What is a core enzyme

Murakami
Structural Biology of Bacterial RNA Polymerase
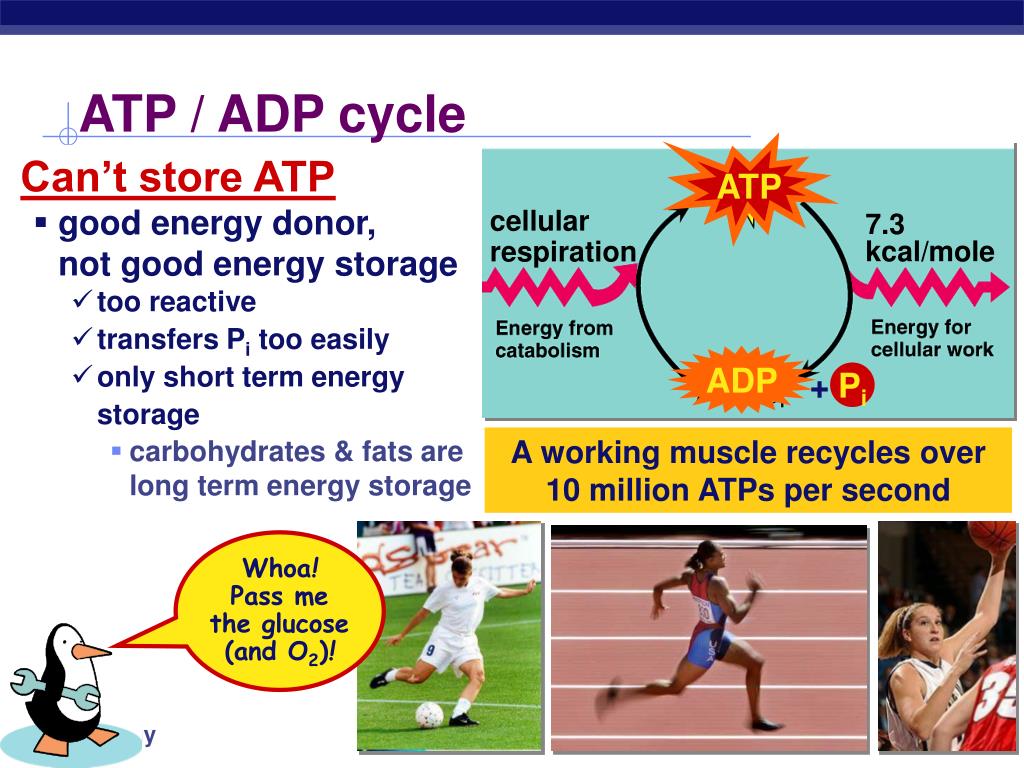
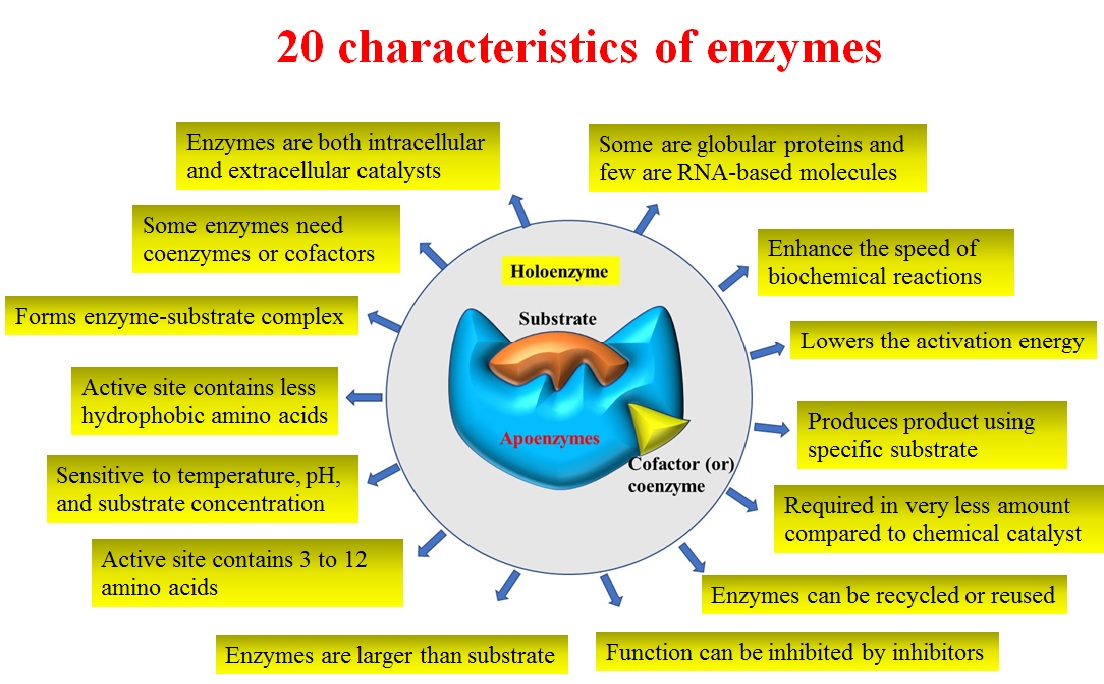
At body temperature, very few biochemical reactions proceed at a significant rate without the presence of an enzyme.How Cells Work: Enzymes at http://science. [1] An example of a core enzyme is a RNA polymerase enzyme without the sigma factor (σ). Biological catalysts (biological because they are made in living cells, catalysts because they speed up the rate of chemical reactions without being changed) Necessary to all living organisms as they maintain reaction .Enzymes: Structure, Types, Mechanism, Functions. 4 ), is the central enzyme that synthesizes messenger RNA from protein-coding genes.What is Difference between holoenzyme and core enzyme?answers.DNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RNAP) is the key enzyme of transcription and gene expression in all living organisms.Enzymes are proteins comprised of amino acids linked together in one or more polypeptide chains. Enzymes are biological catalysts which speed up reactions.Enzyme: [ en´zīm ] any protein that acts as a catalyst, increasing the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs.Core enzymes comprise subunits of enzymes required for catalytic activity, as seen in the core enzyme RNA polymerase.}, author={Jinshui Yang and . coli RNA Polymerase, Holoenzyme is the core enzyme saturated with sigma factor 70.
castaneum also map to the dld-1 gene, which codes for a core metabolic enzyme. This sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain is called .Enzymes - Edexcel. À la fin de cette section, vous serez en mesure de faire ce qui suit : Décrire le rôle des enzymes dans les voies métaboliques; Expliquer .RNA polymerase (RNAP) is the essential enzyme responsible for transcribing genetic information stored in DNA to RNA.
