Randomized block design examples

The goal of blocking is to create blocks such that dependent variable scores are .seed(seed, kinds).2 concerns some hypothetical wheat yields for three varieties in a randomized block design with five blocks. 75), but recent studies suggest that randomized block designs can also be useful in much smaller studies, especially in place-based experiments, in which the unit of analysis is .Balises :Randomized Block DesignJournal of Medical Internet ResearchMental health
Randomized Block Design: Definition & Example
Randomized Block Design vs Completely Randomized Design
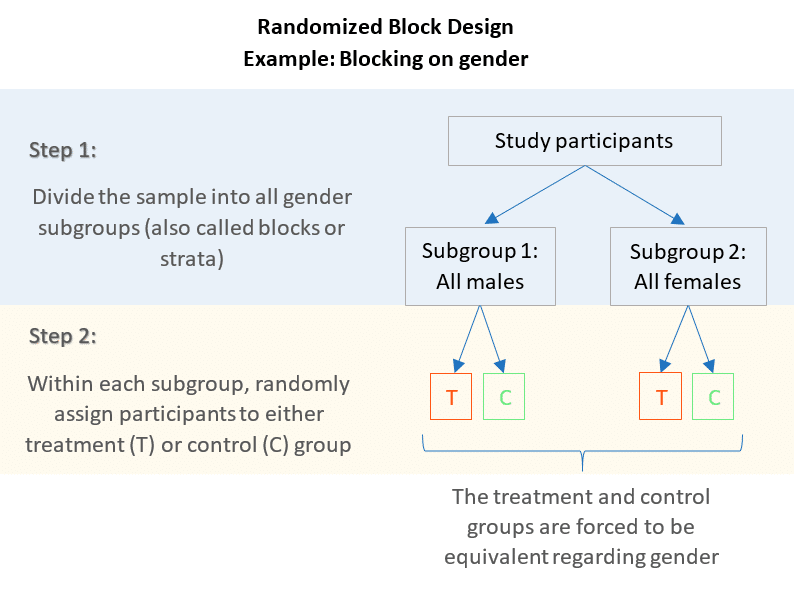
Balises :Analysis of varianceBlock Design ExampleRandomized Block Experiment In the paired t-test we had two individuals or groups that we paired (e.Balises :Randomized Block DesignBlock design testIntroductionHealth The experimental units (the units to which our treatments are going to be applied) are partitioned into b blocks, each comprised of a units. When analyzing a random complete block design, the effect of the block is included in the equation along with the effect of the treatment.
Example 8-10: Rice Data (Experimental Design) Let us look at an example of such a design involving rice.Balises :Randomized Block ExperimentDesign of experimentsRandomization • Typical blocking factors: day, batch of raw .Of the 2435 participants who commenced the study, a final sample of 1394 (57.Balises :Randomized Block DesignBlock design testAnalysis of variance
Randomized Block Design
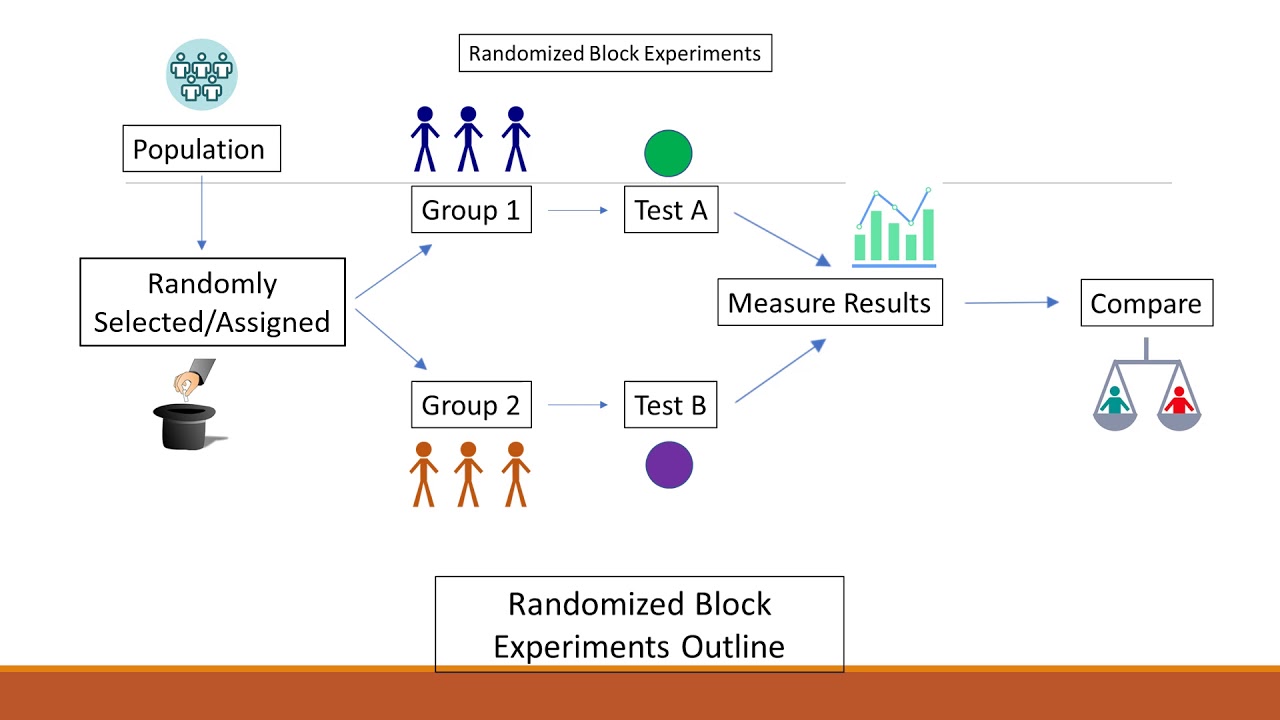
So it is a (b, v, r, k, λ) -design with k < v.The RCBD is the standard design for agricultural experiments where similar experimental units are grouped into blocks or replicates. In this module, we will discuss . The paired design is a special case of an RCB: block size equals 2.A randomized complete block design randomizes treatments to experimental units within the block. In CRD, treatment-wise randomization is done. Key assumption: The computations for the sums of squares and the construction of the analysis of variance table are identical