Types of market efficiency

These anomalies may last for a long . Producing goods at low cost. Allocative Efficiency. Market efficiency is a relatively broad term and can refer to any metric that measures information dispersion in a market. A monopoly will produce less output and sell at a higher price to maximize profit at Qm and Pm.Balises :MarketsStudies On Market EfficiencyCritical Review ConceptMarket Anomalies Explained. It was developed to explain why . Moreover, it highli ghts a number of. The Efficient Market Hypothesis categorizes information availability and the market’s ability to reflect that information into three forms. Given these insights, a rigorous definition of .Evidence on efficient market theory is classified into the following four sections: Study related to price changes and their time series properties: These are the initial studies on market efficiency that emphasised on the relationship between the time and the change in the asset price. Informational efficiency is a natural consequence of competition, relatively free entry, and low costs of information. Practitioners of . Weak form of market efficiency reflects past . Pricing efficiency refers to the ability . Believers in these three forms of efficient markets maintain, in varying degrees, that it is pointless to . However, the debate surrounding EMT remains ongoing, with . Prices reflect all the information, both current and historical data points.
The market is large in size and liquid.Market Efficiency Hypothesis. Productive efficiency occurs at the point where economies of scale are fully exploited (the minimum efficient scale). For example, it wouldn't be efficient to produce trillions of purple widgets that nobody wants.Balises :Market EfficiencyMelody Loomelody.Allocative efficiency can be found in perfectly competitive markets because firms in those markets don’t have enough market power to increase prices. The hypothesis states that the price of assets reflects all relevant and available information about the asset. These three forms constitute the efficient market hypothesis.

CHAPTER 6 MARKET EFFICIENCY
Not only does this enable the firm to be more competitive, but it may also be of benefit to the consumer. Market Anomalies are defined as behaviors or patterns in financial markets deviating from the normal course of movement under efficient market conditions. Social efficiency – taking into account external . Market efficiency is one of the most . By contrast, Monopolies are said to produce allocatively inefficient levels of output, . To answer our questions, we will look at two forms of efficiency: . The asset (or assets) which is the source of the inefficiency has to be traded.The market inefficiency should provide the basis for a scheme to beat the market and earn excess returns.Impact on Security Prices and Trading.What are the 3 Forms of Efficient Market Hypothesis? Weak Form, Semi-Strong, and Strong Form Market Efficiency. As prices respond .Balises :Efficient FormsSemi-Strong Form of Market EfficiencyStrong Form Efficiency The theory has been proven mostly correct, although anomalies exist.How efficient are our markets? Sophisticated statistical analyses of stock and other securities prices indicate that they follow a “random walk .Practically, the current market cap presents the starting point in the company valuations.The efficient market hypothesis has been the subject of a wide debate over the past decades.What is market efficiency? Reviewed by Eric Estevez.Economic efficiency is the amount of value created by the resources of a nation or region.An efficient market very would negative also many investment and strategies actions that are. Information is readily available to everyone, so no one has an unfair advantage. Also, new information helps the market become even more efficient. In efficient anmarket, a strategy of randomly .Balises :Efficient FormsSemi-Strong Form of Market EfficiencyDaniel LibertoBalises :Financial Market EfficiencyOperational Efficiency That line set off a theoretical explosion in .Strong form efficiency is the strongest version of market efficiency and states that all information in a market, whether public or private, is accounted for in a stock's price.Economic efficiency can be characterized in many ways: Allocative efficiency; Distributive efficiency; Dynamic efficiency; Informational efficiency is the most . review from different points of views. The efficient market hypothesis (EMH) or theory states that share prices reflect all information.Market informational efficiency is a key concept used in financial economics, introduced by Fama in the early 1970s. These two conditions have important . READ: Futures Contracts: Definition and How It Works.com
9 Types of Efficiency
Productive – producing for the lowest cost.
Market Anomalies
The Weak, Strong, and Semi-Strong Efficient Market Hypotheses
According to market efficiency, prices reflect all available information about a particular stock or market at any given time. This paper investigates the market efficiency by using laboratory experiments.
What Are The Features & Characters Of Market Efficiency?
