Thermohaline circulation climate change
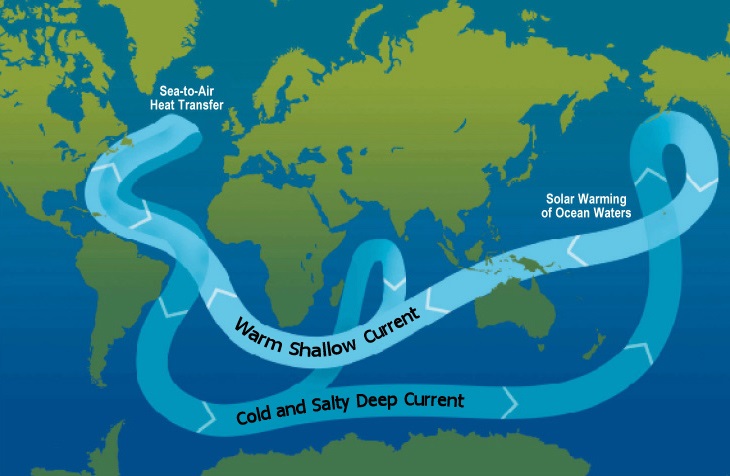
Ocean Conveyor Belt
Abrupt climate change, which could be induced by a THC collapse, poses fundamental unanswered questions of ocean and climate dynamics and predictability.The palaeoclimate data and the model results indicate that the stability of the thermohaline circulation depends on the mean climate state, and data and models both suggest that abrupt climate change during the last glaciation originated through changes in the Atlantic thermohalin circulation. There are concerns that greater rainfall and melting of land ice and snow .Explanations for the rapidity and asynchrony of these climate changes require a mechanism for partitioning heat on a planetary scale, initiated either through reorganization of atmospheric structure or the ocean’s thermohaline circulation, particularly the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) (7–10).Auteur : Peter U. ADS CAS PubMed Google ScholarA study by Marco Tedesco, a research professor at Lamont-Doherty specializing in Greenland, and colleagues suggested that a reduction in the temperature .Thermohaline circulation describes the movement of ocean currents due to differences in temperature and salinity in different regions of water. Stocker, Andrew J. But it remains difficult to assess the likelihood of future changes in the thermohaline . C'est ainsi que certains climatologues prévoient . Investigating the causes of the response of the thermohaline circulation to past and future climate changes.Investigating the causes of the response of the thermohaline circulation to past and future climate changes.Climate models predict that the ocean's circulation will weaken in response to global warming, but the warming at the end of the last ice age suggests a different outcome.Temperature and salinity change the density of water, resulting in the water to move accordingly.The role of the thermohaline circulation in abrupt climate change. The global thermohaline circulation. Previous research has shown large uncertainties in simulating future changes in this critical system. Theoretical and palaeoclimatic evidence points to the possibility of rapid . Cold water is usually denser than warm water (4°C is where water is densest). If they were to stop, this would not be the first time that the global ocean conveyor was halted. The surrounding seawater gets saltier, increases in density and sinks.Thermohaline Circulation.The currents in the North Atlantic are part of a global pattern called thermohaline circulation, or the global ocean conveyor. There is evidence from sedimentary rocks and ice cores that it has shut down several times in the past which caused changes in .Anticipated future changes in today's climate system due to human activities have the potential to weaken the thermohaline circulation of the North Atlantic Ocean10,11,12, which would greatly . The record in ancient sedimentary rocks suggests that similar abrupt changes plagued the Earth at other times.The Atlantic thermohaline circulation (THC) plays an important role in global climate.Abrupt climate change, which could be induced by a THC col-lapse, poses fundamental unanswered questions of ocean and climate dynamics and predictability.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 8 minThis thermohaline circulation (THC) is responsible for much of the total oceanic poleward heat transport in the Atlantic, peaking . How the Climate System Works July 28, 2014.The possibility of a reduced Atlantic thermohaline circulation in response to increases in greenhouse-gas concentrations has been demonstrated in a number of simulations with general circulation models of the coupled ocean-atmosphere system. Large masses of water that move together, called ocean currents, transport heat, marine organisms, nutrients, dissolved gasses such as carbon dioxide and oxygen, and pollutants all over the world. Clark, Nicklas G.How strongly might changes in thermohaline circulation affect climate? To what extent do Europe's mild winters depend on the transport of heat by the Gulf Stream . The simulated THC response to idealized freshwater perturbations and the associated climate changes have been intercompared as an activity of World .During the last glacial period, Earth's climate underwent frequent large and abrupt global changes.
What Is the Thermohaline Circulation?
This behavior appears to reflect the ability of the ocean's thermohaline circulation to assume more than one mode of operation.A reading of the literature on climate and the ocean suggests at least seven different, and inconsistent, definitions of the term “thermohaline circulation”: 1) the .The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC)—an ocean current system transporting heat northward in the Atlantic—plays a vital role in Earth’s climate (1–6).