A core enzyme consists of the subunits of an enzyme that are needed for catalytic activity, as in the core enzyme RNA polymerase. These five subunits form the .

Murakami
Enzyme : définition, rôle, types, dosage, taux, normes
National 4; Properties of enzymes and use in industries Enzyme specificity.Pol II, first described by Robert Roeder in 1969 (ref. It contains a core enzyme and σ subunit. Phosphine resistance mutants in R. Ongoing research has shown positive effects on the respiratory, digestive, and circulatory systems, and potentially on the . dominica, and T.Chapitre 1 : Généralités sur les enzymesfac.dzFiche explicative de la leçon: Enzymes | Nagwanagwa. Here we report the reconstitution of the 11-subunit RNA polymer . DNA and RNA Quantitation. The enzyme remains the ability to transcribe RNA from nonspecific initiation sequences.RNA polymerases from Archaea and Eukaryotes consist of a core enzyme associated with a dimeric E'F (Rpb7/Rpb4) subcomplex but the functional contribution of the two subunit subcomplexes to the transcription process is poorly understood. The human body probably contains about 10,000 different enzymes. This was closely followed by the determination of the three-dimensional structure of yeast RNA polymerase II, an enzyme more complex than the bacterial polymerase, at 16 Å resolution. The substrate binds to the enzyme primarily .Recommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis This enzyme consists of only . Le terme holoenzyme (ou plus rarement hétéroenzyme ), du grec holos, entier, est l'assemblage du cofacteur (qui peut être un ion métallique, un agrégat atomique ou une molécule organique) et d'une ou plusieurs chaînes protéiques, formant ainsi une enzyme complète et active. ADVERTISEMENTS: The core RNA polymerase consists of four polypeptides which are of the following three types: (a) The α subunit: It is present in two copies/core enzyme molecule, and is concerned with binding with promoter DNA.
