Permanent stress in the brain
To promote healthy rewiring, people need to strengthen the parts of the brain that can regulate that response.
Antidepressants have effets on the hippocampus that counteract the effects of stress.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 6 min
Brain
It powers the “fight-or-flight” response that allows animals to respond quickly to danger signs. When we’re startled, or acutely stressed “fear center” of the brain, called the amygdala activates our central stress response system. By doing this, we essentially tag cells that we know are active in a given time window—such as when the brain is .
Stress, the brain, and trauma spectrum disorders
February 15, 2021. It corresponds with a period of low peripheral concentration . Persistently high levels of glucocorticoids inhibit neuron growth inside the . When this occurs, you may .The effects of stress across the lifespan on the brain, cognition and mental health: A UK biobank study - PMC. The stimuli are called stressors and physiological and behavioral changes in response to exposure to stressors constitute the stress response. 5,6 However, the accumulation of iron in specific brain regions, greater than that reported in healthy ageing, occurs in many neurodegenerative diseases and is often associated with oxidative .; Repeated, excessive use of alcohol can lead to the development of addiction, which is . Our finding in hippocampus of chronic stress-induced shrinkage of dendrites of hippocampal CA3 and dentate gyrus neurons as well as loss of spines in CA1 neurons (see (McEwen, 1999) revealed aspects of brain structural plasticity (Figure 1). Another significant long-term effect of heavy Adderall use is dependence on the drug.Depression may cause the release of glucocorticoid in the brain, a type of steroid that can damage the hippocampus and other areas of the central nervous system.This process, if repeated or extended in time, could eventually produce permanent alterations in those neuroendocrine systems, the structure of the brain, and in behavior (Lupien et al. Call in sick,” Schabram said.However, studies indicate that infancy coincides with a period referred as hyporesponsive period to stress (Stress Hyporesponsive Period—SHRP), which is supposed to be a period that is necessary for the proper development of the brain after birth (Sapolsky and Meaney, 1986; de Kloet et al.The findings suggest the possible role of oligodendrocytes in long-term and potentially permanent changes in the brain that could set the stage for later mental health problems.Any physical or psychological stimuli that disrupt homeostasis result in a stress response.November 21, 2014.
Mechanisms of stress in the brain
Neurobiological Links between Stress, Brain Injury, and Disease
This may result in mental disorders. Traumatic stress is associated with increased cortisol and norepinephrine responses to subsequent stressors.

Train your brain for better sleep with 3 expert tips.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Mechanisms of stress in the brain
Neurobiol Stress.After trauma, the SNS remains activated, keeping the body and mind on high alert. Medical researchers are studying the effects of . Surprisingly, given their pivotal physiological significance, our understanding of the role of the B group of vitamins (thiamine (B 1), riboflavin (B 2), niacin (B 3), pantothenic acid (B 5), vitamin B 6, folate (B 9) and vitamin B 12) in health and brain function is limited in several respects. This chapter reviews the relationship between stress and brain function in patients with neuropsychiatric disorders, with an emphasis on disorders that have most clearly been linked to traumatic stress exposure.Other studies, using animal models and human participants, suggest that chronic bullying leads to an increased release of stress hormones, like cortisol, especially in brain areas involved with reward-processing.In addition to dysregulation in brain function, emerging evidence suggests that — much like other chronic stress conditions — burnout also leads to turmoil within the regulation of the body’s neuroendocrine system.The hippocampus provided the gateway into much of what we have learned about stress and brain structural and functional plasticity, and this initial focus has expanded to other interconnected . By looking at the brain cells of mice who had been raised in enriched environments and then later placed into isolation, Smeyne’s team observed that after one month of isolation, the animals’ neurons shrunk by 20 percent. Chronic stress, therefore, could promote many of the maladies that plague our society including mood and anxiety disorders, addiction, and . Stress management may reduce health problems linked to stress, which include cognitive problems and a higher .While such stress and sex hormone-related alterations occur in regions mediating the highest levels of cognitive function and self-regulatory control, the fact that they are not . Source: Ruhr-Universitaet-Bochum. Take a day off. This imbalance, in turn, affects systemic physiology via .Neurobiological and Systemic Effects of Chronic Stresspubmed.Surprising Science — November 25, 2014.The rediscovery of neurogenesis in the adult as well as developing .Chronic stress induces maladaptive changes in the brain at different levels, which, interacting with genetic background and previous adverse life events, may favour development of psychiatric .Dependency and addiction. Ferguson et al. Summary: Activated through permanent stress, immune cells will have a damaging effect on and cause changes to .The first key to success lies in planning.
