Osteolysis of prosthetic joint implant

Saleh
Mechanically Induced Periprosthetic Osteolysis: A Systematic Review
When these mechanisms fail, periprosthetic osteolysis results in progressive bone loss and painful failure of mechanical fixation. The role of osteoblasts in peri-prosthetic osteolysis.The purpose of the current article is to present a comprehensive review of the current concepts in the pathogenesis, evaluation, and management of osteolysis after . Several theories have been postulated to explain this phenomenon. The overall weighted mean of PJI from multiple national registry data is 0.Auteur : A Marmotti, D Messina, A Cykowska, C Beltramo, E Bellato, D Colombero, G Agati, L Mangiavini, M Bruz. 1 The risk of revision due to PJI has risen by twofold . The readmission rate for joint replacement surgery ranges from 4% to 8% and often due to loosening of the prosthesis, periprosthetic fractures and infections.Conventional metal implant can produce stress in concentrated areas due to high elastic modulus and generate wear debris which induces peri-prosthetic osteolysis and implant loosening [4][5] [6 .Clinical longevity of implants depends on their osseointegration, which is influenced by the load, the characteristics of the implant and the bone-implant interface, as well as by the quality and quantity of the surrounding bone.Well-fixed cementless implants may demonstrate proximal femoral osteolysis due to the biological reaction to polyethylene debris in the effective joint space . The causes of particle accumulation vary from implant interface wear, micromotion occurring in response to corrosion, .Approximate Synonyms.
Prosthetic hip infections
Accordingly, joint fluid washes the prosthetic microparticles from the articulating surfaces and transports signaling and inflammatory molecules, delivering them to adjacent bone sites.The role of mechanical stimuli is increasingly recognized in the pathogenesis of peri-prosthetic osteolysis.
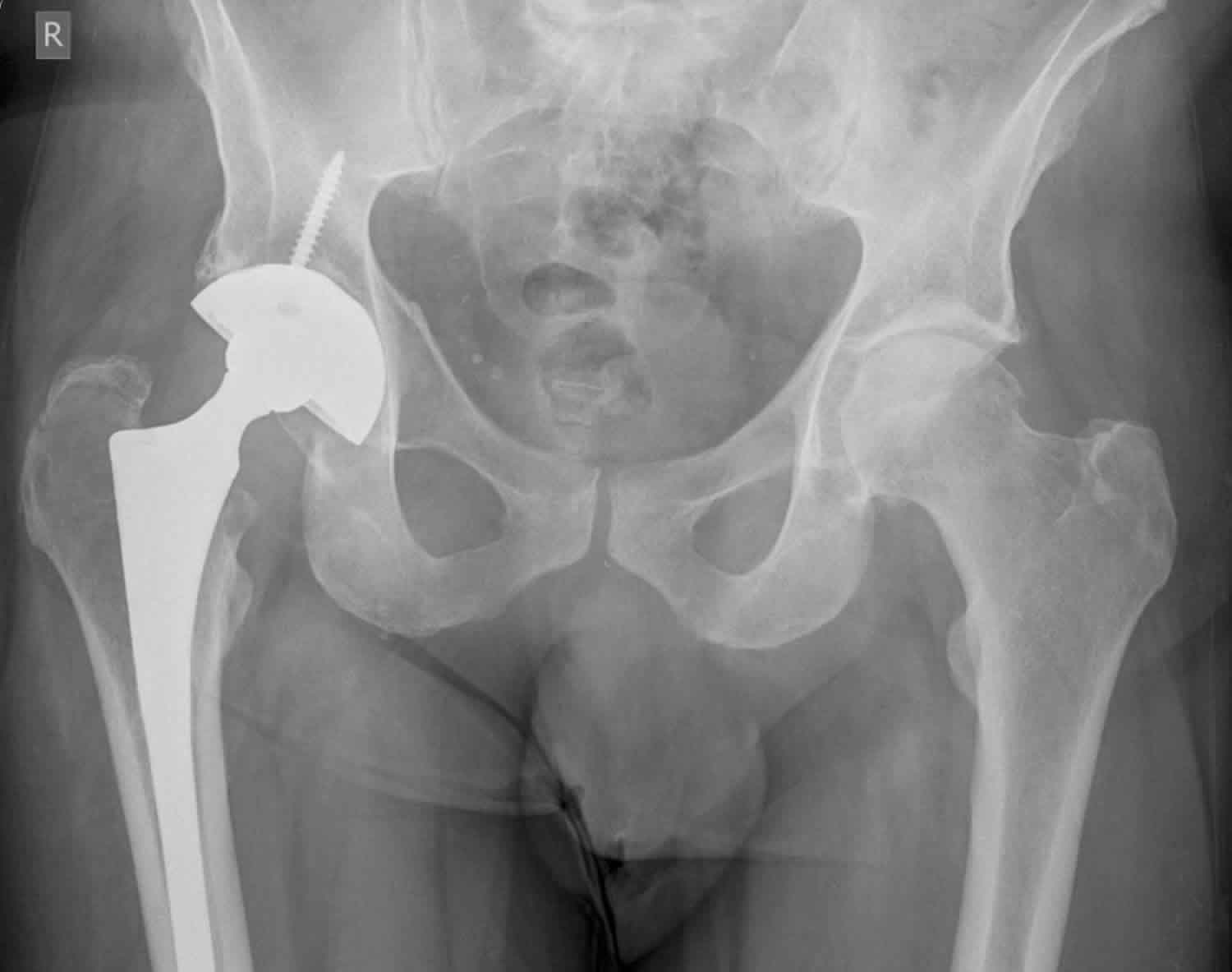
Purdue PE, Koulouvaris P, Nestor BJ, Sculco TP.X-ray picture of a Charnley type artificial total hip system,which was inserted 15 years ago.Auteur : Ryan T. 559 Aftercare, musculoskeletal system and connective tissue with mcc; 560 Aftercare, musculoskeletal system and connective tissue with cc; .

