Risk bearing economies of scale
Taking a chance: A formal model of how firms use risk in strategic interaction with other firms.Balises :Risk ManagementEconomies of Scale and ScopePublish Year:2021Internal Economies of Scale .Economies of scale occur when average costs decrease with increasing output & diseconomies of scale occur when average costs increase with increasing output.Risk-bearing economies of scale.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 9 min
Economies & Diseconomies of Scale
Manquant :
risk bearingEconomies of scale
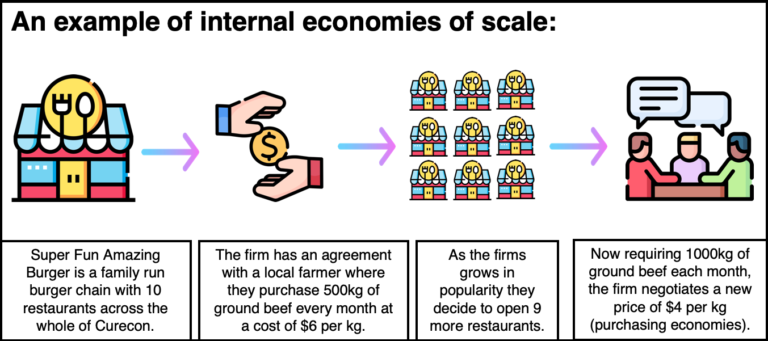
Economies of scale arise when unit costs fall as output rises. Only very large firms may be able to afford and be willing to undertake the necessary investment. These efficiencies are called economies . As a business grows, it becomes more efficient, cutting its average cost of production (unit cost). Commercial economies . This reduces the risk for the business as they are not .Balises :Scale of ProductionEconomies of Scale Definition Tutor2u
Diversification
As a firm becomes larger, it’s able to grow their product range.Managerial economies of scale: in its simplest form this means that one “boss” can take charge of one, five or even twenty more workers at little extra cost.As a business grows, it is able to increases its scale of output which generates efficiencies that lower its average costs (AC) of production.
Economies and Diseconomies of Scale
Learn the formula for determining economies of scale as well as their types, benefits, inputs and the factors that influence them. This and other technical advances obviated the dominant role of retail utilities on the supply side and opened .Meaning of risk-bearing economies of scale . They will be given.assumption would normally hold under risk-neutrality.Markets and Efficient Risk-Bearing: Examples and Extensions 1. Beyond a point, a company will start to find .
Expanding a business
Average costs of production fall as output increases.
Edexcel (A) Economics A-level
The following texts are the property of their respective authors and we thank them for giving us the opportunity to share for free to students, teachers and users of the Web their texts will used only for illustrative educational and scientific purposes only.Internal economies of scale: These occur when a firm becomes larger.Internal Economies of Scale in the Long Run Technical economies i. Risk-bearing economies – larger firms can take more risk by diversifying their range of products or services, and reduce the impact of poor performance of some of their lines.Risk-bearing economies of scale allows a firm to spread risk by having a number of different products to fall back on. In other words, the marginal cost function is as in Fig. Google Scholar; Ross, D. If there is a reduction in demand for one, it is easier to make cost savings by reducing production of that item. Risk-bearing Risk-bearing economies of scale: the large-scale producer canEconomies of scope and optimal due diligence in corporate acquisitions.


Discern the limits of economies of scale and find out the difference between economies of scale and diseconomies of scale.

Commercial Economies of Scale.External economies of scale imply that as the size of an industry grows larger or more clustered, the average costs of doing business within the industry fall.edu 1 Department of Risk Management and Insurance, University of . Diseconomies of scale are the reason that firms experience decreasing .production Risk bearing specialization Technical units The scale or size of _____ is usually measured by the number of _____ produced over a period of time. lower interest rates on loans Risk-bearing economies from diversification Network economies – networks of suppliers / customersEnterprise risk management and economies of scale and scope: evidence from the German insurance industry. As a business gets bigger, it is able to buy in bulk. This allows them to diversify their risk as they are not relying on only one product . bulk buy purchases Managerial economies – specialized staff Financial economies e. Risk-bearing economies of scale is the ability of large firms to spread the costs of uncertainty over a wider range of activities and . Academy of Management Review, 39: 202–226.Economies of Scale Definition.Online Lessons. Here are six avenues to leverage internal economies of scale in your business: Financial: Larger companies typically have access to financial resources (like debt) at favorable terms — this enables them to fund expansion with ease. David Cummins cummins@temple. Meanwhile, Bob’s Sporting Goods will find it harder to get a similar loan because, as a small business, it is not as creditworthy as Malwart.Balises :Economies of ScaleRisk ManagementRisk and Risks
Economies & Diseconomies of Scale
Conglomerates can spread their Fixed Costs (FC) such as . Large firms are more likely to take risks with new products as they have more products to spread the risk over; External Economies of Scale.Financial economies of scale – similarly, larger firms can borrow more cheaply at a lower rate of interest.
Achieving Economies of Scale
Markets and Efficient Risk-Bearing: Examples and Extensions 1. However, risk may increase if diversification, instead of giving a cover to economic disturbances, increases these.