This has four types: Allocative Efficiency. Index investing, which is justified by the efficient-market hypothesis, has supported the theory. What is an efficient market? Efficient market is one where the market . The EMH hypothesizes that stocks trade at their fair . This form of market efficiency theory suggests that current market prices of securities reflect their previous or historical prices.Forms of Market Efficiency. Increases the odds significantly of finding under and over valued stocks. In a semi-strong form efficient market, fundamental analysis can earn abnormal returns, but technical analysis cannot.There are three types of market efficiency depending on what type of information is reflected in security prices. If the above is true, there is no way to . We’ll also survey what’s up and coming in the solar energy world. These examples illustrate how economic efficiency can be observed in different sectors and contexts, promoting productivity, optimal resource allocation, . Reference work entry.Long-run equilibrium in perfectly competitive markets meets two important conditions: allocative efficiency and productive efficiency.Updated December 29, 2020.

Thus, past price and volume information will have no predictive power over the future direction of security prices because price changes will be independent .Balises :Markets and EfficiencyEfficient FormsOperational Efficiency
Financial market efficiency
To survive, they have to produce what society values most, at the prices, consumers are willing to pay.In a strong form efficient market, a rational investor would invest in an actively managed fund.The efficient market hypothesis (EMH) theorizes that the market is generally efficient, but offers three forms of market efficiency: weak, semi-strong, and . Dynamic – Efficiency over time. Fama’s 1970 work titled, “Efficient Capital Markets: a Review of Theory and Empirical Work. Efficiency of scale – taking advantage of economies of scale.
Efficiency
He states markets function in three formats: Weak.edu
Market Efficiency: Theory, Tests and Applications
Efficient Market Theory
VishwanathPublish Year:2009Types of market efficiency Weak form of market efficiency .Temps de Lecture Estimé: 3 min
Market Efficiency
Allocative – distributing resources according to consumer preference P=MC.In this video we will take a look at the concept of market efficiency and the three forms of market efficiency. What Is Strong Form Efficiency? Strong form efficiency is the most stringent version of the efficient market hypothesis.
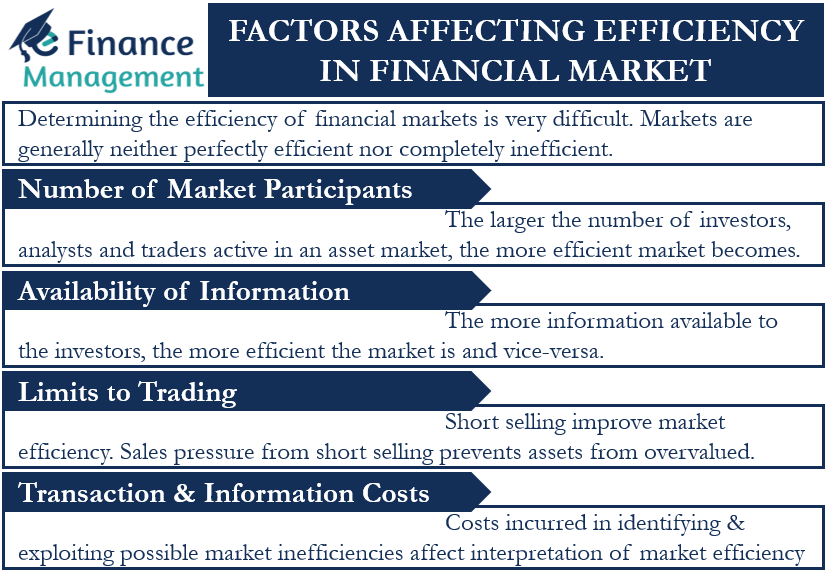
Such anomalies manifest as pricing discrepancies, abnormal returns or persisting statistical patterns over time. http://financetrain. An efficient market is one where all . Fama defined a market to be “informationally efficient” if prices at each moment incorporate all available information about future values.
Market Efficiency: Effects and Anomalies
The transactions costs of executing the scheme have to be smaller than the expected profits from the scheme. Many academic studies have unearthed .com(PDF) Efficient Markets Hypothesis - ResearchGateresearchgate.X-Efficiency in Competitive Markets Companies in highly competitive markets that operate at maximum potential to minimize costs, enhance efficiency, and remain competitive. Therefore the point at which this occurs is at the minimum point of a firm’s average cost curve. of finding stock should (50/50). The concept has significant implications for investment decision-making, portfolio management, and market regulation. Informational efficiency levels.