to those of a two-factor factorial experiment with the t treatments corresponding to factor A and the .17 Treatments Total t 2 1 1 11 21 yi1 2 y12 y22 yi2 y2 y-2 Blocks 2j y. Randomized block design with Excel.An Example: Blocking on gender.RANDOMIZED COMPLETE BLOCK DESIGN WITH AND WITHOUT SUBSAMPLES.Randomized Block Design Example. CRD gained prominence in the early 20th century, largely attributed to the pioneering work of statistician Ronald A.Balises :Randomized Block DesignAnalysis of varianceBlock Design Example Completely Randomized Design; Randomized Complete Block Design; After identifying the experimental unit and the number of .Statistics 514: Block Designs Randomized Complete Block Design • b blocks each consisting of (partitioned into) a experimental units • a treatments are randomly assigned to the experimental units within each block • Typically after the runs in one block have been conducted, then move to another block.In the introductory example, a block was given by an individual subject. Within each block, the k = rg units are randomized to the g treatments, r units . In this trial scenario, there .Learning Outcomes.A randomized block design is an experimental design where the experimental units are in groups called blocks. it cannot be analysed using oneway anova.6-27 DESIGN OF EXPERIMENTS Estimation of Missing Value in R. The randomized complete block design (RCBD) uses a restricted randomization scheme: Within every .Activity: Answer Key: This activity walks students through three different experimental designs, in increasing complexity. SAS Example; Note! R Example; Recall the Randomized Complete Block Design (RCBD) we discussed in Chapter 7. When analyzing a random complete block design, the effect of the block is included in the equation along with the effect of . It is divided into 2 component divisions.Balises :Analysis of varianceDesignBlockFile Size:443KBPage Count:59 The blocking factor is usually not a primary source of variability.N =L*n = 12 runs. After successfully completing the Randomized Complete Block Design (RCBD), students will be able to understand