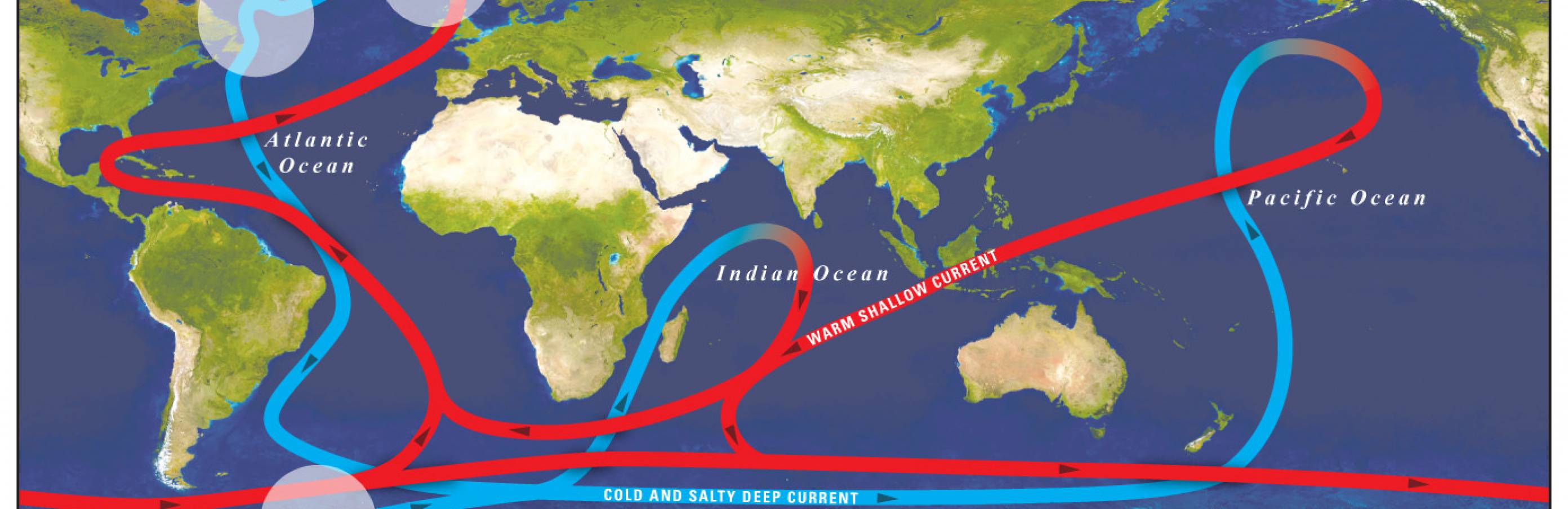
La circulation thermohaline s'affaiblirait et les côtes européennes seraient alors moins réchauffées par les courants chauds.
Thermohaline Ocean Circulation
The four main controlling factors are: the world’s circulation system the ocean conveyor belt .Abstract In this study, a mechanism is demonstrated whereby a large reduction in the Atlantic thermohaline circulation (THC) can induce global-scale changes in the Tropics that are consistent with paleoevidence of the global synchronization of millennial-scale abrupt climate change.Ocean circulation.
The role of the thermohaline circulation in abrupt climate change
(THC) consists of cooling-induced.Planet Earth; Antarctica 'Unprecedented,' 'Gobsmacked', 'Unbelievable': Changes in Antarctica's sea ice could have dramatic impacts, says climate scientist .These, however, are superimposed on the much more sluggish circulation driven by horizontal differences in temperature and . Thermohaline Circulation. The ocean covers 71% of Earth’s surface and is constantly in motion.transport of the thermohaline circulation makes it important for climate, and its non-linear and potentially abrupt response to forcing have been invoked to explain abrupt glacial .
North Atlantic ocean circulation and abrupt climate change
The mid-Pleistocene transition (MPT) marked a fundamental change in glacial-interglacial periodicity, when it increased from ~41-thousand-year to 100-thousand-year cycles and developed higher-amplitude climate variability without substantial changes in the Milankovitch forcing. Climate and ecosystems everywhere on Earth, even those far .thermohaline circulation will change; alter thermohaline forcing, and the wind-driven currents will also change.Thermohaline circulation begins in the Earth's polar regions.cause of abrupt climate change on all timescales of decades and longer.Thermohaline circulation ( THC) is a part of the large-scale ocean circulation that is driven by global density gradients created by surface heat and freshwater fluxes.The Atlantic thermohaline circulation (THC) is an important part of the earth’s climate system.5°N in the North Atlantic (), although this . Across the globe, changes in . Pisias, Thomas F.
Decades of Data on a Changing Atlantic Circulation
atmis a function of the .The occurrence of a large climate event plausibly linked to a circulation change about 8000 years ago, when temperatures typically were similar to or warmer than .Because of the process of thermohaline circulation, the scientists reviewed in situ (on-site within the ocean, as opposed to remotely-sensed, such as satellite data) .