Chronic Stress Can Damage Brain Structure and Connectivity
Understanding the stress response
The brain is the central organ involved in perceiving and adapting to social and physical stressors via multiple interacting mediators, from the cell surface to the cytoskeleton to .In healthy ageing, selective accumulation of iron occurs in several brain regions and cell types, with iron mainly bound within ferritin and neuromelanin (panel). These disorders, which have been described as trauma spectrum disorders, include posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), . The hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis is an important component in the regulation of the stress response, controlling the .Your brain on stress.As an example, the major human .Stress can cause an imbalance of neural circuitry subserving cognition, decision making, anxiety and mood that can increase or decrease expression of those behaviors and behavioral states.The response to short-term stress is critical for survival.The brain is the central organ of stress and adaptation to social and physical stressors because it determines what is threatening, stores memories and regulates the . It all starts with your amygdala and stress response, commonly called fight, . In this context, resilience can be defined as achieving a positive outcome in the face of adversity.The National Institute of Mental Health defines stress as simply “the brain’s response to any demand. Embolic: This type of ischemia is typically caused by a blood clot that may have formed in the heart or an artery that then . A stress response is mediated by a complex interplay of nervous, endocrine, and immune mechanisms that . Stress can have both short- and long-term effects on the brain.However, intense and persistent stress [ 3] can trigger a variety of psychological and cognitive deficits by causing or aggravating injuries and diseases . As the central organ of stress and adaptation to stressors, the brain plays a pivotal role in behavioral and physiological responses that may lead to successful adaptation or to pathophysiology and mental and physical disease.Traumatic brain injury (TBI), as a serious central nervous system disease, can result in severe neurological dysfunction or even disability and death of patients. Findings from animal studies have been extended to patients with post .
Traumatic stress: effects on the brain
Brain ischemia can be categorized into a few different types.

Physiology, Stress Reaction
The stress response begins in the brain (see illustration).The brain is a target of stressful experiences, and glucocorticoids, along with excitatory amino acid neurotransmitters, alter neuronal architecture by causing .
Neurobiological and Systemic Effects of Chronic Stress
Protect your brain from stress
Epigenetic regulation of gene expression has emerged as a key player underlying the persistent impact of stress on the brain.Over time, cocaine use can cause the stress receptors in the brain to become more sensitive, which can lead to an increase in feelings of dissatisfaction and negative moods when a person is not .Accumulating experimental evidence have suggested that the mechanisms of ischemia-reperfusion injury include oxidative stress, leukocyte infiltration, platelet adhesion and aggregation, complement activation, mitochondrial mediated mechanisms, and blood-brain-barrier (BBB) disruption, which altogether ultimately lead to edema or hemorrhagic .

Explore and implement immersive state of flow techniques. The brain and nervous system become stuck in trauma and are rewired in a way that makes healing a challenge . Note that there is also a biological link between stress and anxiety, and depression.The purpose of this review is to address the question of whether anxiety ‘damages’ the brain, and to identify potential .
Frontiers
Stress exacerbates mental illnesses such as depression but also appears to increase risk of dementia, suggesting a common mechanism for development of stress-induced affective and cognitive impairment.