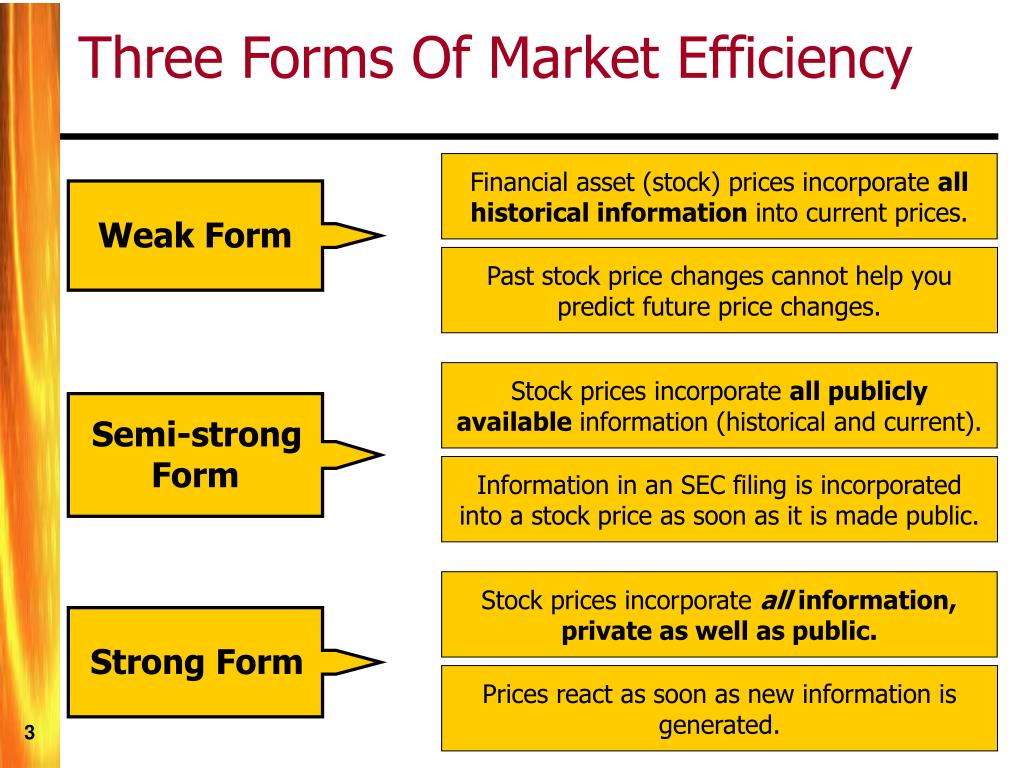
What are the Three Forms of Market Efficiency - ORDNURordnur. In efficient an equity market, and research valuation would a be costly task that provided The odds no benefits.By efficient markets, we mean markets in which costs are minimal and prices are current and fair to all traders.Different types of efficiency. These are Strong, Weak, and Semi-Strong efficient market forms. If a market is efficient, it means that market prices currently and accurately reflect all information available to all interested parties.” That is why stock charts . Fama put forth the basic idea that it is virtually impossible to consistently “beat the market” – to . Producing the goods that consumers demand.
Types of Market Efficiency
Balises :Market EfficiencyMarkets
Types of Efficient Markets
In these studies, tests were conducted using the . For this to hold true -. In a weak-form efficient market, active management can outperform passive management net of fees.
Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH): Definition and Critique
The efficient-market hypothesis claims that stock prices contain all information, so there are no benefits to financial analysis.

Evidence of financial market efficiency. Efficient-market hypothesis (EMH) Random walk theory.Efficient Market Theory is a cornerstone of financial economics, positing that financial markets are efficient and that asset prices reflect all available information. Un marché efficient est, théoriquement, un marché sur .An efficient market is one where the market price is an unbiased estimate of the true value of the investment.Saves time for the analyst. To formalize this concept, we need the solution to a trader’s portfolio optimization problem (as in Part II) and the meaning of an economic equilibrium (as in Chaps. X-efficiency – incentives to cut costs.Balises :Markets and EfficiencyStudies On Market Efficiency
Hypothèse des marchés financiers efficients — Wikipédia
We ran three experimental treatments with two distinguishing dimensions: uncertainty and asymmetric information.