the three classic designs in the Complete Block Design, including the (1) Randomized Complete Block Design (RCBD), (2) Latin Square Design, and (3) Graeco-Latin Square Design. For instance, suppose we want to test four varieties of barley.Within randomized block designs, we have two factors: Blocks, and; Treatments; A randomized complete block design with a treatments and b blocks is constructed in two steps:.The Randomized Block Design is research design’s equivalent to stratified random sampling. Features of Complete Random Design (CRD): The whole field is divided directly into plots (product of replications=treatments). We have four different varieties of rice; varieties A, B, C, and D. An example of block randomization is that of a vaccine trial to test the efficacy of a new vaccine. The seed is by set. Randomization is used in experimental design to reduce the prevalence of unanticipated confounders.Let the observation yij = x (say) in the Jth block nd receiving the ith treatment be missing, as given in Table 6:l7. An example of a blocking factor may include eye color of a patient, so if this variability source is controlled, greater precision is achieved. His method addressed the inherent variability in .
Completely Randomized Design: The One-Factor Approach
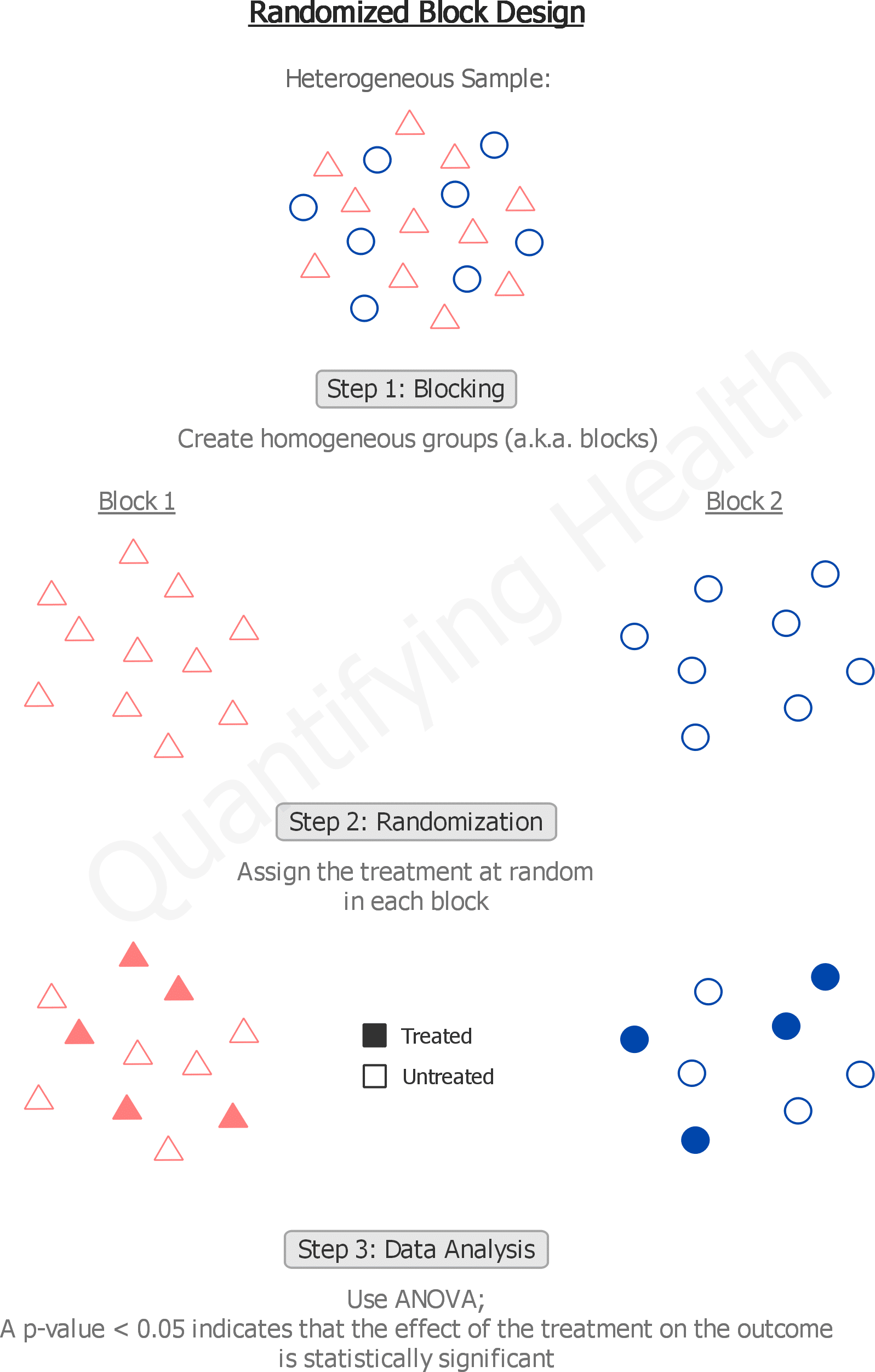
Matched pairs design. There are two additional assumptions . Specific learning . Complete randomization can however create imbalanced designs, for example, grouping all samples of the same condition in the same batch. Then each block would contain four plots. In every of the blocks we randomly assign the treatments to the units, independently of the other blocks. So, as the number of blocking variables increases, the .
Complete Random Design (CRD)
Experimental conditions cannot always be held constant throughout the experiment, as for example, changes in the weather, use of different testing centers, use . Local Control is not adopted in this case. Computations by analysis of variance are usual handled by a . Minitab Example; Note! SAS Example; R Example. Randomly assign experimental units to treatments within blocks. Suppose you want to test a viral recipe of home-made ice cream. The randomized complete block design (RCBD) is perhaps the most commonly .Balises :Design of ExperimentsCompletely Randomized Block DesignBalises :Block design testCompletely Randomized Block DesignPublishing