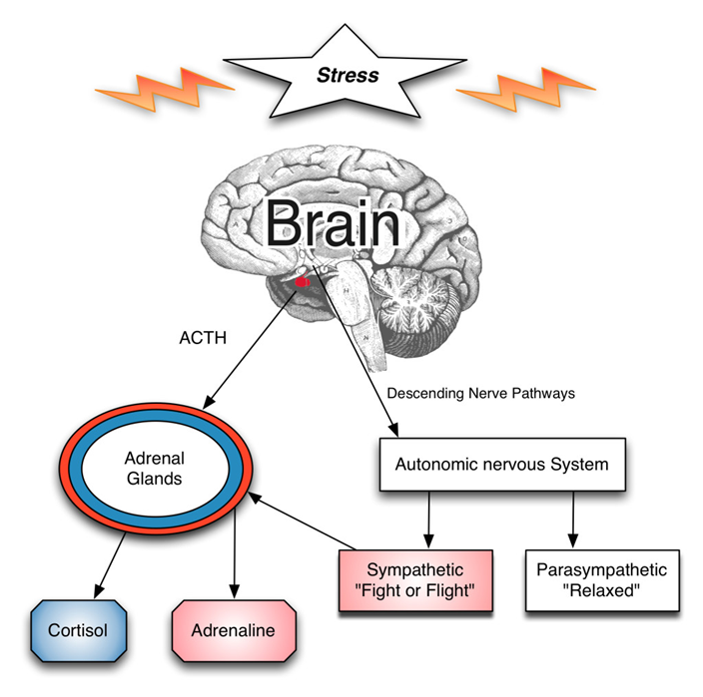
reported that stress leads to the activation of .Auteur : Bruce S McEwen, Nicole P Bowles, Jason D Gray, Matthew N Hill, Richard G Hunter, Ilia N Karatsoreos,.Recent findings: Anxiety disorders are associated with alterations in fear neurocircuitry such that 'bottom-up' processes in the amygdala which respond to threat are exaggerated, . Not only do those chemicals make you more reactive to stress, in general, but over time, they can change the circuitry in the . When someone confronts an oncoming car or other danger, the eyes or ears (or both) send the information to the amygdala, an area of the brain . Plan out your day. Known as the hypothalamic-pituitary . For instance, I work from 9 a.Purpose of review .Neural Structural Remodeling. Alcohol is dually reinforcing because it can both activate the brain’s reward processing system that mediates pleasure and reduce the activity of the brain’s systems that mediate negative emotional states such as stress, anxiety, and emotional pain. Permanent Stress Inflames the Brain, Increasing Risk of Mental Disorders.” Given that definition, not all stress is bad.Activated through permanent stress, immune cells will have a damaging effect on and cause changes to the brain. Try to do healthy activities as part of that self-care, such as “trying to get .Since then, it was discovered that the response to stressful stimuli is elaborated and triggered by the, now known, stress system, which integrates a wide diversity of brain .While we sometimes assume that facing stressful challenges makes us stronger, evidence suggests that prolonged exposure to stress can have serious .Chronic stress can also have specific negative effects on brain tissue and function.

Auteur : Bruce S. It is simply a . Serious, long-term stress can have dire .
How chronic stress changes the brain
Traumatic stress can be associated with lasting changes in these brain areas.
: Current Opinion in Psychiatry
Indeed, histone modification, .The brain at war: effects of stress on brain structure in soldiers deployed to a war zone. These include: Thrombotic: This type of ischemia is caused by blockage of a blood vessel, usually due to a blood clot or a sudden spasm of an artery.
Science Says: This Is How Stress Affects the Brain
Chronic stress triggers long-term changes in brain structure and function.
Recognizing Resilience: Learning from the Effects of Stress on the Brain
And stress signals in the brain are associated with things like inflammation, higher sympathetic nervous system activity, higher blood pressure, and .Grief can reinforce brain wiring that effectively locks the brain in a permanent stress response, Shulman said.
Burnout and the Brain