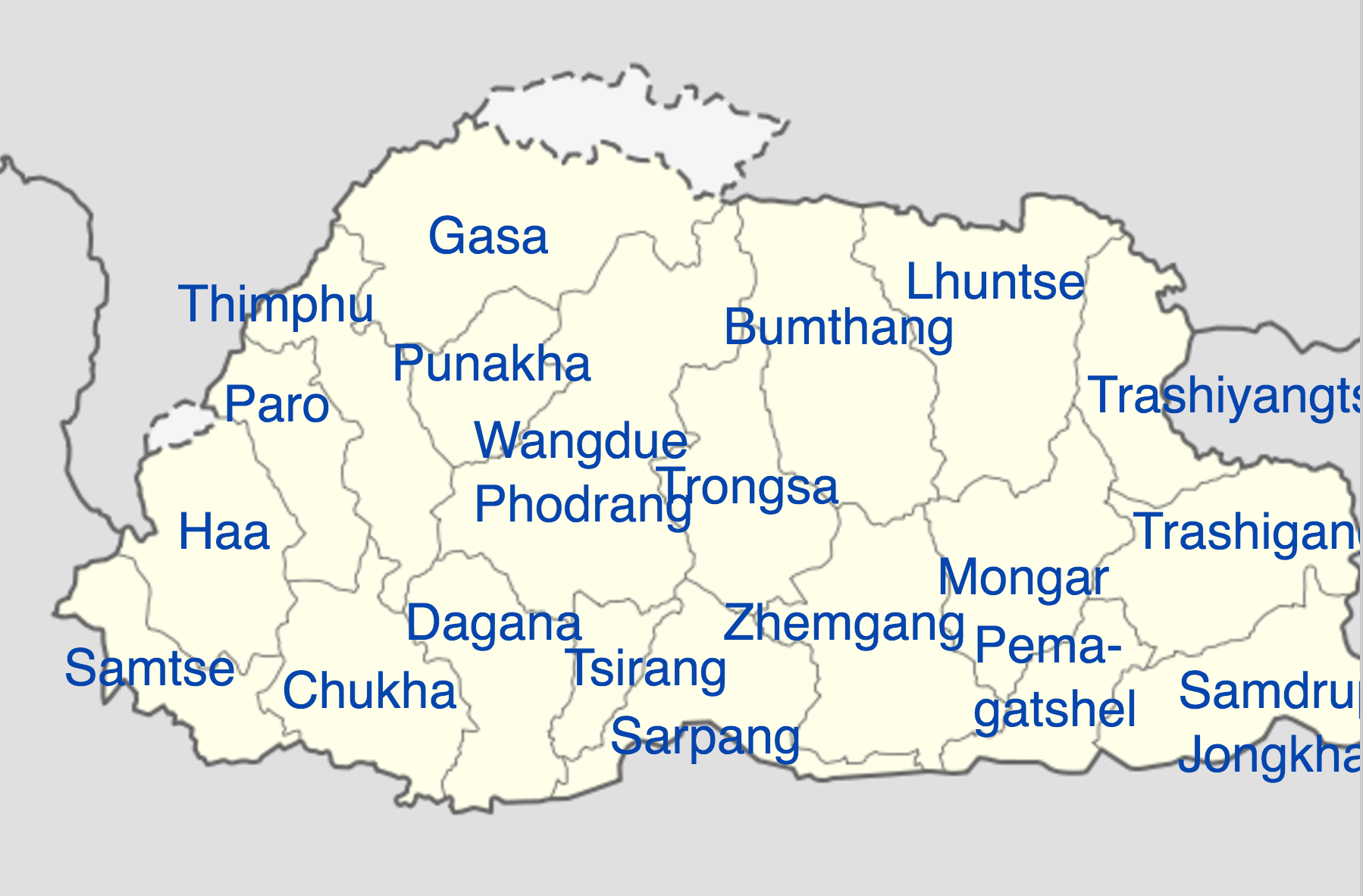
Bhutan’s official language is only spoken by 30% of its population, and people from each . Starting in the 1980s, college-level textbooks in Dzongkha were published, and . Though Bhutan is a small country, its villages and . More than 19 languages are spoken . Central Bodish languages predominate in the west of Bhutan.Dzongkha, or Bhutanese, is spoken by about 130,000 people in Bhutan, where it is the national language, and also in Nepal and India. Bhutan is a multilingual country where approximately 20 languages are commonly spoken.
Bhutan Culture : Language, Religion, Food
Among the languages spoken in Bhutan, Dzongkha is not only the Bhutan official language but also the heart of Bhutanese literary life.