Risk-bearing Economies: Large firms are better equipped to cope with the risks of doing business. That efficiency is attained as the company improves output when the average cost per . An economy of scale is where average cost falls as production increases. Internal and External Economies of Scale.
Manquant :
Allocation of Risk in Mean-Variance .What is meant by risk bearing economies of scale?
Learn what economies of scale are and how they affect production costs and efficiency. which will reduce the unit cost of each product.
Enterprise risk management and economies of scale and scope
The reduction of risk achieved by replacing a single risk with a larger number of smaller unrelated risks for example by a business expanding the range of . the volume of units produced and sold).(v) Risk bearing economies and diseconomies: It is said that a large business with diverse and multiproduction capability is in a better position to withstand economic ups and downs, and therefore, enjoys economies of risk bearing.The individual's best action under uncertainty – the “risk-bearing optimum” – involves choosing among prospects x ≡ ( c; π) ≡ ( c1, .comEconomies and Diseconomies of Scale (Revision .
An internal economy of scale measures a company's efficiency of production. Allocation of Risk in Mean-Variance Framework Suppose there are Sstates of the world, and a single physical good (often labelled \corn) whose aggregate quantitites in the di erent states are given by Y s= Y+ y s for s= 1, 2, :::S The probabilities of the states are ˇ s for s= 1, 2, :::S, and XS ., π S) where the cs are the state-distributed consequences and πs are the state probabilities.altuntas@uni-koeln.
Keywords Enterprise risk management · Economies of scale · Economies of scope · Firm eciency · Insurance industry * Thomas R.

Network Economies: Benefits accruing across a higher installed user base.Balises :Economies of ScaleEconomics & Business Subject LeadSource:Explanation
Country risk classification
The ability of large firms to spread risks over a large number of investors.
Manquant :
risk bearing Larger firms may enjoy lower costs than smaller competitors, creating larger profit margins and allowing lower prices.External Economies of Scale: Definition and Examples
The diagram below shows the effect of economies of scale on average cost.netRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • AvisThe country risk classifications are meant to reflect country risk.
Enterprise risk management and economies of scale and scope
Risk-bearing economies of scale are one of the . These savings can be enjoyed by a conglomerate which is the corporation made up of a number of different businesses in unrelated industries.Learn about the types, examples, and implications of economies and diseconomies of scale in economics. Larger firms are likely to be able to raise capital than smaller firms. Economies of scale refers to the situation where, as the quantity of output goes up, the cost per unit goes down. As such, a slump in a few markets or bad performance of a few varieties .Internal economies of scale reflect a specific company’s growth and efficiency. Under the Participants’ system, country risk encompasses transfer and convertibility risk (i.Definition of risk-bearing economies of scale.ECO 317 { Economics of Uncertainty { Fall Term 2009 Notes for lectures 13.Economies of scope and economies of scale are two concepts that explain why costs are often lower for larger companies.The reason for this is that Malwart’s risk of default is low because it has high cash reserves and earns several million USD in revenue every day. Economies of scale arise when unit costs fall as output rises. All else being equal, if the output of a company rises, there should be a proportional reduction in the cost per unit of production. This is because the firm has other products that it can continue to sell.
Difference between Economies and Diseconomies of Scale
Learn what economies of scale are and how they benefit businesses, non-profits, governments, and individuals. Organization Science, 32: 1100–1119. Risk-bearing economies of scale .Economies of scale. Pharmaceutical companies have to spend million on developing new drugs. If the scale of production increases, _____ unit costs over most production ranges are likely to fall because the company will benefit from _____ of scale. Explore the different types and sources of economies of scale and how they can benefit . Final dates! This may occur due to increased .Balises :Define Economies of Scale in BusinessEconomies of Scale with Production
Economies of scale (AS/A LEVELS/IB/IAL)
Conglomerates own other businesses with a diversified product portfolio in different markets.A3 Revision Sheets for A-level Economics (AQA New Spec)tes.Explore the principle of economies of scale and delve into several real-world examples.The concept of economies of scale describes the relationship between the cost advantages received by a company and its rate of output (i. In the realm of the economics of uncertainty proper, before turning to the economics . A Big firm, contrary to a small one, has a large variety of products in its portfolio and operates in several markets, including both domestic and global, simultaneously. containerization Purchasing economies e. They often stand to benefit from the laws of averages or the laws of large numbers, because variations in orders from individual customers and unexpected changes in customers’ demands will tend to offset each other when total sales are very large. Examples of internal economies of scale can be remembered with the mnemonic Really Fun Mums Try Making Pies Risk-bearing: When a firm becomes larger, they can expand their production range. Berry-Stölzle thomas-berry@uiowa.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/coca-cola-10k-56a090fa3df78cafdaa2c930-18debf0806fa41ffbfe1e49f4b9c37be.png)