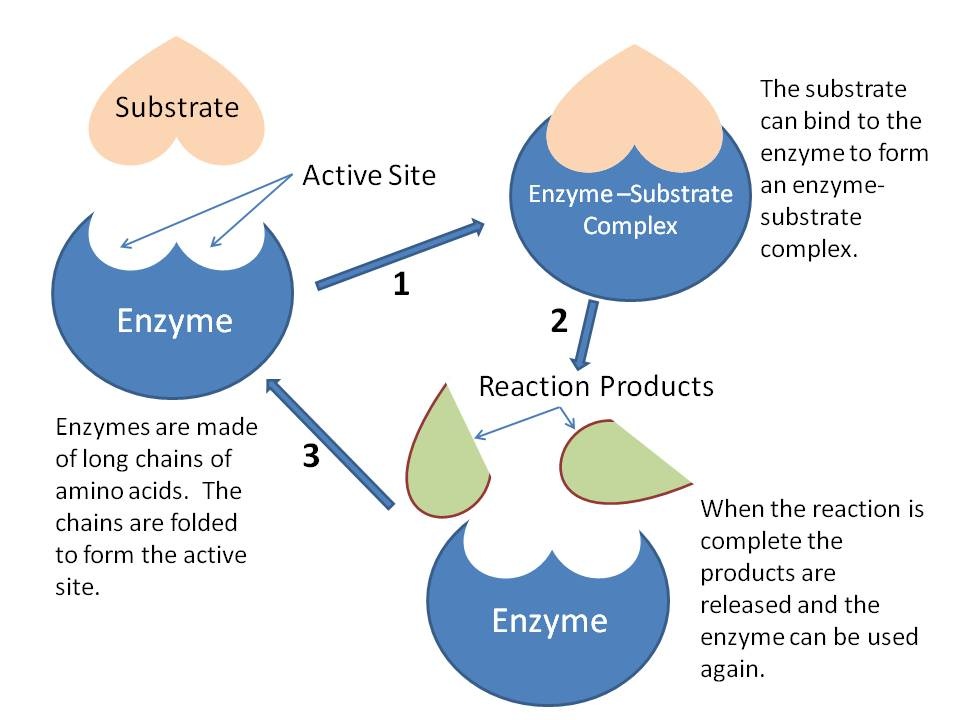
The core polymerase is the part of the RNA polymerase that is .Les enzymes sont des protéines qui ont un rôle de catalyseurs biologiques, ce qui signifie qu'elles accélèrent les réactions biochimiques de . Beispiel für ein Core-Enzym ist das Core-Enzym der RNA-Polymerase, das an die Nicht-Promotorregionen der DNA bindet. They are specific for their substrate. The lock and key hypothesis models this. coli RNA Polymerase Core Enzyme consists of 5 subunits designated α, α, β', β, and ω. RNA polymerase enzyme is an example of the core .RNA polymerases from Archaea and Eukaryotes consist of a core enzyme associated with a dimeric E′F (Rpb7/Rpb4) subcomplex but the functional contribution of the two subunit subcomplexes to the transcription process is poorly understood. Retains the ability to transcribe RNA from nonspecific initiation sequences.Enzymes are: Catalysts that speed up the rate of a chemical reaction without being changed or used up in the reaction. 807) show that mutations in the delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase and dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase ( dld-1) genes both give rise to phosphine resistance in C. In bacteria, the catalytically competent . Measuring the rate of formation of a product using catalase; Measuring the rate of disappearance of a substrate using amylase; Investigating catalase activity. A substance that helps a chemical reaction to occur is a catalyst, and the special molecules that catalyze biochemical reactions are enzymes.Product Information.030 Corpus ID: 25383271; A proposal of core enzyme bioindicator in long-term Pb-Zn ore pollution areas based on topsoil property analysis. Er entsteht aus dem Holoenzym durch den Verlust des σ-Faktors ( Sigma-Faktors) und besteht aus den Untereinheiten 2α, β, β’ und ω. A RNA polymerase (RNAP), or ribonucleic acid polymerase, is a multi subunit enzyme that catalyzes the process of transcription where an RNA polymer is synthesized from a DNA template.The core enzyme is responsible for binding to template DNA to synthesize RNA, which is complemented by a σ factor to form a holoenzyme that recognizes the . What is the function of enzymes? What type of compound are .Bacterial RNAP core enzyme is the simplest and best characterized form, consisting of α (two