It is a South Tibetic language closely related to Sikkimese.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 5 min Religions: The tantric form of Mahayana Bhuddhism (Drukpa Kagyupa) is state religion, Indian- and Nepalese-influenced .
9 most spoken languages of Bhutan » Tilti Multilingual
English was widely understood and was the medium of instruction in secondary and higher-level schools.Ngalongkha became an official language in the administrative offices and momastic institutions based in large døng.The Dzongkha language is the country’s national language.
Language and identity in Bhutan
About 30% of the population speaks Dzongkha.Along with Dzongkha and English, Nepali was once one of the three official languages used in Bhutan.Overview
Which Languages Are Spoken in Bhutan?
Dzongkha or Bhutanese is a Sino- Tibetan language spoken by over half a million people in Bhutan and it is sole official and national language of the Kingdom of .This is a list of official languages by country and territory. It includes all languages that have official language status either statewide or in a part of the state, or that have status as a .Bhutan’s national identity is grounded in a shared history and culture and even in two shared languages, Chöke and Dzongkha. Besides Brokpa and Dzongkha, four other Central Bodish languages are spoken in Bhutan: Chocangacakha, Brokkat, Lakha, and Tibetan (B’ökha). Historically a remote kingdom, Bhutan became less isolated in the second half of the 20th .There are two dozen languages of Bhutan, all members of the Tibeto-Burman language family except for Nepali, which is an Indo-Aryan language, and Bhutanese Sign Language.
Dzongkha language, alphabet and pronunciation
In 2024, of the more than 100,000 ethnic Nepali -- predominantly Lhotshampa -- refugees who fled or were forced out of Bhutan in the .
Language Diversity in Bhutan
Is Bhutanese A Language?
The Wangchuck hereditary monarchy has wielded power since 1907. Despite this, Chokê remains the medium of primary . There is no absolute majority, and Dzongkha, Bhutan’s official language, is only spoken by 30% of its .
Bhutan National Language: Dzongkha
There is no absolute majority, and Dzongkha, Bhutan’s official language, is only spoken by 30% of its population, and people from each region have their own native . Not only do many people feel this way, this view is also the official standpoint of many governments. Languages: Sharchopkha 28%, Dzongkha (official) 24%, Lhotshamkha 22%, other 26% (includes foreign languages) (2005 est.Key Takeaways: Dzongkha is the official language of Bhutan. Languages spoken. These languages are spoken in the Tibetan Plateau and in the Himalayas in Gilgit-Baltistan, .BHUTAN LANGUAGE. Dzongkha is Bhutan’s official language.The official language of Bhutan is Dzongkha. In regions, a multitude of languages enjoy official or regional status, embodying the country's commitment to preserving cultural heritage and linguistic identity.

In 2018, the incumbent party again lost the parliamentary election.Dzongkha is the national language of Bhutan.Dzongkha, the official language of Bhutan, is a dialect or form Tibetan.

The national language is Dzongkha (Bhutanese), one of 53 languages in the Tibetan language family.GNI per capita PPP: $ 3 330 (year) Ethnic groups: Bhutan has three main ethnic groups, Sharchops, Ngalongs (50%) and Lhotsampas, one of several Nepalese ethnic groups (35%), indigenous or migrant tribes 15%. It is also related to other .Official language. Bhutan, landlocked country of south-central Asia, located on the eastern ridges of the Himalayas. Dzongkha is the most common language in the west of Bhutan, Tshangla in the east. Gradually, Ngalongkha was used as the official language in the administrative . It is one of the many variations Tibetan spoken by people in the Himalayas (sometimes called the Bhote . Dzongkha, the national language, is the only language with a native literary tradition in Bhutan, though Lepcha and Nepali are literary languages in other countries.Country Official language Continent; Abkhazia: Abkhazian, Russian: Asia: Afghanistan: Dari, Pashto: Asia: Albania: Albanian: Europe: Alderney: English: Europe .The Bhutanese name for Bhutan, Druk Yul, means Land of the Thunder Dragon and it only began to open up to outsiders in the 1970s.Official status; Official language in Bhutan: Regulated by: Dzongkha Development Commission: Language codes; ISO 639-1: ISO 639-2: ISO 639-3: dzo – inclusive code Individual codes: lya – Laya luk – Lunana adp – Adap: Glottolog: nucl1307: Linguasphere: 70-AAA-bf: Districts of Bhutan in which the Dzongkha language is spoken natively are . It was declared the national and official language of Bhutan in 1971. Figure 2 gives the subgrouping of the Bodish .The major languages of Bhutan are Dzongkha, Nepali and Tshangla. Its prevalence resonates in everyday discourse, education, and cultural . Esperanto: Lingvoj de Butano. It has about 160,000 native speakers and about 470,000 second language speakers.The national language is Dzongkha, one of 53 languages in the Tibetan language family. Bhutan 's linguistic landscape flourishes with diverse tongues that hold regional significance. A list of Bhutan languages with at least 10,000 native speakers is shown in the following table: . Lepcha is spoken in parts of western Bhutan; Tshangla, a close relative of Dzongkha, is widely spoken in the .Bhutan experienced a peaceful turnover of power following a parliamentary election in 2013, which resulted in the defeat of the incumbent party. Dzongkha has same alphabets and similar way of speaking as the Tibetan language but it uses a different script. It literally means ‘the language spoken in the dzongs and administrative centers in all the districts of Bhutan’.The Bhutanese language, also known as Dzongkha, is the official language of Bhutan. Besides Brokpa and .