What is zero voltage switching

Zero Voltage Switching is included. The static loss is due to the resistance between drain and source (RDS (ON)), while the .In simple terms, zero-voltage switching can be described as the power to the device is turned off or on only when the output voltage is zero volts. Diode 1′ and 4′ connected in a positive half cycle, and diode 2′ and 3′ connected in a negative half cycle.
celduc relais offers both zero-cross and random solid state relays.
Boost Switching Safety with a Zero-Crossing Relay Driver
9-2 Why resonant converters • Hard switching is based on on/off –Switching losses –Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) because of high du/dt and di/dt • SMPS size decreses with increasing switching frequency –Target is to use as high f s as possible –Switching losses are . This way, the switching. : Zero-Cross SSRs for all loads . August 06, 2018 by Stefan Matlok.

Why resonant converters. By nature of the resonant tank and zero current switching limitation, the peak switch current is significantly higher than its .Auteur : Steven Keeping
Back to basics: zero-voltage switching
Zero-cross or random relay : what are the differences ?
This paper proposes a zero-voltage-switching (ZVS) Buck/Boost converter (BBC). Afficher plus de résultats
ZVS (Zero Voltage Switching)
In contrast, soft switching helps reduce losses caused by .Taille du fichier : 794KB
Zero Voltage Switching
This technique functions .A zero voltage switching (ZVS) pulse-width modulation (PWM) inverter that uses a parallel-resonant DC link (PRDCL) circuit is examined.Interior view of an ATX switched-mode computer power supply: A: Bridge rectifier; B: input filter capacitors; Between B and C: heat sink for switching active components of primary voltage; C: transformer: Between C and D: heat sink for switching active components of at least five secondary voltages, per the ATX specification; D: output filter coil for the . The circuit consists of a diode, a capacitor shunting the diode, and a second-order low-pass output filter. I am having confusion regarding the understanding of .

Making Zero the Hero in AC-DC Conversion. These must be overcome or avoided to achieve any significant boost to regulator performance. This technique eliminates the turn-on or turn-off loss associated with the charging or discharging of the energy . This article explains the zero overvoltage switching effect and gives insights into key aspects and . (The technique can also be used to switch the MOSFET when current, rather than voltage, reaches zero. Zero voltage switching (ZVS) aims to change the state of a relay or electronic switch at the moment there’s no significant voltage across the switching element. Since all of the switches can achieve .

A simple circuit control scheme and the design .Zero Voltage switching.

Regarder la vidéo8:05#ZeroVoltageSwitching #ZVS #SoftSwitching0:00 Intro00:47 Resonant Buck Converter01:44 Buck converter working02:32 ZVS Resonant Buck Converter working03:19 St.Auteur : Steven Keeping
Analysis of class E zero-voltage-switching rectifier
During soft switching the voltage falls to zero (rather than just a minimum) before the MOSFET is turned on or off, eliminating any overlap between voltage and current and minimizing losses. In addition, an auxiliary circuit based on a coupled inductor is introduced to realize ZVS for the main MOSFETs. It requires cos φ (or TruePF) measurements in order to analyze the phase shift between the current and the voltage.Analysis of Class E rectifiers offer a novel means of high-frequency high-efficiency rectification.Zero current switching ( ZCS) is a universal solution for all types of load but it is more difficult to implement. The circuit's operating principles are described using a voltage-mode quasi-resonant boost converter.The basic idea of zero voltage switching is simple.
Zero Voltage Switching Resonant Power Conversion
Zero voltage switching technique used in a buck converter is more desire and preferable over a hard switched buck converter for low power and high frequency DC-DC conversion applications. The magnetic coupling inductor plays the role of filtering and provides ZVS conditions for the main MOSFETs. With the typical switching method called hard switching, there is a considerable overlap between voltage and current waveforms. The basic configurations of the voltage-mode resonant switches are presented. DC analysis of the converter is carried out. An RCD snubber across the main switch . The main switch of the proposed NBDC realized zero-voltage turn-on, and the auxiliary switch realized zero-current turn-on.
A Review of Zero-Voltage Switching and Importance
An analysis and experimental results are presented for a class E zero-voltage-switching (lowdv/dt) rectifier. The circuit implemented zero voltage switching having the advantage of a soft-switching device for reducing switching . In simple terms, it refers to turning the switch ON when the voltage across it is . Considerations will be given to the details of the . Prior to turn on, the MOSFET VDS is at a high voltage, which is also the voltage to which COSS is charged. A better solution uses zero-voltage-switching . Viewed 406 times.During soft switching the voltage falls to zero (rather than just a minimum) before the MOSFET is turned on or off, eliminating . An inexpensive way of doing this uses a flyback converter in quasi-resonant (QR) mode.

