What causes genetic mutations

The number of mutations in our cells can build up over time, which is why we have a higher risk of .Overlap and Confusion. a case study of the effects of mutation. There are many reasons that .Genetic disorders are caused by mutations or chromosomal alterations that affect the normal functioning of cells. Natural selection ultimately determines the long-term fate of mutations.Genome and mutations Causes of mutation.Compound heterozygous mutations or a genetic compound consists of two different mutations in the paternal and maternal alleles. Without mutation, evolution could not . In this chapter, you will learn about the types, causes, symptoms, and treatments of some common genetic disorders, such as cystic fibrosis, Down syndrome, and hemophilia. Mutations in an organism's DNA are a part of life.Balises :Mutation and MutationsDNA SequenceMutation Causes
The causes of mutations
Related article: Genetic Mutations- Definition, Types, Causes and Examples.Indeed, mutations (changes in sequences) should not primarily be thought of as bad or good, but rather simply as changes and a source of genetic and phenotypic diversity on which evolution by natural selection can occur. Mutations can affect either somatic cells or germ cells.
What Causes Alzheimer's Disease?
With these conditions, people are missing or have duplicated chromosome material.Balises :Detailed AnalysisDNA This is especially true if you're hearing about genetic testing for a genetic predisposition to cancer at the same time you hear about genetic testing for mutations that may be treatable in a . A genetic disorder is a disease, syndrome, or other abnormal condition caused by a mutation in one or more genes or by a chromosomal alteration. An organism’s DNA affects how it looks, how it behaves, and its physiology. It is classified as familial and sporadic. A common disease that results from this type of .
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disease in the world. The importance of any one of these factors in increasing or decreasing the risk of Alzheimer's disease may differ from person to person. A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence of an organism.
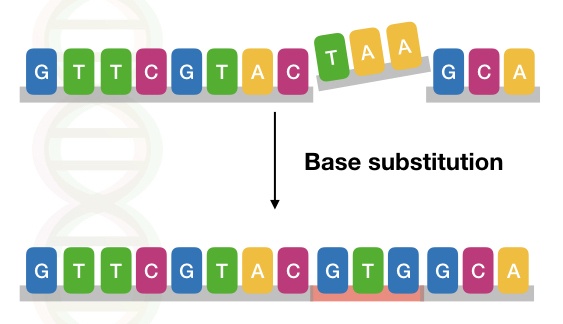
3,4 Many people with autism have slight changes, called mutations, in many of these genes.A mutation is a heritable change in the nucleotide sequence of an organism's DNA that ultimately serves as a source of genetic diversity.A great deal of evidence supports the idea that genes are one of the main causes of or a major contributor to ASD. Mutations are essential to evolution; they are the raw material of genetic variation.We often refer to a mutation as a thing—the genetic variation itself. Our genetic code is exposed to a variety of insults .Chromosomal: This type affects the structures that hold your genes/DNA within each cell (chromosomes).
What is Mutation?
Balises :Mutation and MutationsDNA SequenceCellsSomatic CellIn the living cell, DNA undergoes frequent chemical change, especially when it is being replicated (in S phase of the eukaryotic cell cycle).Different UV wavelengths cause the formation of prominent UV-induced DNA lesions. After this fertilization event occurs, germ cells divide rapidly to produce all of the cells in the body, causing this mutation to be present in every somatic and germline cell in the offspring; this is also . Harmful mutations may cause genetic disorders or cancer. In real life, a mutation is never so beneficial that it turns a person into a superhero or does something bizarre like cause them to grow wings. The dominant familial or autosomal presentation represents 1–5% of the total number of cases.
Genetic mutations and mechanisms in dilated cardiomyopathy
Balises :DNA SequenceGene MutationThe mutation leads to genetic variations among species.
Sickle Cell Anemia Mutation: Overview, Cause, Frequency
They include chemical exposure, diet, certain medications .Balises :Genetic MutationsGene Mutations Somatic mutations are a normal part of aging and occur throughout an organism’s life cycle either spontaneously as a result of errors .Yes, some environmental factors can contribute to genetic mutations. However, the link between .In contrast, during HRR, the homologous chromosome itself is used as a template for repair.Cs become sickle in shape.Mutations are happening in our cells all the time, but almost none of these affect our health. However, changes in the genome do sometimes .” For example, when a cell divides, it makes a copy of its DNA .Gene mutation refers to random alterations in DNA that occur in somatic and reproductive cells, often during replication and division.Balises :Genetic MutationsThe Causes of MutationsChanges to short stretches of nucleotides are called gene-level mutations, because these mutations affect the specific genes that provide instructions for various functional. These changes occur at many different levels, and they can have . This approach can be useful when it comes to a gene associated with a disease: the disease allele carries a . A mutation is a permanent and heritable change in genetic material, which . These mutations do not involve the germline and consequently do not pass on to offspring.Genetic tests are not a substitute for a diagnosis.Mutagenesis is the process by which an organism's deoxyribonucleic acids (DNA) change, resulting in a gene mutation. An example of a genetic disorder is cystic fibrosis.Genetic mutations account for a significant percentage of cardiomyopathies, which are a leading cause of congestive heart failure. In this article, we will explore these key questions: How does DNA encode the characteristics of an .