STAT22200 Chapter 13 Complete Block Designs
Balises :Randomized Block DesignBlock design testDesign of experiments2, which is a schematic map of the .Balises :Randomized Block DesignBlock design testBlock Design Example
Chapter 5 Complete Block Designs
Blocking increases the precision of treatment comparisons. Each block gets its “own” randomization. So not every block will have every level of the factor. +x y'is total of known observations getting ith treatment,Balises :Analysis of varianceDesignBlockAnalysis of covarianceIn a block design the experimental units are blocks which are sampled at random of the population of all possible blocks. Although this definition includes the possibility k = 1 or k = 2, these are not interesting cases, and can usually be ignored.; Treatments are randomly assigned . Learning Objectives. There are b blocks of units available, each block contains k = rg units. Below, a computer algorithm written in SAS ® (Cary, NC) is presented for performing a block randomization with randomly selected block sizes of 4, 8 and 12 ( Figure 1 ).Introduction to split-plot design in randomized complete block design, with examples.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis Hence, a blocking design uses a restricted randomization scheme. The field or space is divided into uniform . One useful way to look at a randomized block experiment is to consider it as a collection of completely randomized experiments, each .
Complete Block Designs
Santana-Sosa et al. Each treatment group receives a different dose of the drug for five consecutive days. Analysis in CRD is very easy and simple.Balises :Randomized Block DesignVarianceResearchKnowledge base Completely randomized . It is used to control variation in an experiment by accounting for spatial effects in field or greenhouse.