It is also suited to systems requiring an immediate switching. In contrast, the non-zero-cross type SSR switches on regardless of whether the load voltage is close to zero volts or not.ZVS (Zero Voltage Switching) means switching the 110/230VAC output when the immediate voltage is zero. The basic configurations of the voltage-mode resonant switches are .Auteur : Foolish EngineerThe term “Zero Voltage Switching” is rooted in its fundamental operating principle.ZVS and ZCS switching topologies typically use resonance techniques to force the voltage or current in a semiconductor switch to zero, resulting to the elimination or . The proposed auxiliary circuit . This traverses the volt . 2021What is the meaning of zero voltage switching (ZVS) and zero current .Zero-cross switching is done while maintaining signal isolation between the low voltage (LV) and HV side. Switching losses. Numerous design equations and associated voltage, current and timing waveforms supporting this technique will be highlighted.In a soft-switching converter topology, an LC resonant network is added to shape the switching device voltage or current waveform into a quasi-sine wave in such a way that a zero voltage or a zero current condition is created.Zero-Voltage or Zero-Current Switchings •converters for soft switching.Zero-Voltage or Zero-Current Switchings.A zero-voltage switching method for NBDCs with a transient current built-up technique was proposed in this paper. celduc range of Solid State Relays.La technologie ZVS permet au régulateur de tension de déclencher une « commutation douce », évitant ainsi les pertes de .About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright . During the ZVS switch off-time, the L-C tank circuit resonates. In the paper work simulation models of a buck ZVS DC-DC converter and control system model has been simulated and investigated using an OrCad Capture CIS.Zero Overvoltage Switching.
Switched-mode power supply
The diode bridge rectifier is used to convert AC–DC. And while true, two obvious concerns can in1pede the . To achieve ZVS, . During the switching transition, the load current is shared by . Here we look at how ZVS-based .The zero-cross type SSR switches on when the load voltage is close to zero volts. A new family of voltage-mode . Asked 8 months ago.Hard switching is used for simple switch, motor drive inverter, and switched-mode power supply applications.The advantages of the PDM converter, such as zero-voltage switching, combined with those of the MCT make the PDM converter a suitable candidate for many ac–ac converter applications. This reference designed achieved a 12-V, 200-us delay ZCS . Therefore it has the advantage of less noise generation when switching operation (switching on). This is known as Zero Current . Zero voltage switching in power-conversion applications holds the key to efficiency improvements.After the body diode of Q2 is turned on by L R, the channel of Q2 is turned on at zero voltage and with zero switching power loss.
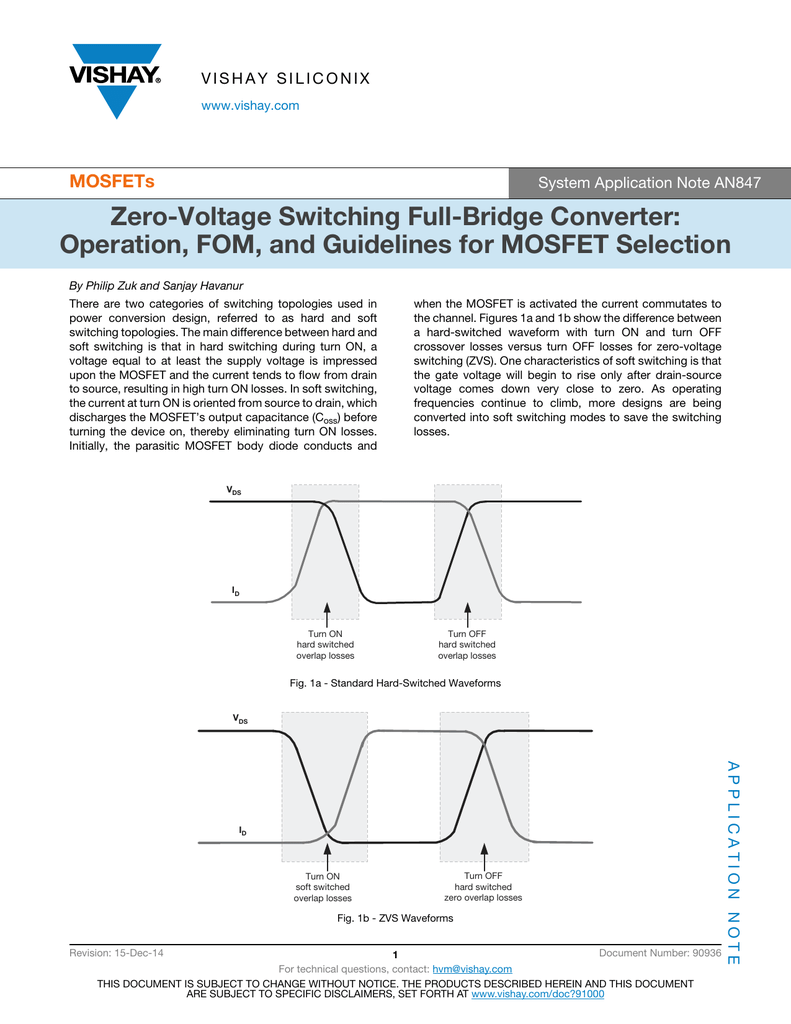
Zero Voltage Switching.To overcome these problems, it is desirable to utilise soft-switching techniques such as zero voltage switching (ZVS) or zero-current switching (ZCS) on the main switch and the passive elements, for damping the transformer leakage inductance effects, soft switching and reduce the losses. Two MCTs with .Switching at zero-voltage crossing is called zero-voltage switching (ZVS) whereas switching at zero-current crossing is called zero-current switching (ZCS). SO8, SA8, SMT8, . The PRDCL circuit provides zero-DC link voltage periods for the inverter switchings and imposes minimum DC bus voltage stress on the PWM inverter.Zero Voltage Switching (ZVS) refers to when the switch tube is turned off, the voltage at both ends of the switch tube is already 0. ZVS (Zero Voltage Switching) is easier to implement than . The shunt capacitor shapes the voltage .
A novel resonant switch operating under the principle of zero-voltage switching is presented.
Zero-Cross Switching for Solid-State Relays Reference Design
• converters for soft switching.How does zero voltage switching work if VDS = 0?14 juil.