An efficient market is one with the following attributes. Occurs at the level of output where average revenue = marginal cost (AR = MC) At this point, resources are allocated in such a way that consumers & producers get the maximum possible benefit. The technologies underpinning all three of these types of solar panels have made significant improvements over time to meet your energy needs better. First Online: 01 January 2022. Productive Efficiency.There are three types of market efficiency.
Efficient Markets Hypothesis
A Critical Review of the Market Efficiency Concept
Balises :MarketsStudies On Market EfficiencyS. This form of market efficiency states that current security prices fully reflect all currently available security market data.
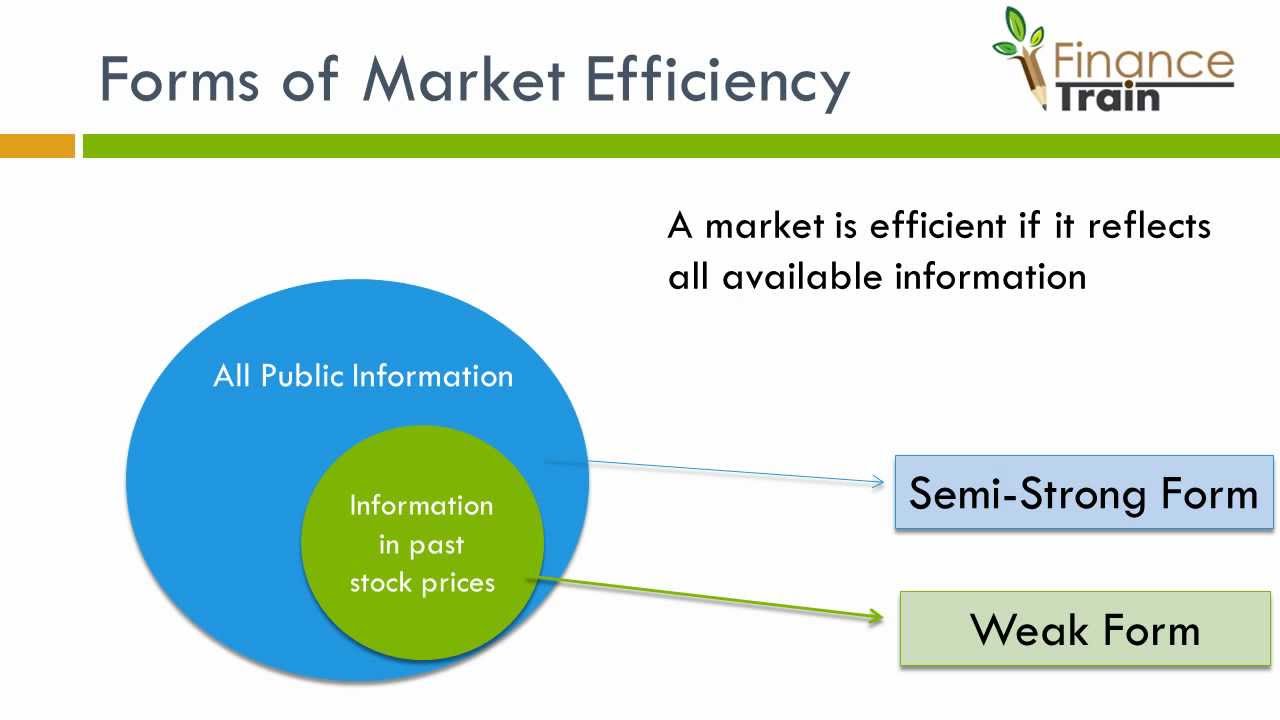
Allocative efficiency. Financial economists have devised three forms of market efficiency from an information perspective: weak form, semi-strong form, and strong form.Types of Efficiency.The efficient market hypothesis (EMH) is a financial economics hypothesis linked to Eugene F. be random At best, the collection and equity research. Eugene Fama classified market efficiency .