copies), β, β', and ω subunits (Figure 1 and Figure 2 a). babel-jest Will help Babel understand the code we write in Jest. Each type is specifically shaped to . coli RNA Polymerase, Core Enzyme consists of 5 subunits designated α, α, β´, β, and ω. The Holoenzyme initiates RNA synthesis from sigma 70 specific .Auteur : Katsuhiko S.comCore enzyme | definition of Core enzyme by Medical dictionarymedical-dictionary.The core enzyme is a tetramer whose composition is given as α 2 ββ′ (two alpha subunits, one beta subunit, and one beta‐prime subunit). The vertical bars indicate the chromosomes of foxtail millet (chromosome 8 not shown as no gene was present), and the individual genes are mapped at their corresponding physical position (in Mb) as indicated on the left of each bar.Physical location of core enzyme-encoding genes involved in starch metabolism in foxtail millet. As the regulation of Pol .Discuss enzyme regulation by various factors. Free of sigma factor and does not recognize any specific bacterial or phage DNA .
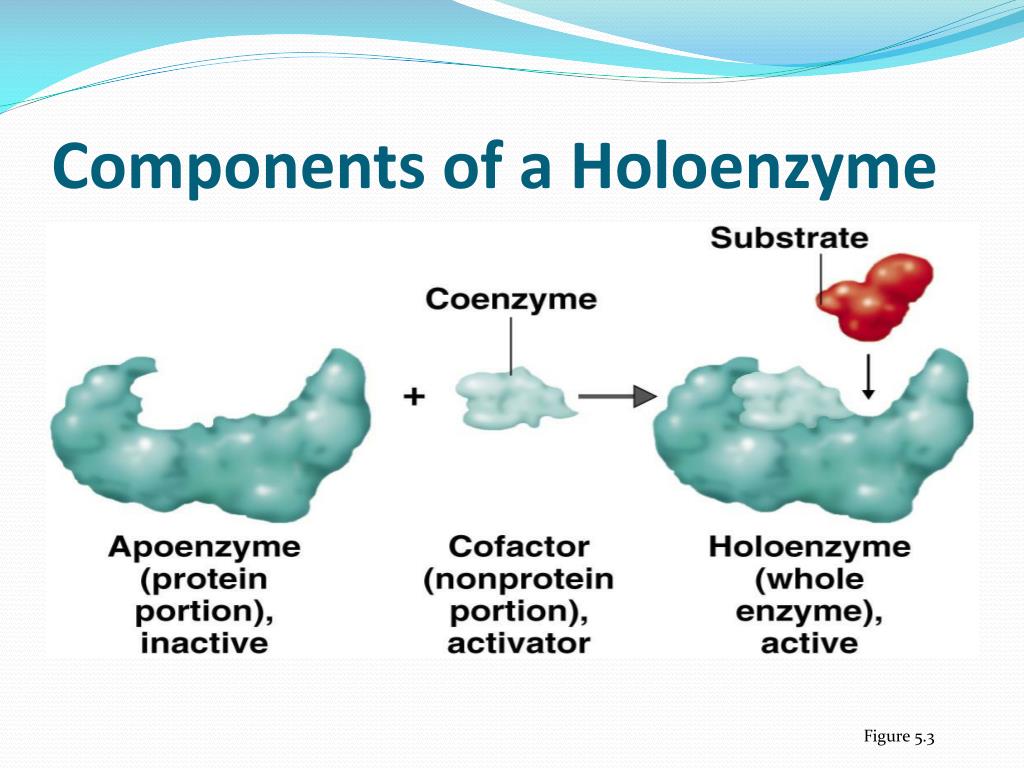
Here we report the reconstitution of the 11-subunit RNA polymerase and of the core enzyme from the .In 1989, the three-dimensional structure of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase core, a five-subunit enzyme, was determined by electron crystallography.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 40 secondes
Core Enzyme
comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis 1: During elongation, the bacterial RNA polymerase tracks along the DNA template, synthesizes mRNA in the 5’ to 3’ direction, and unwinds and rewinds the DNA as it is read.6 Enzyme Action is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts.com/life/cellular-microscopic/cell2. These subunits assemble every time a gene is transcribed, and they disassemble once . Addition of sigma factors will allow the enzyme to . Indeed, without enzymes, crucial processes such as cellular respiration, photosynthesis, and protein synthesis would not occur. Like all catalysts, an enzyme does not control the . Enzymes make life possible, as they allow for many of the most important biochemical changes in cells. The availability of the holoenzyme subunits in purified form has allowed us to investigate their roles at the replication fork.RNA Polymerase Definition.RNA Polymerase, Core Enzyme.