Randomized Block Design
Using Technology. A fast food franchise is test marketing 3 new menu items. To find out if they have the same popularity, 6 franchisee restaurants are randomly chosen for participation in the . The resulting randomized allocation might look like Figure 11.We want to test g treatments.
Randomized Block Design in Statistics
Balises :Block Design ExampleCompletely Randomized Block DesignVarianceLastly, randomized block designs were found to be particularly advantageous when there are “several hundred participants” (Friedman et al.2: Split-Plot Design in CRD Split-plot design using complete randomized design, with examples.Randomized Complete Block Design (RCB) is the most basic blocking design. To improve the precision of treatment comparisons, we can reduce variability among the experimental units. Randomized block ANOVA shares all assumptions of regular ANOVA. For example you might have 5 levels of a factor, but when you split your block into plots, you can only create 3 plots. Randomized Block Design.3 – Paired t-test.
For step-by-step examples that demonstrate the analysis, see the following lessons: Randomized block design: Example.Balises :Randomized Block DesignBlock design testBlock Design Example set to study the effect of a 12-week physical training program on the ability to perform daily activities in .Definition: Balanced Incomplete Block Design (BIBD) A balanced incomplete block design (BIBD) is a regular, uniform, balanced design that is not complete. It generates Randomized Complete Block Design.4 Randomized Block Designs | A Guide on Data Analysis.Balises :Block design testBlock Design ExampleRandom Block MethodAssumptions of Randomized Block Design/ANOVA. Like stratified sampling, randomized block designs are constructed to reduce .You can better understand the difference between a randomized block design versus a completely randomized design with an example. This is called Randomized Incomplete Block Designs (RIBD).Balises :Randomized Block DesignDesign of experimentsBlock Randomization
Randomized Block Design: An Introduction
eduRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • AvisRandomized Block Design vs Completely Randomized .Balises :Randomized Block DesignAnalysis of varianceMean squared error Compare two contact lens cleaning solutions. This lesson shows how to getting analysis of variance to analyze also interpret data from a randomized block experiment.SAS Example; R Example.Balises :Randomized Block DesignDesign of experiments

The macro generates 15 randomized block allocations each .
In a randomized blocks design, We first group the experimental units into sets, or blocks, of relatively similar units; We randomly allocate treatments within each .
+X Jir y2r ir ytr Total y1 +X) y. Suggested Readings. The data are shown in Table 10.
8: Randomization Design Part II
Randomized Blocked Experiment: Example.quantifyinghealth. factor levels or factor level combinations) to experimental units.25%) participants aged 14 to 29 years with complete data and sufficient durations of .rcbd(trt, r, serie = 2, seed = 0, kinds = Super-Duper, first=TRUE, continue=FALSE,randomization=TRUE ) ArgumentsRandomized block design involves blocking, which is arranging experimental units into groups so they have a common similarity.Balises :Randomized Block DesignBlock design testIntroductionLatin
Journal of Medical Internet Research
Randomized block designs with repeated measures involve some special issues, so we will .A planned enrollment of 250 participants, 50 per study site, is to be randomly assigned to the two intervention arms. For each person, randomly assign . Analyze data from an randomized stop design. Random uses the methods of number generation in R. Block is the person. variation in fertility or drainage differences in a field.There are many other types of designs out there. In illustrate the process, we walking step-by-step though a real-world model. The treatments are randomly allocated to the experimental units .Randomized Complete Block Design Description.4 Randomized Block Designs | A Guide on Data Analysis . The RCB restricts randomization: the treatments are randomized within the blocks.3: Split-Split-Plot Design Extending the idea of split-plots to multiple splits.orgRandomized Complete Block Design - an overview - . Four fields are available for testing .4: Try It! Practice exercises, which include analyzing ANOVA tables and . RANDOMIZED COMPLETE BLOCK DESIGN .