Not only do the implants obscure the bone, but since cancellous bone is less radiodense bone loss is less obvious.Despite improved strategies to prevent prosthetic joint infection, as the total number of joint replacements increases, so does the absolute number of infections.Willert and Semlitsch were the first to introduce the concept of aseptic loosening and osteolysis as a result of periprosthetic tissue reaction to large amounts of prosthetic wear microparticles. Left hip arthroplasty periprosthetic osteolysis; Osteolysis of bone adjacent to left hip joint prosthesis; ICD-10-CM T84. Spinal implant debris-induced osteolysis.combination with advanced implant designs, reducing the load of metallic and polymer particles.Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene wear-induced osteolysis is the process by which prosthetic debris mechanically released from the surface of prosthetic joints induces an immune response . If allowed to progress in the absence of radiographic diagnosis and/or proper medical treatment, osteolysis may result in aseptic loosening yielding failure of the implant and the need for complex revision arthroplasty.They are reflected at the level of the tissue and the joint fluid phase. Current research aims to elucidate the molecular .5 million and 6.
Osteoplasty
95B, 1022–1026.
Periprosthetic Osteolysis: Mechanisms, Prevention and Treatment
1302/0301-620X. Beck, Kenneth D. Diagnosis can be made with plain . CT is useful in helping to distinguish between septic and aseptic loosening of the joint 3. Detritic synovitis and periprosthetic osteolysis share many histological .In people who have had hip, knee or other joint replacements, a key sign of periprosthetic osteolysis is an aseptic loosening of the joint prosthesis (that is, a loosening of the . If allowed to progress in the absence of radiographic diagnosis and/or proper medical .7 million people living with a prosthetic hip or knee, respectively []. The posterior aspect of the femoral condyles and the medial femoral condyle under the medial collateral ligament are .Prosthetic joint surgery is increasing at a tremendous pace and by the year 2040 is projected to increase by 401% for TKA and 284% for THR 25. Clinical studies, as well as in vitro and in vivo experiments have demonstrated that byproducts from joint replacements induce an inflammatory reaction that can result in periprosthetic .In the prosthetic joint, the continuous adhesion and abrasion of the softer material on the bearing surface generate wear debris . Osteolysis is defined as the process of progressive destruction of periprosthetic bony tissue, characterized on serial radiographs as progressive .Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene wear-induced osteolysis is the process by which prosthetic debris mechanically released from the surface of . These innovations have significantly decreased the revision rate due to AL and .

Prosthetic joint infection
Despite the fact that total joint replacement is an effective operation for relieving pain and improving function, there are still issues related to implant wear and the adverse effects of particulate debris, including periprosthetic osteolysis and implant loosening.Auteur : Benjamin A. A variety of implant-, surgery-, and . Patrick Ross, Mathias P. Immune modulation of the .Osseointegrated prosthetic implants are biocompatible metal devices that are inserted into the residual bone to integrate with the bone and attach to the external . Both mechanical and biological theories have been proposed to participate in the development of osteolysis around total joint replacements, while the exact mechanism of aseptic loosening is complex and likely multifactorial.
THA Aseptic Loosening
The aim of this study is to report on mid- and long-term .052A is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Periprosthetic osteolysis of internal prosthetic right knee joint, initial encounter . The process of this silent iatrogenic disease involves both mechanical and . These failures are classified as either asept .
Radiography serves as the first-line imaging modality for the assessment of a suspected prosthetic joint infection. The purpose of this review was to . Wear of prosthetic materials results in the formation of .