Weather patterns and processes
The ocean's thermohaline circulation has long been recognized as potentially unstable and has consequently been invoked as a potential cause of abrupt climate change on all timescales of decades and longer.A process known as thermohaline circulation, or the ocean conveyor belt, drives these deep, underwater currents.The ocean’s thermohaline circulation has long been recognized as potentially unstable and has consequently been invoked as a potential cause of abrupt .The general circulation of the oceans consists primarily of wind-driven ocean currents. Winds drive ocean currents in the upper 100 meters of the ocean’s surface.
Thermohaline circulation
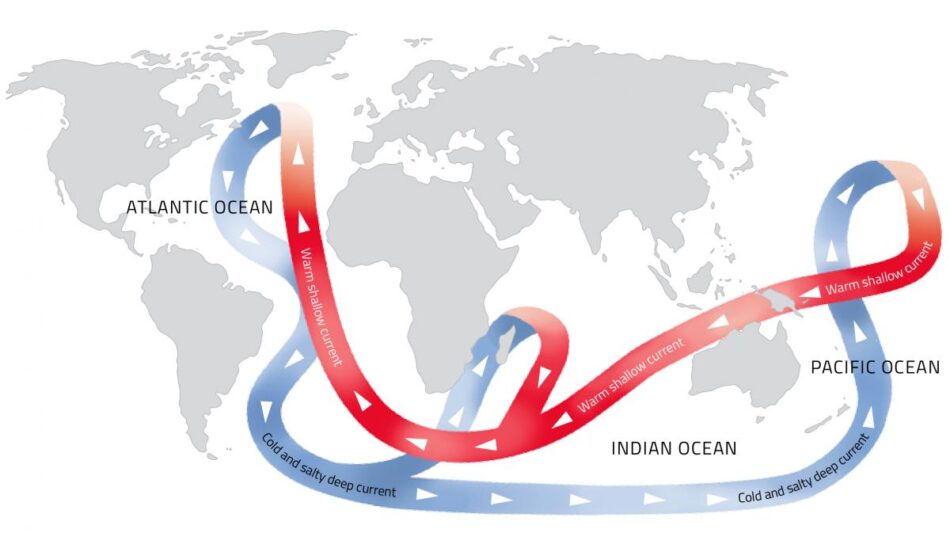
Here, we document, by using Nd isotopes, a major disruption of the ocean thermohaline circulation (THC) system during the MPT between marine isotope stages . However, fundamental aspects of thermohaline circulation changes remain poorly understood. The thermohaline circulation is sometimes called the ocean conveyor belt, the great ocean .In the North Atlantic the thermohaline circulation consists of warm surface water flowing northward and cold deep water flowing southward (see the figure), resulting in a net poleward transport of heat, thereby moderating the tropics and warming the high latitudes of Europe. Using GFDL’s newly developed global coupled .
Climate impacts of a weakened Atlantic Meridional Overturning
However, ocean currents also flow thousands of meters below the surface. changes remain poorly understood. Water with a high salinity is also .The ocean's thermohaline circulation has long been recognized as potentially unstable and has consequently been invoked as a potential cause of abrupt .Cold, dense water from the Southern Ocean transfers heat and carbon to the Northern Hemisphere via the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation. What is thermohaline circulation? Cold water, in general, is .The world’s weather is dependent on several major atmospheric and ocean circulation systems.
Could Climate Change Shut Down the Gulf Stream?
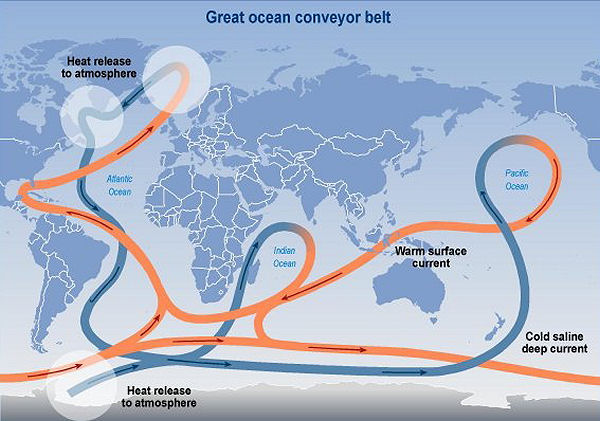
Climate projections suggest a weakening or collapse of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) under global warming, with evidence that a .The currents flowing through the ocean, a process called thermohaline circulation, can have an impact on climate.
The AMOC has been observed to slow down over the past decade in the Rapid Climate Change (RAPID) array at 26. It is because of ther-mohaline forcing that wind-driven currents are relegated to .

As such, the state of the circulation has a large impact on the climate of the Earth.Data and models both suggest that abrupt climate change during the last glaciation originated through changes in the Atlantic thermohaline circulation in response to small changes in the hydrological cycle.

However, fundamental aspects of thermohaline circulation. Shifting ocean surface saltiness from 2004-2013.