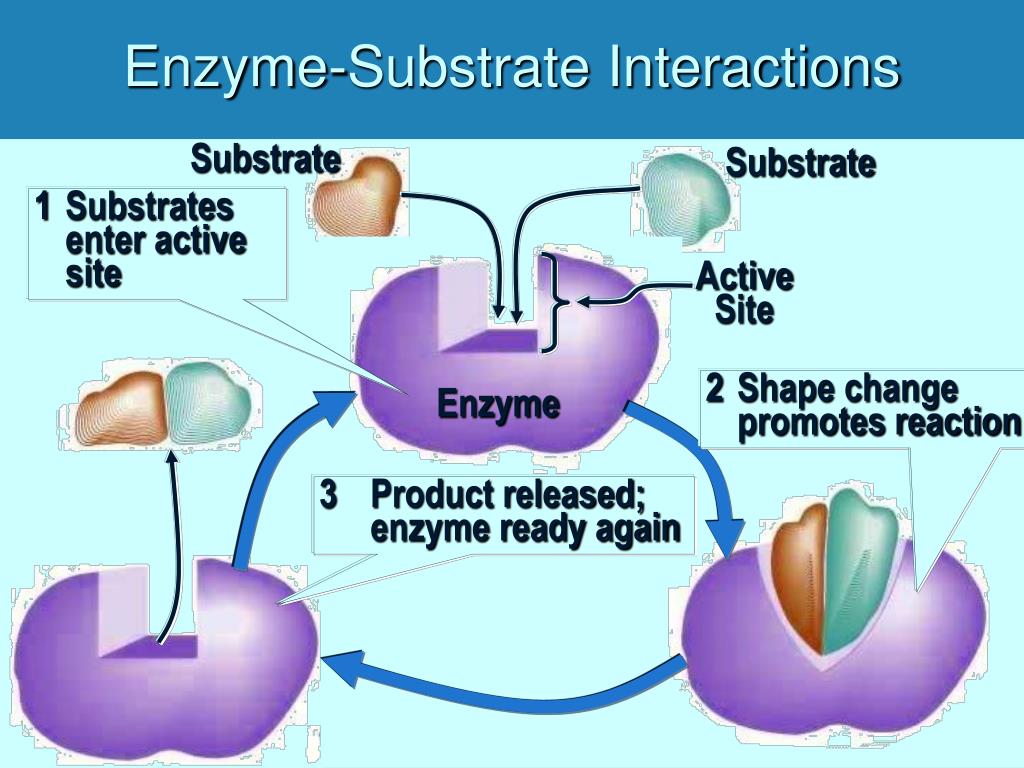
Four of these subunits, denoted α, α, β, and β' comprise the polymerase core enzyme.Core polymerase and holoenzyme. Core RNA polymerase is .
enzyme This is an assertion library that makes it easier to assert, manipulate, and traverse your React Components’ output. Together, the σ subunit and core polymerase make up what is termed the RNA polymerase holoenzyme. Beispiel für .
Core enzyme
Here we report two Escherichia coli RNA polymerase structures: an 11.