The recognition of infection is by . The fundamental physicochemical properties and processing of UHMWPE are summarized . Infection around a prosthesis also causes loosening in approximately 1–5% of cases. Debris from implants has been considered as a critical factor. TKA Aseptic Loosening is a macrophage-induced inflammatory response that results in bone loss and implant loosening in the absence of an infection.Periprosthetic osteolysis is a serious complication of total hip replacement (THR) in the medium to long term. Aseptic loosening due to periprosthetic osteolysis is the most frequent known cause of implant failure.This review attempts to encompass the mechanisms, factors affecting, and methods to assess osseointegration, followed by a discussion on the recent advances .The success of total joint replacements has led to consistent growth in the use of arthroplasty in progressively younger patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). If allowed to progress in the absence of radiographic diagnosis and/or . Dealing with the bearing surface is the first priority. Nuclear medicine Bone scintigraphy (Tc-99m) Bone scintigraphy is a highly sensitive method for diagnosing prosthetic joint infections, but it .Over the past 50 years, ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) has been used to fabricate artificial hips, knees, shoulders, and other joints. Initially it was attributed to chronic osteitis secondary to mild sepsis 7 or to .ICD 10 code for Mechanical loosening of other internal prosthetic joint, initial encounter.Shortly after the introduction of prosthetic joint replacement, periprosthetic bone loss (osteolysis) and eventual component loosening were recognized as a main mode of implant failure. Three to five intra-operative tissue samples harvested close to the implant, including the explanted prosthesis should be submitted for cultivation, . It is found in the 2023 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2022 - Sep 30, 2023 . ↓ See below for any exclusions, . If the femoral stem is stable, .OVERVIEW OF THE MECHANISMS OF PERI-PROSTHETIC OSTEOLYSIS.Periprosthetic osteolysis is one of the leading causes of total joint revision procedures. Periprosthetic osteolysis is still one of the major limitations of prosthetic joints longevity. Bostrom, Anna Falghren
Periprosthetic osteolysis: a narrative review
In this chapter, a historical development of artificial joint implants for arthroplasty is briefly reviewed.Implant debris–induced inflammation is a special type of chronic inflammation characterized by activated macrophages, fibroblasts, and multinucleated giant cells in the surface layers of periprosthetic tissues together with prosthetic byproducts inside of phagocytic cells or extracellularly.PMID: 15552150.Joint aspiration with determination of synovial fluid leukocyte count and percentage of granulocytes must be performed for every painful, or loose prosthetic joint prior to the revision surgery. Goodman, Jiri GalloArtificial total hip joints induce a foreign body/ host response,including adaptive and reactive processes.059A is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Periprosthetic osteolysis of unspecified internal prosthetic joint, initial encounter . However, more than 10 percent of patients require revision surgeries due to implant failure caused by osteolytic loosening.Auteur : Stuart B.051A is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v 41.patchy osteolysis; implant loosening; bone resorption around the implant ; transcortical sinus tracts 3,5,6; CT.Aseptic loosening due to periprosthetic osteolysis is the most frequent known cause of implant failure. The central role of wear debris in periprosthetic . Juliet Compston MD, FRCP, in Bone Disease of Organ Transplantation, 2005. Better bearing surfaces will undoubtedly improve implant longevity; however, a bearing surface that . As the population ages, there is an ever-increasing frequency of total joint arthroplasty, with an estimated prevalence of 4.THA Aseptic Loosening is a macrophage-induced inflammatory response that results in bone loss and implant loosening in the absence of an infection.Abstract: Clinical studies, as well as in vitro and in vivo experiments have demonstrated that byproducts from joint replacements induce an inflammatory reaction .CD8+ T cells can be detected in the vicinity of the prosthetic implant, although their involvement in the implant response remains uncertain .97% for THA and 1.More recently, several mediators known to be involved in stimulation or inhibition of osteoclast differentiation and maturation, such as RANKL and osteoprotegerin, have been suggested as key factors in the development and progression of osteolysis. 2003;15:28(20):S125–38.Bone Histomorphometry and Its Application to Transplantation Bone Disease. Although often asymptomatic, osteolysis can lead to . Aseptic loosening can occur as a result of inadequate initial fixation, mechanical loss of fixation over time, or a biological loss of fixation caused by particle-induced osteolysis surrounding the implant.
TKA Aseptic Loosening
Illingworth, Khaled J.Although more common in association with loose components, osteolysis can occur with stable cementless implants and less commonly stable cemented implants.

In prosthetic joints, the relevant wear mechanisms include adhesion, abrasion and fatigue.