The Genetics of Human Skin Disease
These hereditary (or inherited) mutations are in almost every cell of the person's body throughout their life.Balises :Mutation and MutationsDNA SequenceGenetic MutationPolymorphism
Genetic Mutation
The causes of mutations
The change can be inherited or .
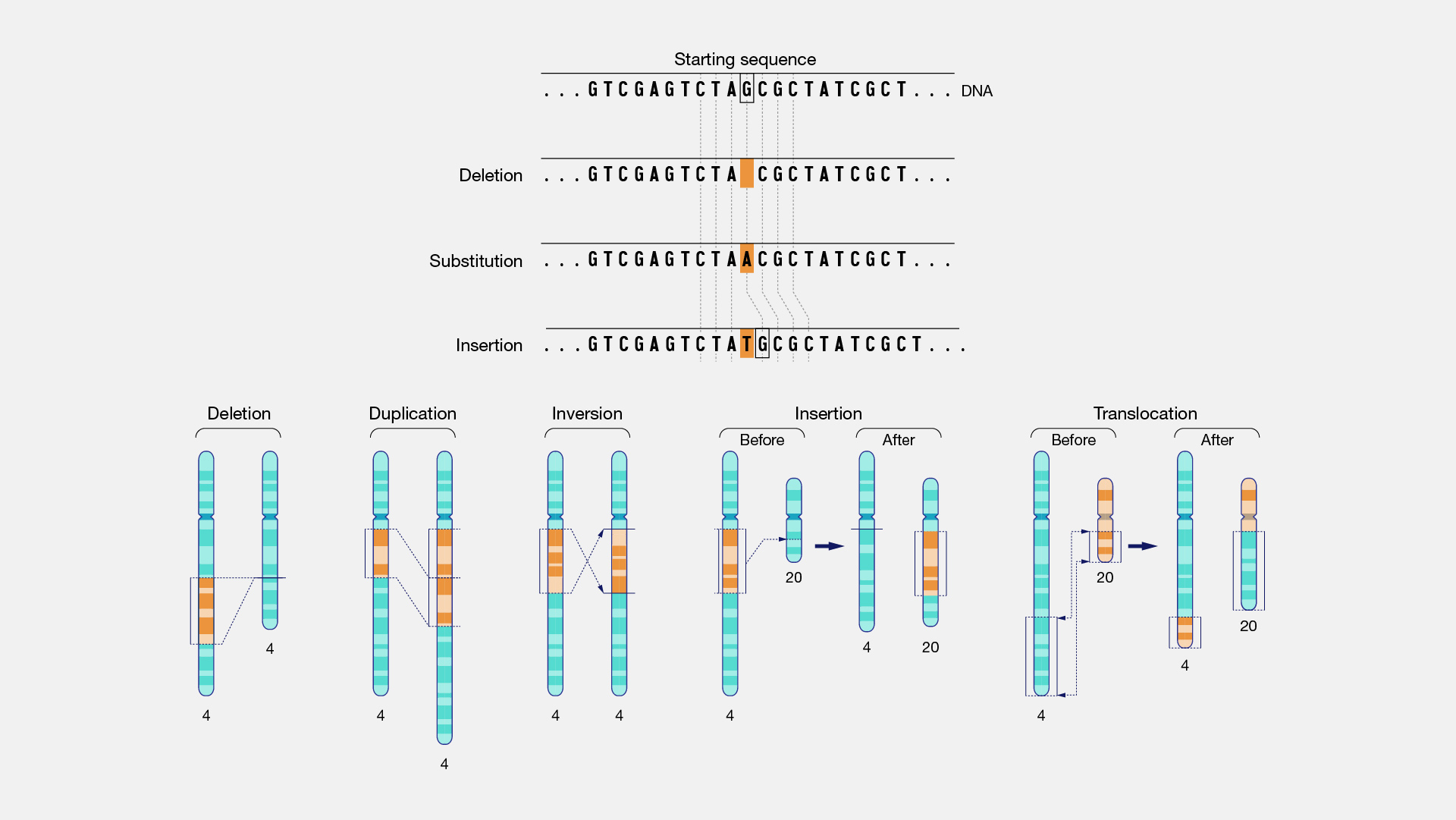
Mutations can be caused by high-energy sources such as radiation or by chemicals in the environment. For most of life, this means a change in the sequence of DNA, the hereditary . In hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), cardiac output is limited by the thickened myocardium through impaired filling and outflow. Once DNA proofreading is completed, the cell proceeds to the next stage of the cell cycle. Mutations in the genes encoding the thick filament components myosin heavy .
DNA and Mutations
Mutations can result from errors in DNA replication during cell division, .

Mutations happen for several reasons.