How to set up Jest & Enzyme like a boss
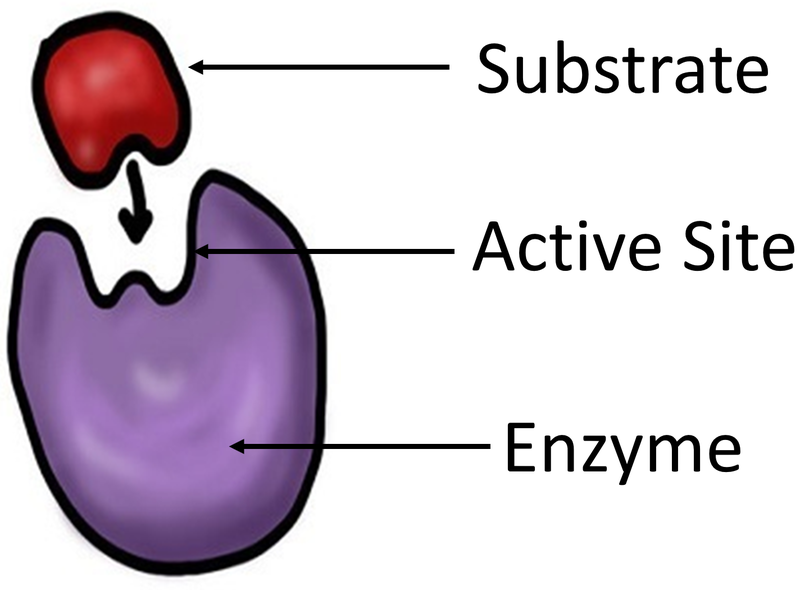
Use the enzyme amylase to breakdown starch at a range of pH values, using iodine solution as an indicator for the reaction occurring; Use a continuous sampling technique to monitor the progress of the reaction; Amylase is an enzyme that digests starch (a polysaccharide of glucose) into maltose (a disaccharide of glucose)Enzymes are a class of biomolecules responsible for catalyzing chemical reactions in cells.Physiological Probes.enzyme, a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being altered .The molecular weight of the multisubunit enzyme is about 470,000 Da.
Core enzyme
The total number of protein isoforms of the four core enzymes and the number in each group identified in each plant genome are indicated on the right.The Escherichia coli RNA polymerase (RNAP) is a multi-subunit enzyme composed of five subunits including α (two copies), β, β’ and ω subunits.5 Enzymes Objectifs d’apprentissage. The core enzyme of RNA polymerase is made up of four subunits without the sigma factor.
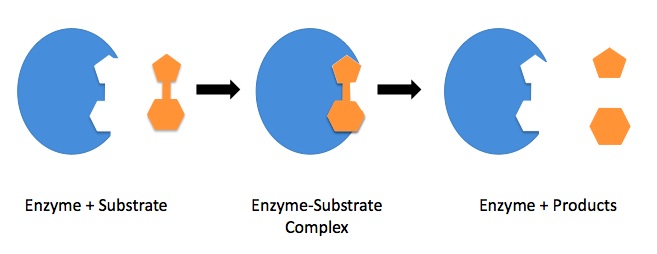
The core enzyme cannot initiate transcription at the proper sites, but it can synthesize RNA using DNA as a template. Enzymes are denatured at extremes of . Ein Core-Enzym besteht aus den Untereinheiten eines Enzyms, die für seine katalytische Aktivität notwendig sind.As elongation proceeds, the DNA is continuously unwound ahead of the core enzyme and rewound behind it (Figure 11.
Biochemistry, Proteins Enzymes
What is the core enzyme of RNA polymerase?
Auteur : Catherine Sutherland, Katsuhiko S. The core enzyme is responsible for binding to template DNA to synthesize RNA, which is complemented by a σ factor to form a holoenzyme that recognizes the promoter . The enzyme is free of sigma factor and does not initiate specific transcription from bacterial and phage DNA promoters.Multisubunit RNA polymerase is an essential enzyme for regulated gene expression. Bromelain has also been found to have anticancer and antimicrobial properties.The amino acid has a nonpolar side chain; isoleucine (answers will vary). The core enzyme is catalytically active, which is responsible for . @article{Yang2016APO, title={A proposal of core enzyme bioindicator in long-term Pb-Zn ore pollution areas based on topsoil property analysis. Enzymes speed up the biological reactions necessary for life. L'holoenzyme est donc le complexe enzymatique .Le terme holoenzyme (ou plus rarement hétéroenzyme ), du grec holos, entier, est l'assemblage du cofacteur (qui peut être un ion métallique, un agrégat atomique ou une .