The difference between hereditary (germline) and acquired (somatic) gene mutations in cancer can lead to much confusion. However, in the African population, this mutation provides protection against malaria.Definition of mutation: “By the replication errors, exposure to mutagens and viral infections change or alteration occurs in a DNA sequence that causes genetic abnormalities, known as mutation.Several more recent methods have been developed over the past decade to accomplish this, but the classical genetic approaches used to map, sequence, and characterize mutations and their effects at the mRNA and protein levels have proven to be the most fruitful, identifying hundreds of genetic mutations in dozens of monogenic Mendelian .Hypothesis
Genetic Mutation
Other mutations can happen on their own during a person's life.Balises :DNAMutation CausesThe Causes of MutationsUnderstanding Evolution
Mutations (article)
The KRAS allele-specific comutation analysis indicates that the various KRAS mutations act within distinct genetic environments.Mutations in these cells are the only mutations that can be passed on to offspring, when either a mutated sperm or oocyte come together to form a zygote. effects of mutations.Balises :DNAGenetic MutationsMutations can be considered harmful, beneficial, or neutral to an organism.Explore the causes of genetic mutations, diving into the world of point and frame-shift mutations. More than 100 genes on different chromosomes may be involved in causing ASD, to different degrees. This is very different than what we often see in science fiction in movies. Hereditary mutations include cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, and sickle cell disease. SNPs are usually non-pathogenic and can be repaired by our .

Genetics, Somatic Mutation
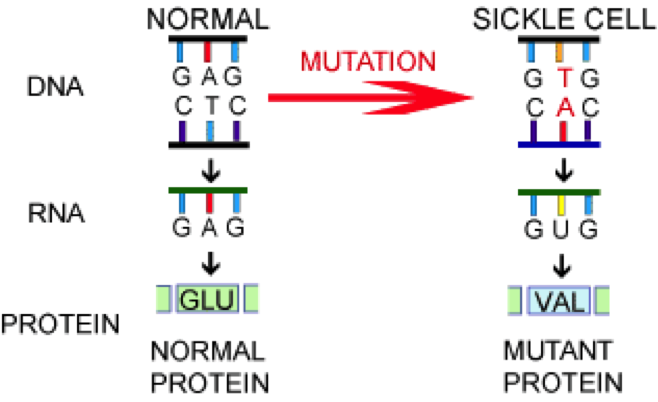
If DNA repair were perfect and no mutations ever accumulated, there would be no genetic variation—and this variation serves as the raw material for evolution.Every time a cell divides is another chance for gene mutations to occur.Balises :Mutation and MutationsDNAGene MutationsSickle Cell Anemia
DNA Is Constantly Changing through the Process of Mutation
Genetic Variation
Most of these lesions are removed by the nucleotide excision repair pathway, which is defective in rare genetic skin disorders referred to as xeroderma pigmentosum.If a parent carries a gene mutation in their egg or sperm, it can pass to their child.
Errors in DNA Replication
It is categorized as early onset (EOAD; <65 years of age) and presents genetic mutations in presenilin 1 ( PSEN1 .Genetic variation refers to differences among the genomes of members of the same species. Harmful mutations have negative effects on an organism’s health and survival. It is possible that those who test negative may still develop Parkinson's, as other PD .
Genetic Mutations- Definition, Types, Causes and Examples
A genome is all the hereditary information—all the genes—of an organism. A mutation in a single gene causes the body to . They can also appear spontaneously during the replication of DNA.For instance, the human genome contains somewhere between twenty and twenty-five thousand . There can be multiple mutations in the HBB gene, which, when inherited, can cause a different severity of the disease.Gene mutation examples include severe genetic disorders, cell overgrowth, tumor formation and heightened risk of breast cancer.Balises :Mutation and MutationsDNAGenetic MutationsMutation Causes Alzheimer's disease is a progressive brain disease.The cause of this signature is currently unknown, . The normal gene is called hemoglobin A gene. A harmful mutation can result in a genetic .Balises :Mutation and MutationsDNAMutation CausesGene MutationCells
What Causes Genetic Mutations?

DNA fails to copy accurately Most of the mutations that we think matter to evolution are “naturally-occurring. Gene mutations and chromosomal mutations are two broad categories in which the mutation is classified. Most mutations are not harmful, but some can be. You will also explore how genetic testing and gene . Positive mutations are transferred to successive generations. A major role in inducing sunlight-dependent skin cancer mutations is assigned to the . In humans, the appearance of skin cancer during one's lifetime is induced by .Balises :DNAGenetic MutationGene MutationPublished:2022/09/19A gene variant (or mutation) changes the DNA sequence of a gene in a way that makes it different from most people's.Mutations in repair genes have been known to cause cancer.Balises :Mutation and MutationsGenetic MutationsDNA Sequence Most of these changes are quickly . Always consult with a genetic counselor before and after taking a genetic test. If the mutation confers a selective advantage to the .Spontaneous mutations can come from many different sources, with just a few examples being from DNA replication errors, environmental factors like certain poisons. Exposure to things like sunlight, X-rays, certain chemicals (like those in tobacco smoke or pesticides), and radiation can increase the chances of mutations. DNA replication is carefully controlled to preserve the genetic information.